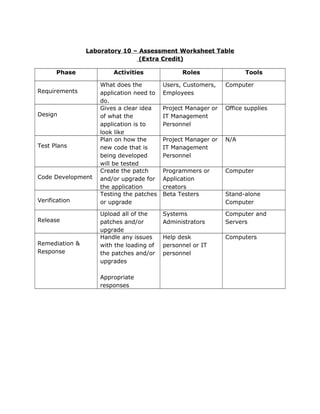
This document provides information about the secure software development lifecycle (SDL) and testing. It describes the key steps in the SDL as requirements, design, test plans, code development, verification, and release. It emphasizes creating test plans before coding to plan how the software will be tested once developed. White box testing should be done after code creation to examine the code. The document also explains what a buffer overflow is and that STRIDE is a threat model that stands for spoofing, tampering, repudiation, information disclosure, denial of service, and elevation of privilege.