The document discusses the composition and structure of Earth's atmosphere. It covers the following key points:
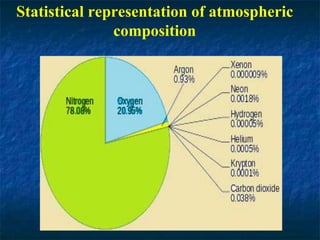
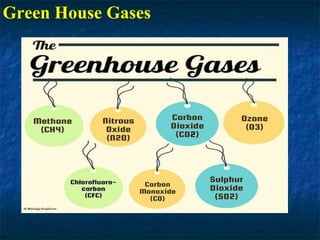
- The atmosphere is composed primarily of nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%), with trace amounts of other gases like carbon dioxide, argon, and ozone.
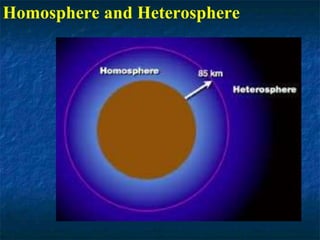
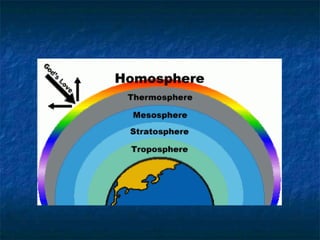
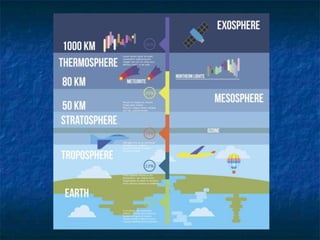
- The atmosphere is divided into five main layers - troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere - with varying temperature and air pressure profiles.
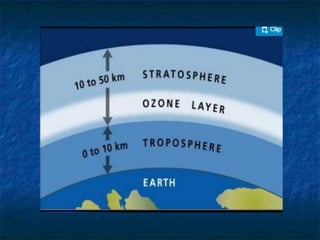
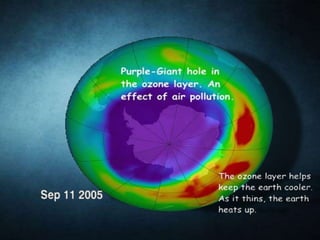
- The troposphere is the lowest layer where weather occurs. The stratosphere contains the ozone layer which absorbs harmful UV radiation from the sun.
- The International Standard Atmosphere defines standard profiles for temperature, pressure, and other variables used in