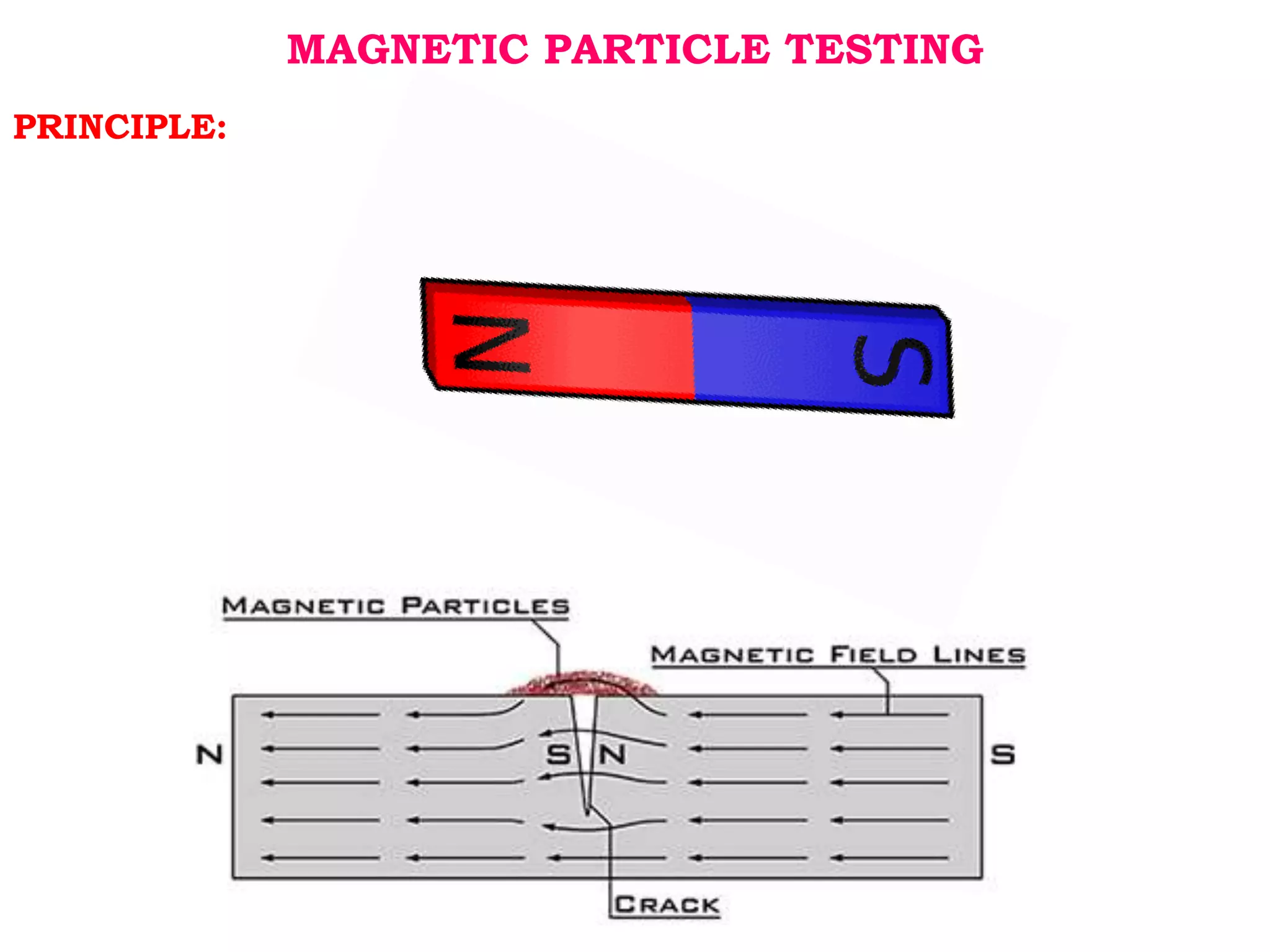
This document discusses magnetic particle testing (MPT), a non-destructive testing method used to detect surface and near surface flaws in ferromagnetic materials. It describes the basic principles and procedure of MPT, which involves magnetizing a component and applying iron particles that cluster at locations of flux leakage indicating defects. The document also outlines various magnetization methods including using permanent magnets, electromagnetic yokes, prods, and stationary equipment. It discusses the types of equipment used like Hall effect meters and pie gauges to determine magnetic field properties and different magnetic particle types for inspection.





![INSPECTION MATERIALS
MAGNETIZATION EQUIPMENT [or METHODS OF MAGNETIZATION]
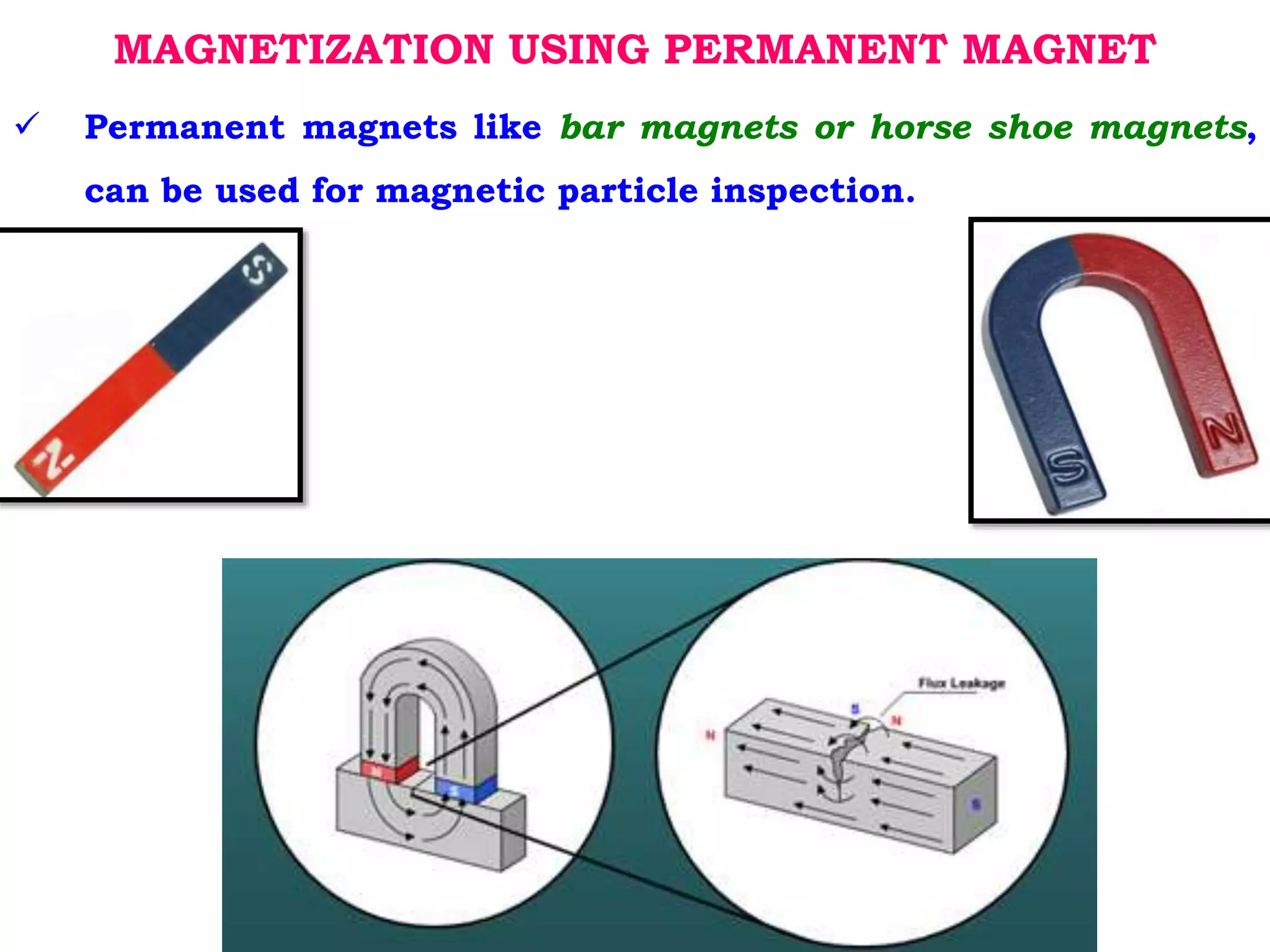
1. Permanent magnet
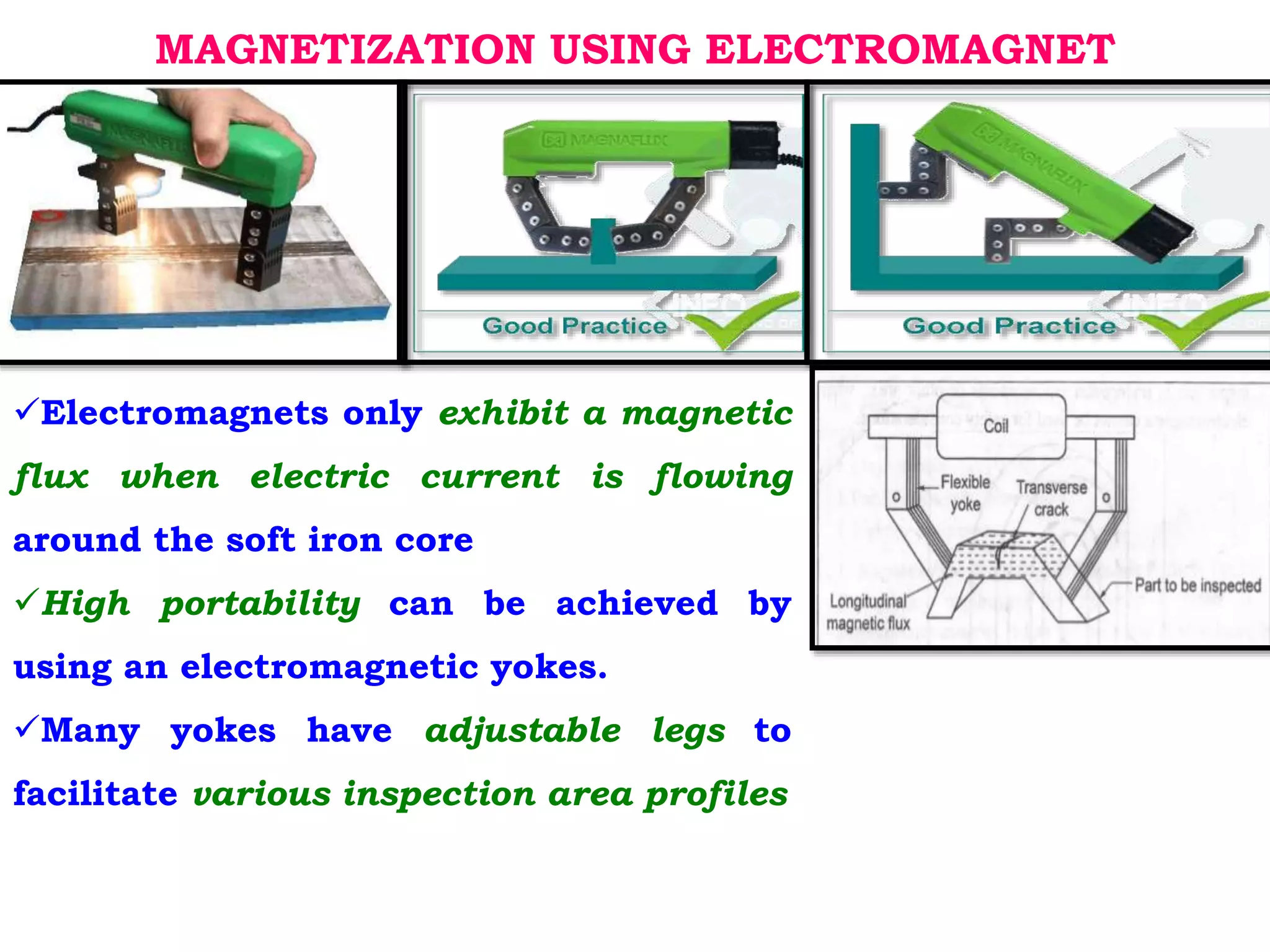
2. Electromagnetic yokes
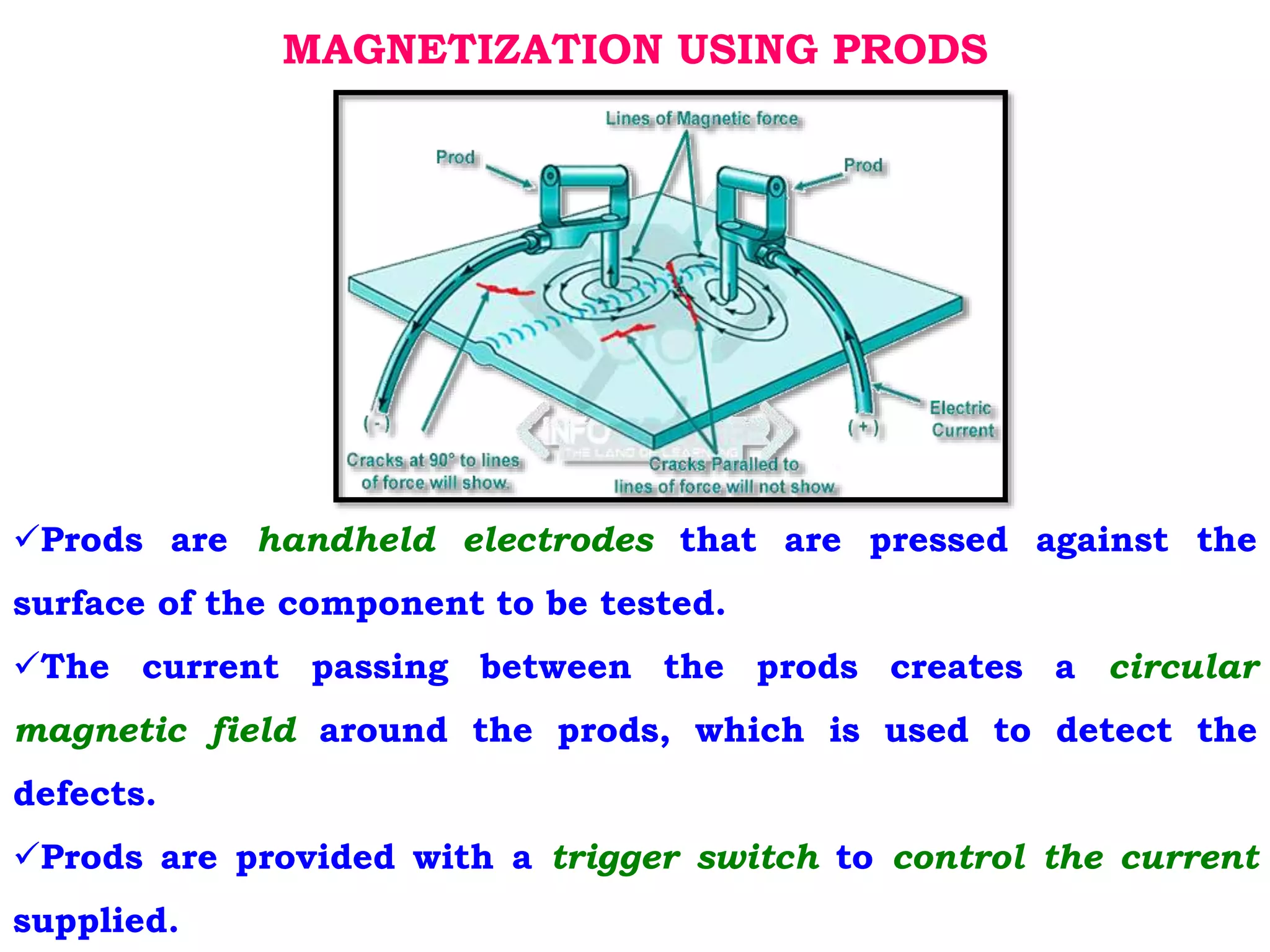
3. Prods
4. Stationary magnetic particle inspection equipment]
EQUIPMENT USED IN DETERMINATION OF MAGNETIC FIELD
STRENGTH AND DIRECTION
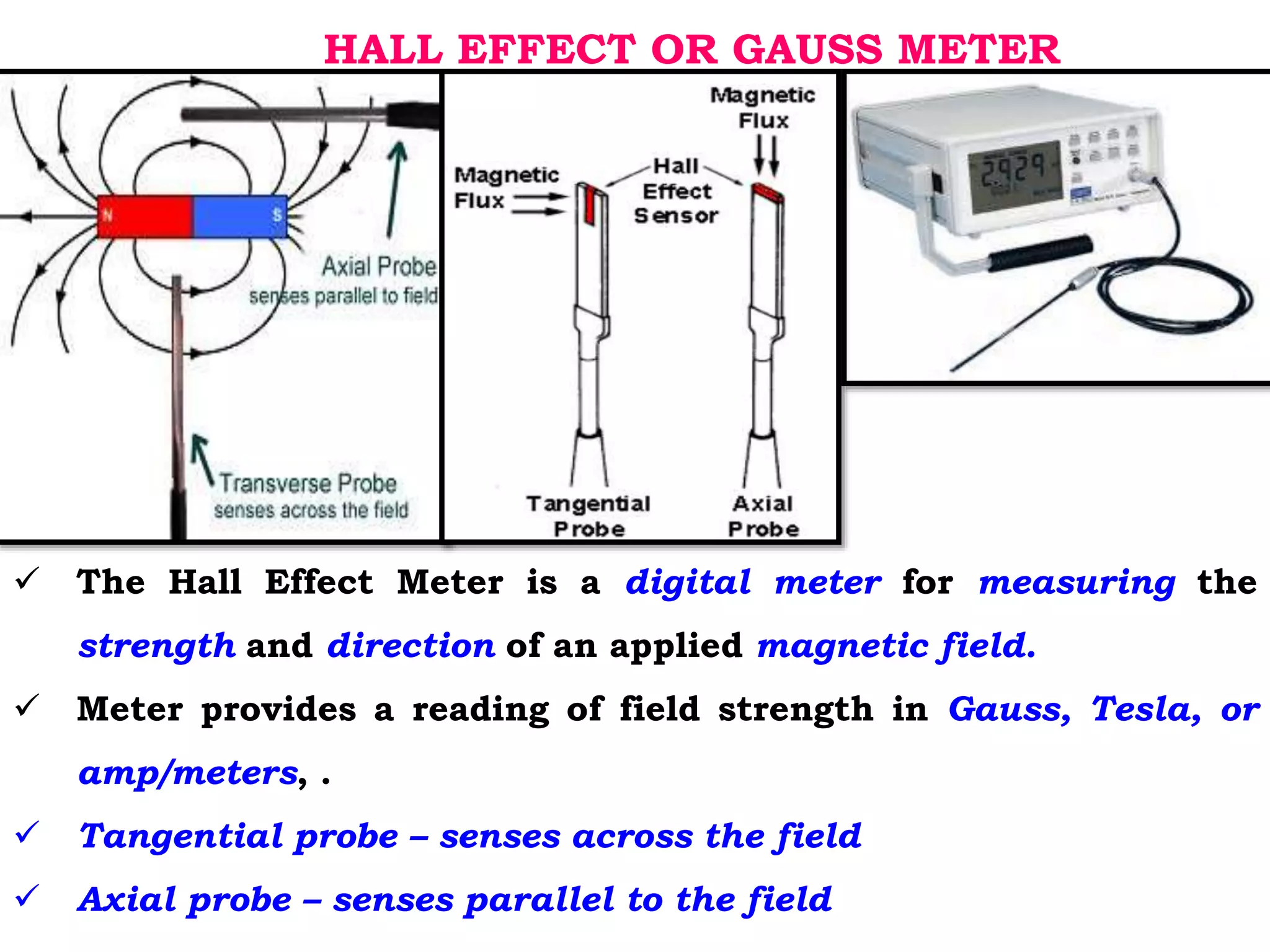
1. Hall effect or gauss meter
2. Pie gauge
3. Quantitative quality indicator [QQI]
MAGNETIC PARTICLES
1. Wet magnetic particles
2. Dry magnetic particles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-7-2048.jpg)
![MAGNETISATION METHODS
1. Magnetization using permanent magnet
2. Magnetization using electromagnet
3. Magnetization using prods
4. Magnetization using circular magnetic field [stationary
magnetic particle inspection equipment]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-8-2048.jpg)
![MAGNETIZATION USING CIRCULAR MAGNETIC FIELD
[stationary magnetic particle inspection equipment]
In this type, a circular magnetic field can be produced in a
cylindrical components.
The part is placed between the headstock and tailstock and
gripped by pneumatic chuck to permit current to flow, thereby
producing a circular magnetic field.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-12-2048.jpg)
![INSPECTION MATERIALS
MAGNETIZATION EQUIPMENT [or METHODS OF MAGNETIZATION]
1. Permanent magnet
2. Electromagnetic yokes
3. Prods
4. Stationary magnetic particle inspection equipment]
EQUIPMENT USED IN DETERMINATION OF MAGNETIC FIELD
STRENGTH AND DIRECTION
1. Hall effect or gauss meter
2. Pie gauge
3. Quantitative quality indicator [QQI]
MAGNETIC PARTICLES
1. Wet magnetic particles
2. Dry magnetic particles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-13-2048.jpg)

![QUANTITATIVE QUALITY INDICATOR [QQI]
Quantitative Quality Indicators (QQI) are magnetic particle test
pieces with artificial defects used to verify field direction](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-16-2048.jpg)
![INSPECTION MATERIALS
MAGNETIZATION EQUIPMENT [or METHODS OF MAGNETIZATION]
1. Permanent magnet
2. Electromagnetic yokes
3. Prods
4. Stationary magnetic particle inspection equipment]
EQUIPMENT USED IN DETERMINATION OF MAGNETIC FIELD
STRENGTH AND DIRECTION
1. Hall effect or gauss meter
2. Pie gauge
3. Quantitative quality indicator [QQI]
MAGNETIC PARTICLES
1. Wet magnetic particles
2. Dry magnetic particles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-17-2048.jpg)


![INSPECTION MATERIALS
MAGNETIZATION EQUIPMENT [or METHODS OF MAGNETIZATION]
1. Permanent magnet
2. Electromagnetic yokes
3. Prods
4. Stationary magnetic particle inspection equipment]
EQUIPMENT USED IN DETERMINATION OF MAGNETIC FIELD
STRENGTH AND DIRECTION
1. Hall effect or gauss meter
2. Pie gauge
3. Quantitative quality indicator [QQI]
MAGNETIC PARTICLES
1. Wet magnetic particles
2. Dry magnetic particles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/l22magneticparticletest-201005050051/75/L22-magnetic-particle-test-20-2048.jpg)
