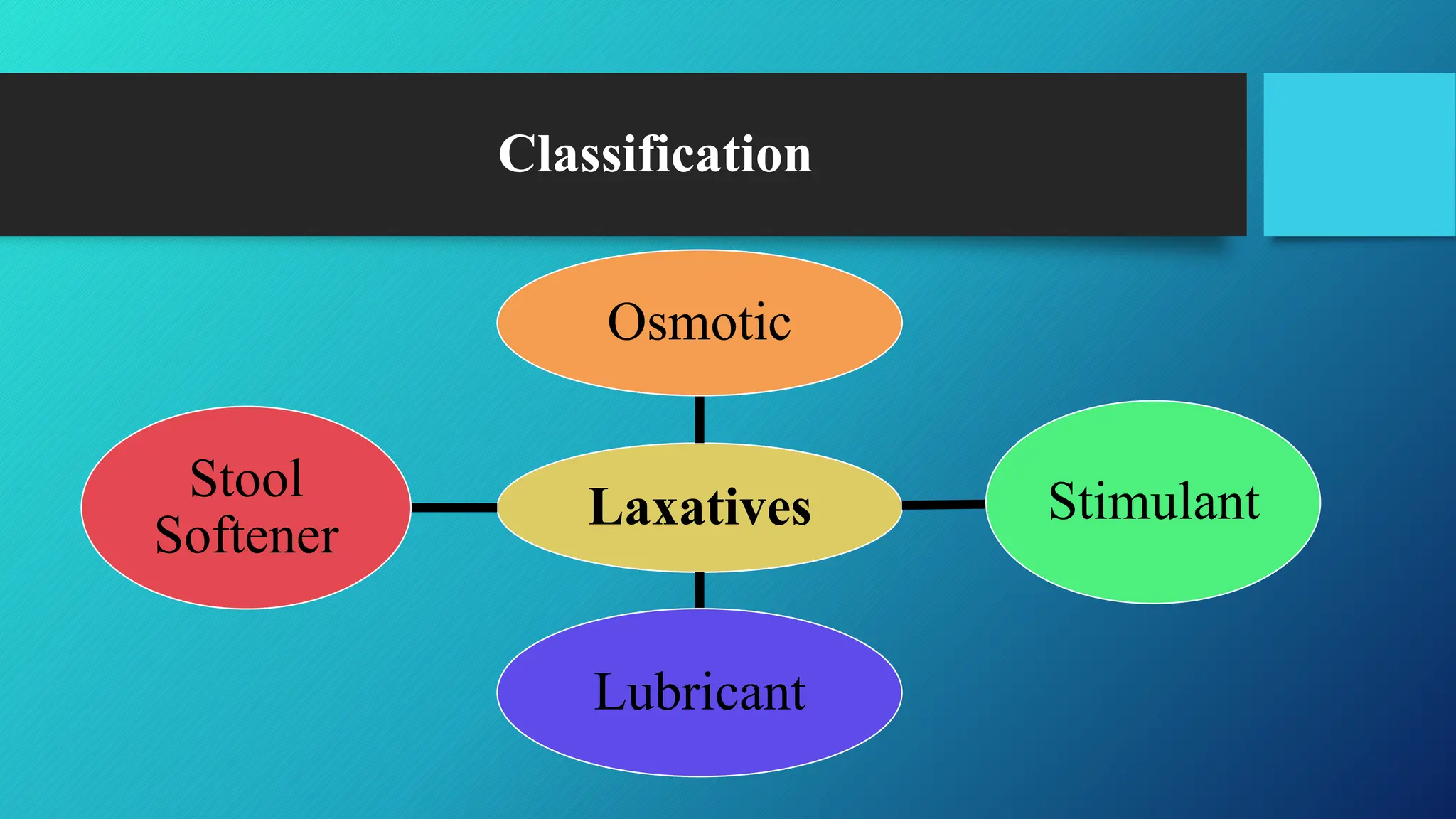
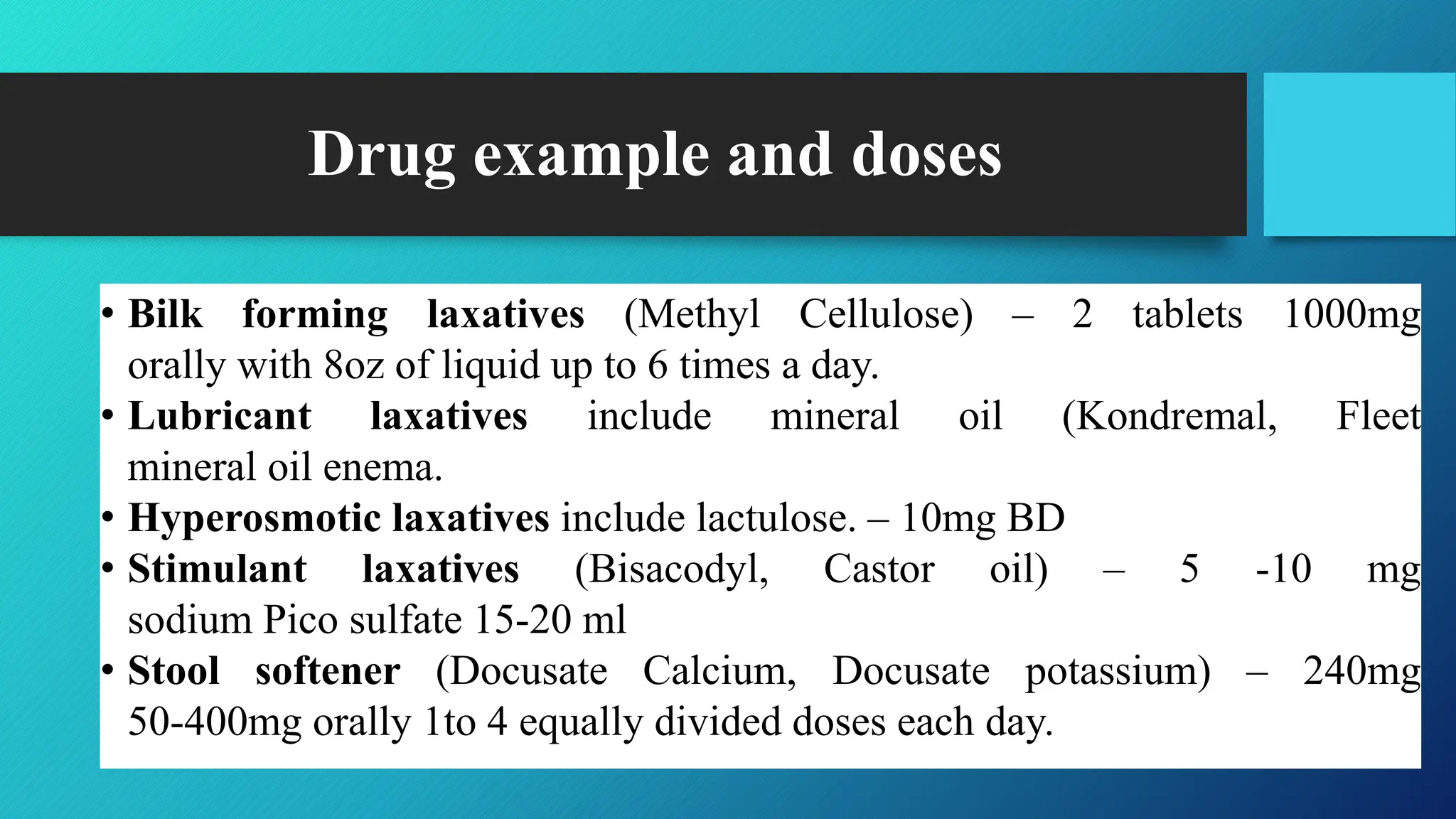
This document discusses laxatives and purgative drugs, detailing their classifications, mechanisms of action, dosage examples, uses, contraindications, and adverse effects. It highlights the importance of proper usage, such as taking them with sufficient water and monitoring for dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. Additionally, it emphasizes the nurse's role in client education and lifestyle modifications to prevent constipation.