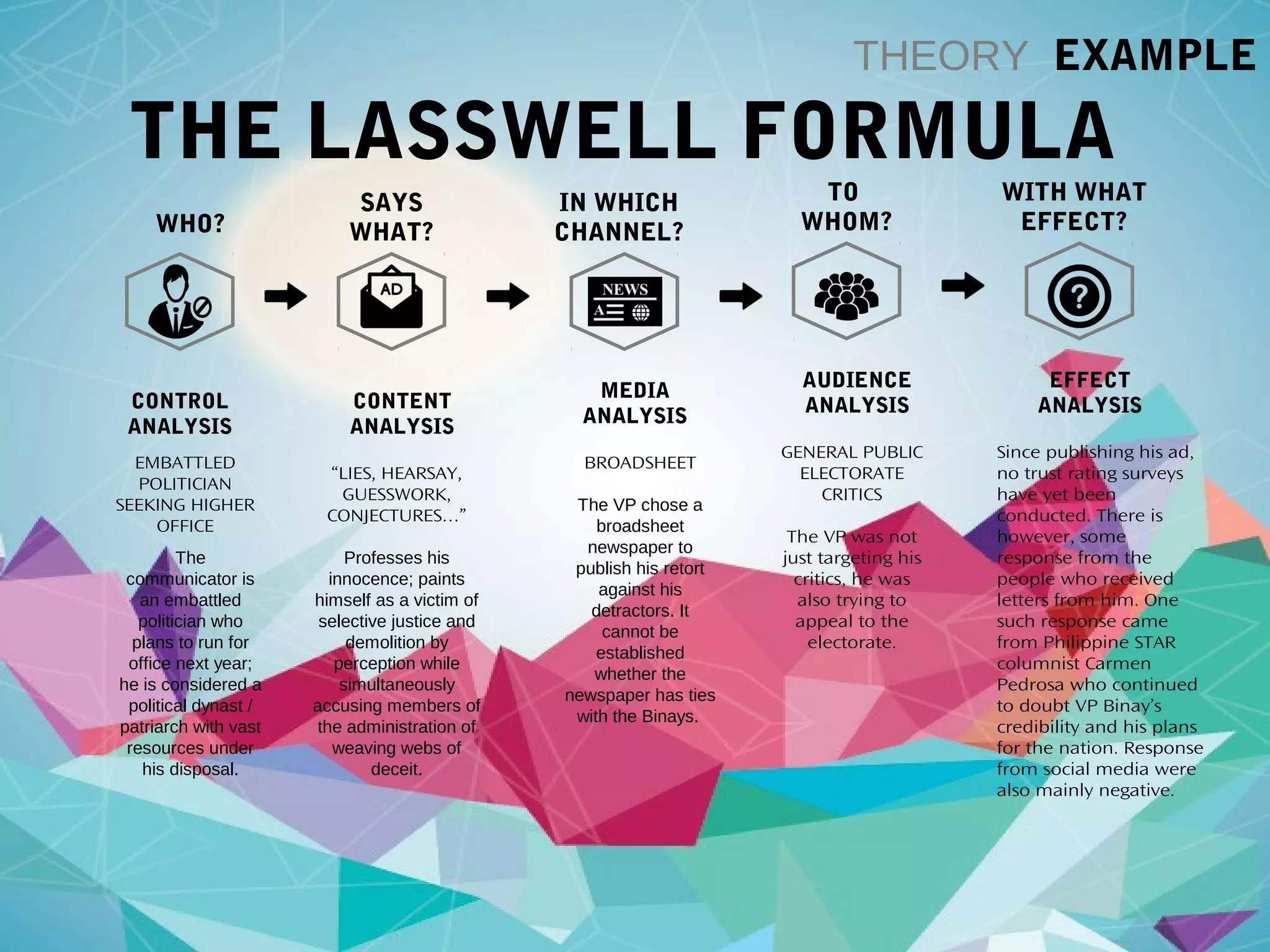
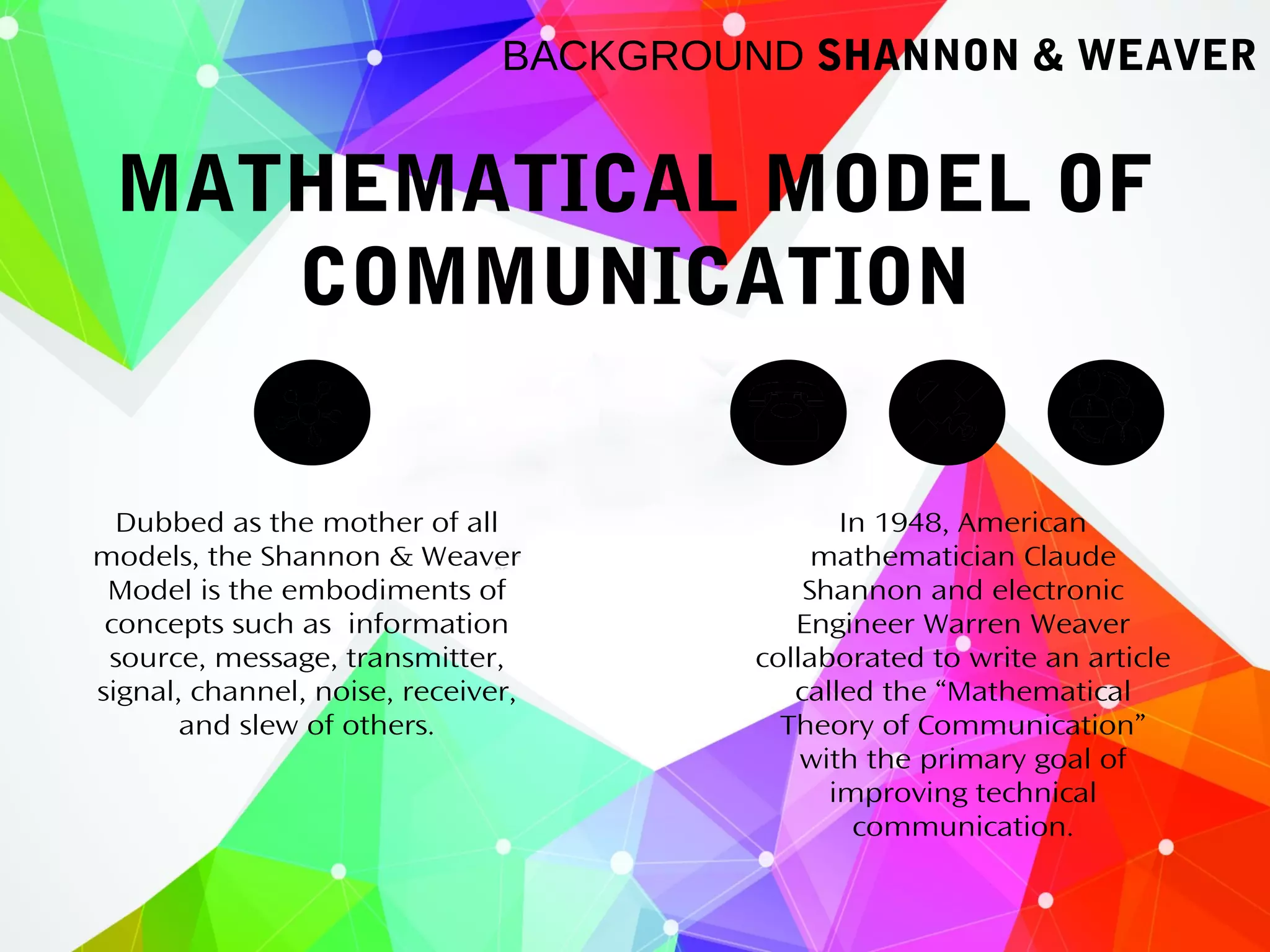
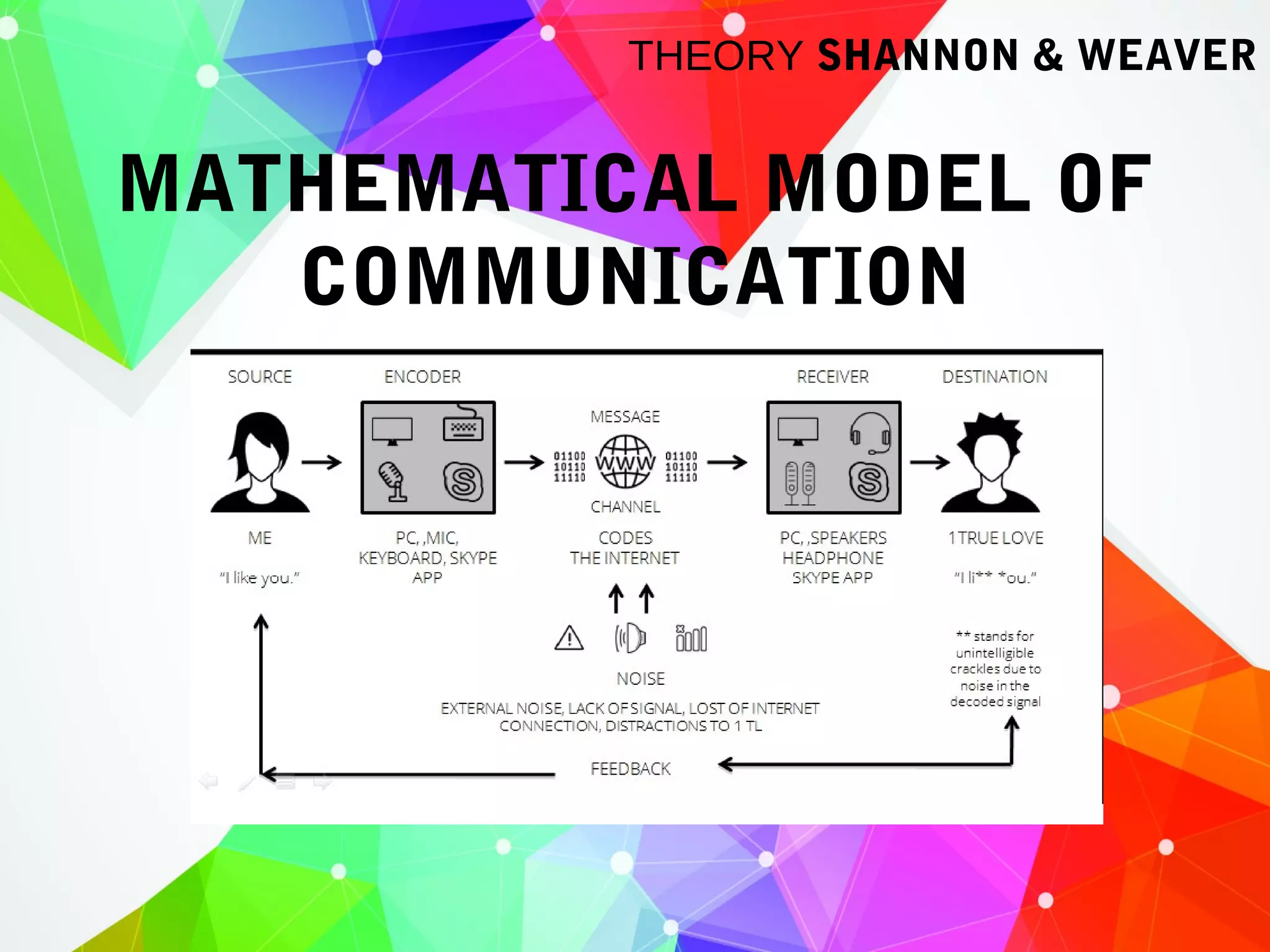
Earl Guzman holds a Bachelor's Degree in Political Science and has 5 years of professional experience. His notable roles include Legislative Staff Officer at the Senate Electoral Tribunal and Catalog Writer for ABS-CBN. He currently works as an Online Content Writer for a tech merchandising company.