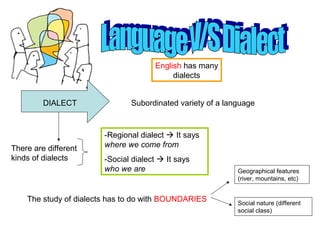
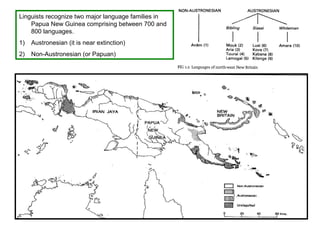
English has many dialects that vary based on region and social class. The document examines dialects in Papua New Guinea, which contains over 1,500 languages spoken by small village groups. A study examined how people from different villages requested betel nut to chew, finding both identical dialects and close relationships between dialects of the same language. While languages and dialects exist on a continuum, political and social factors also influence whether varieties are considered separate languages or dialects.