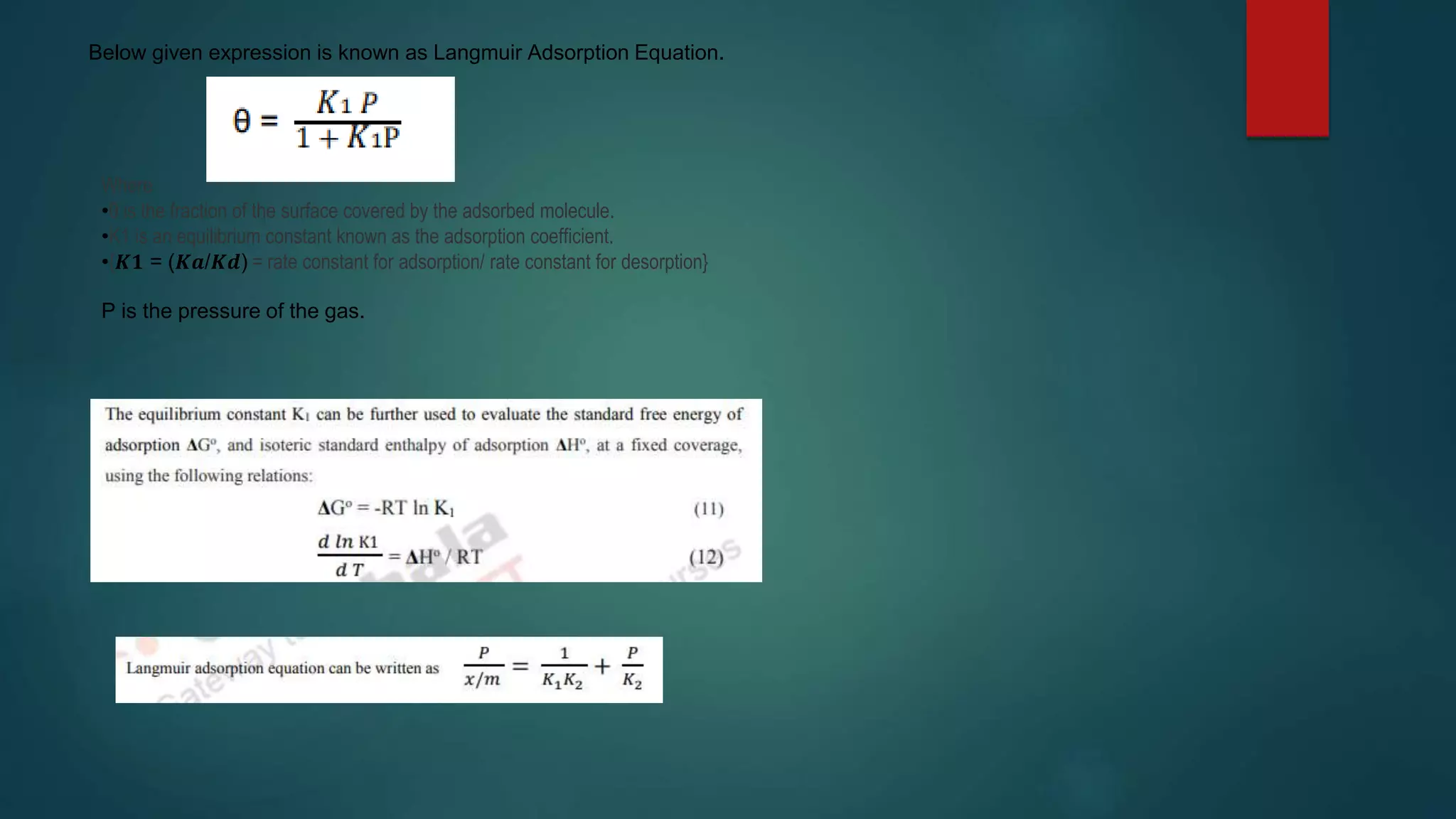
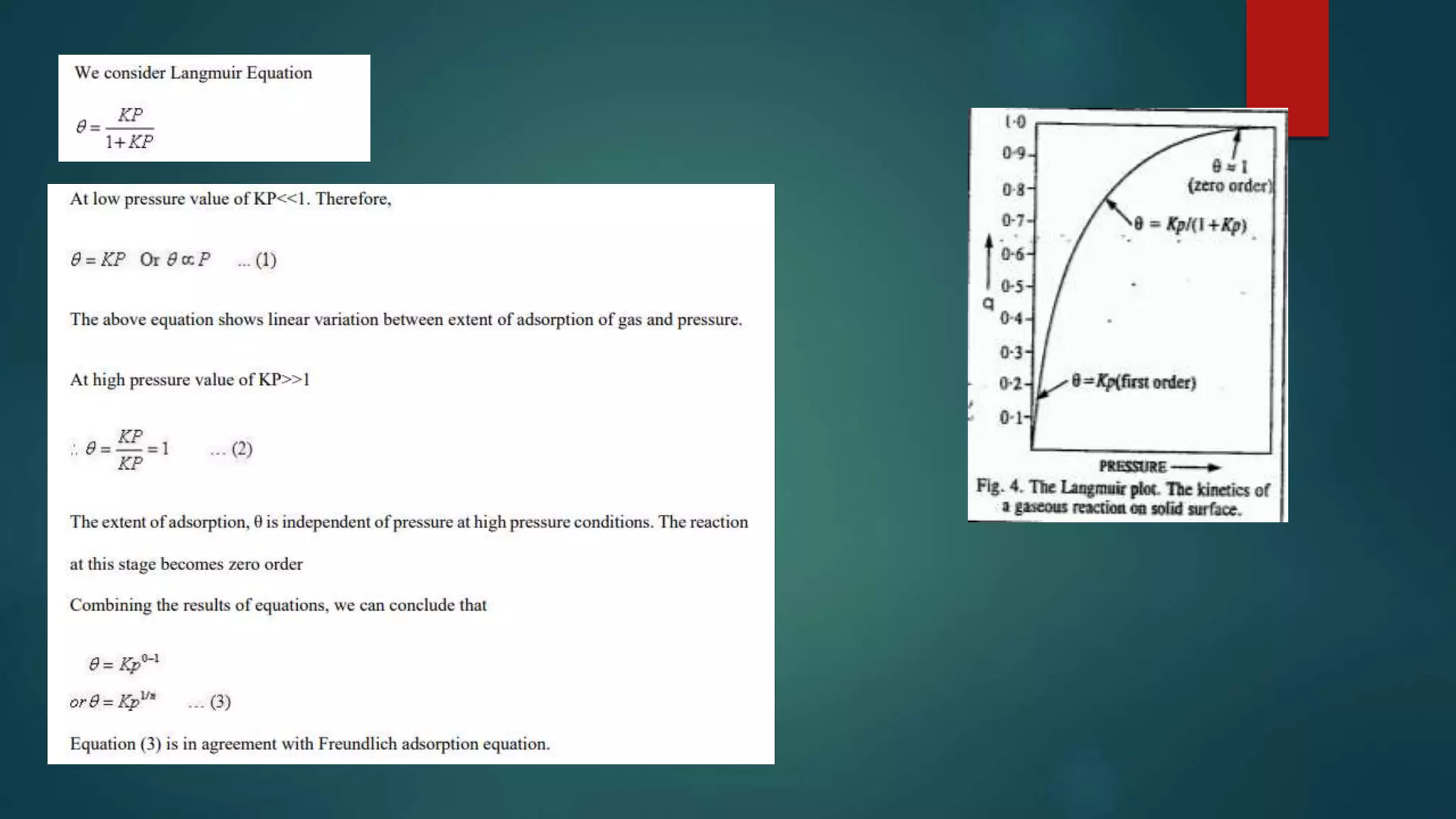
This document discusses adsorption and adsorption isotherms. It defines adsorption as the accumulation of molecules at a solid surface rather than in the bulk. There are two main types of adsorption: physisorption due to weak van der Waals forces and chemisorption due to chemical bond formation. The document describes several important adsorption isotherms including the Freundlich isotherm, Langmuir isotherm, and BET isotherm. It provides the equations and assumptions for the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms.