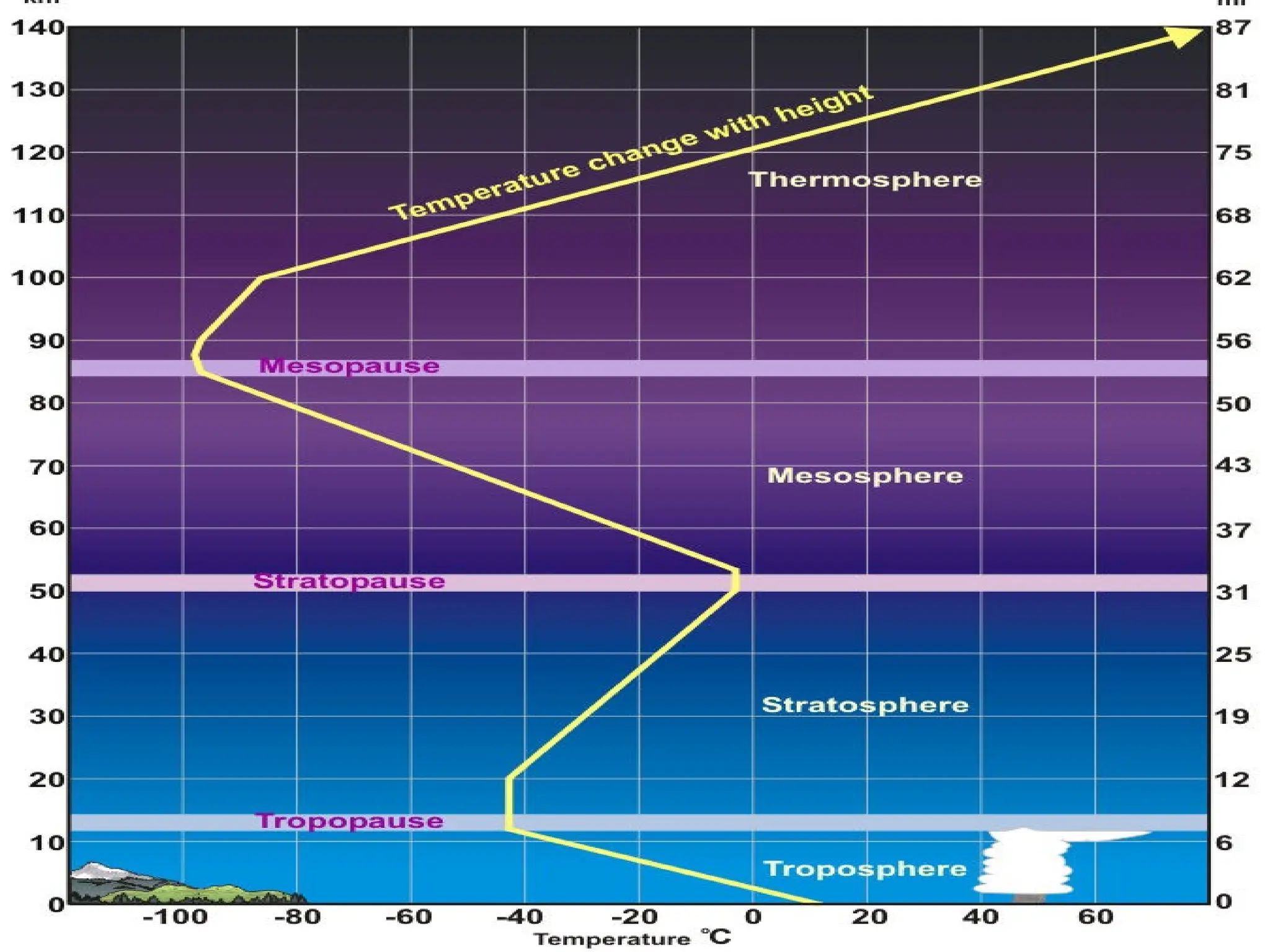
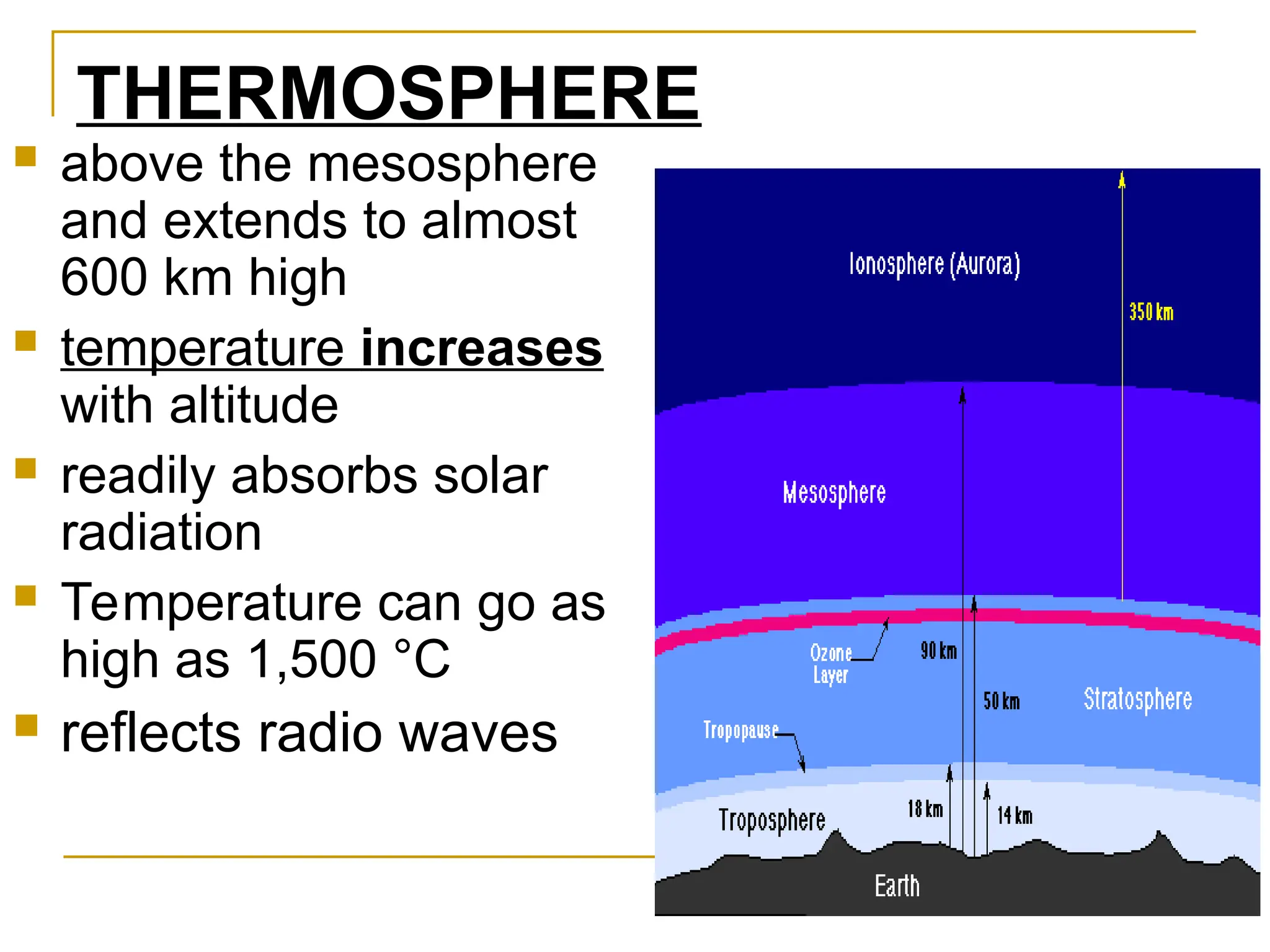
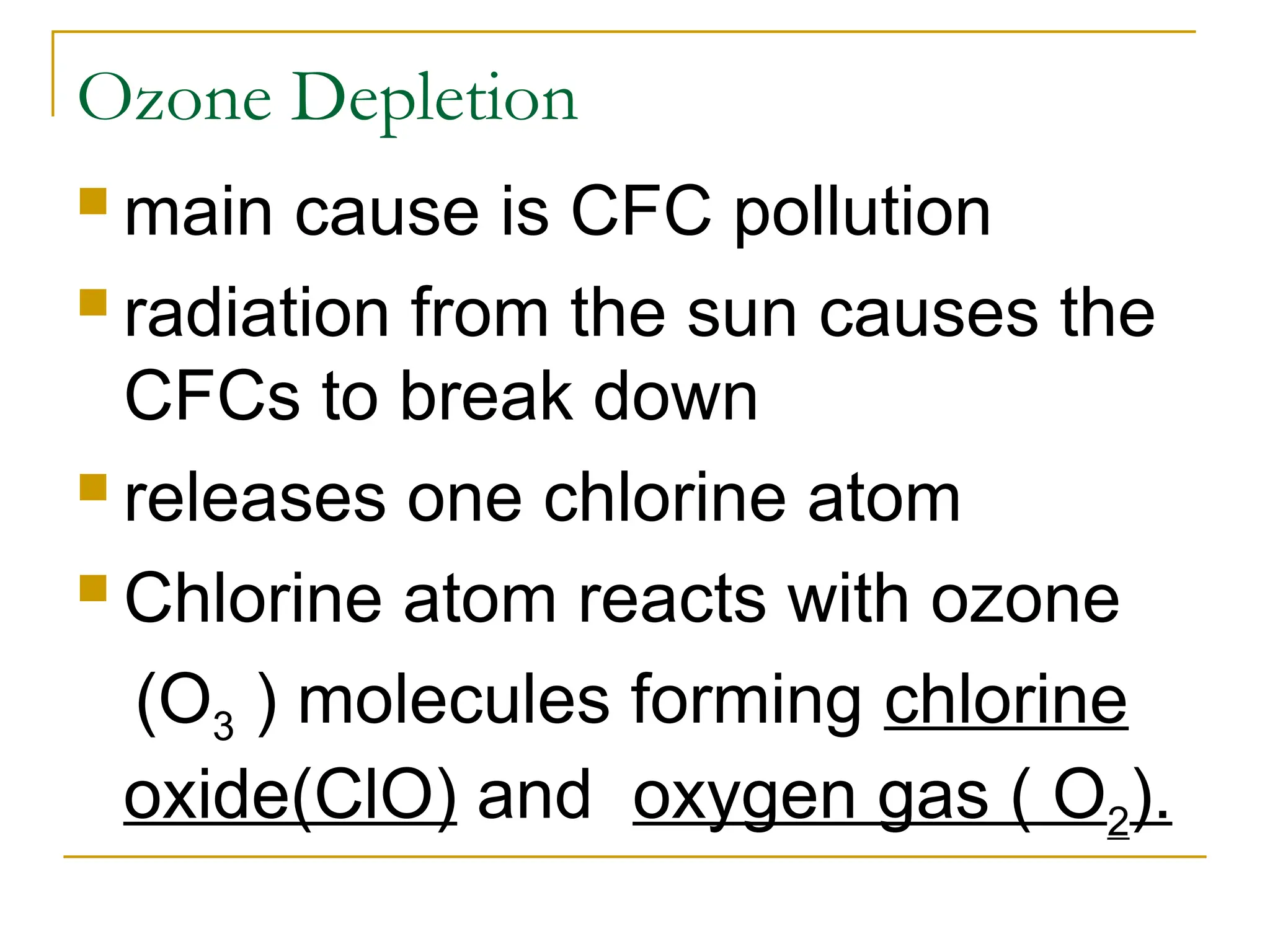
The document outlines the layers of the Earth's atmosphere, detailing their characteristics, temperature variations, and environmental significance. It describes how the troposphere is the lowest layer where weather occurs, while the stratosphere contains the ozone layer that protects Earth from UV radiation. Additionally, it addresses issues related to ozone depletion from CFCs and the impact of greenhouse gases on global warming.