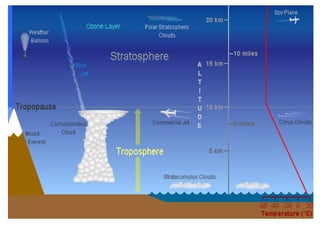
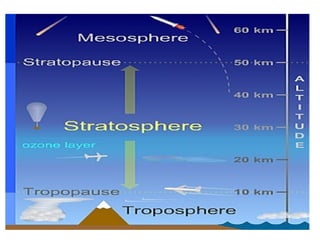
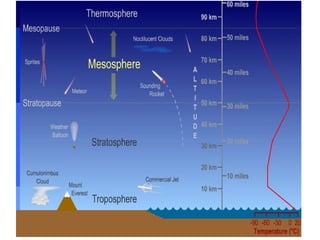
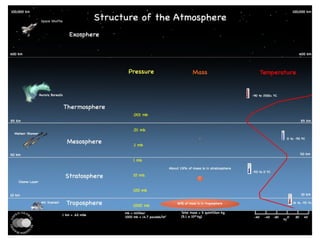
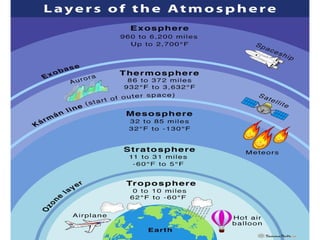
The document outlines the different layers of the atmosphere, including descriptions, altitudes, and features of each layer such as the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, ionosphere, and exosphere. It also discusses ozone types and their environmental impact, along with the causes and effects of global warming due to greenhouse gas pollution. Lastly, it highlights the health issues related to air pollution, particularly in urban areas, and the need for pollution control measures.