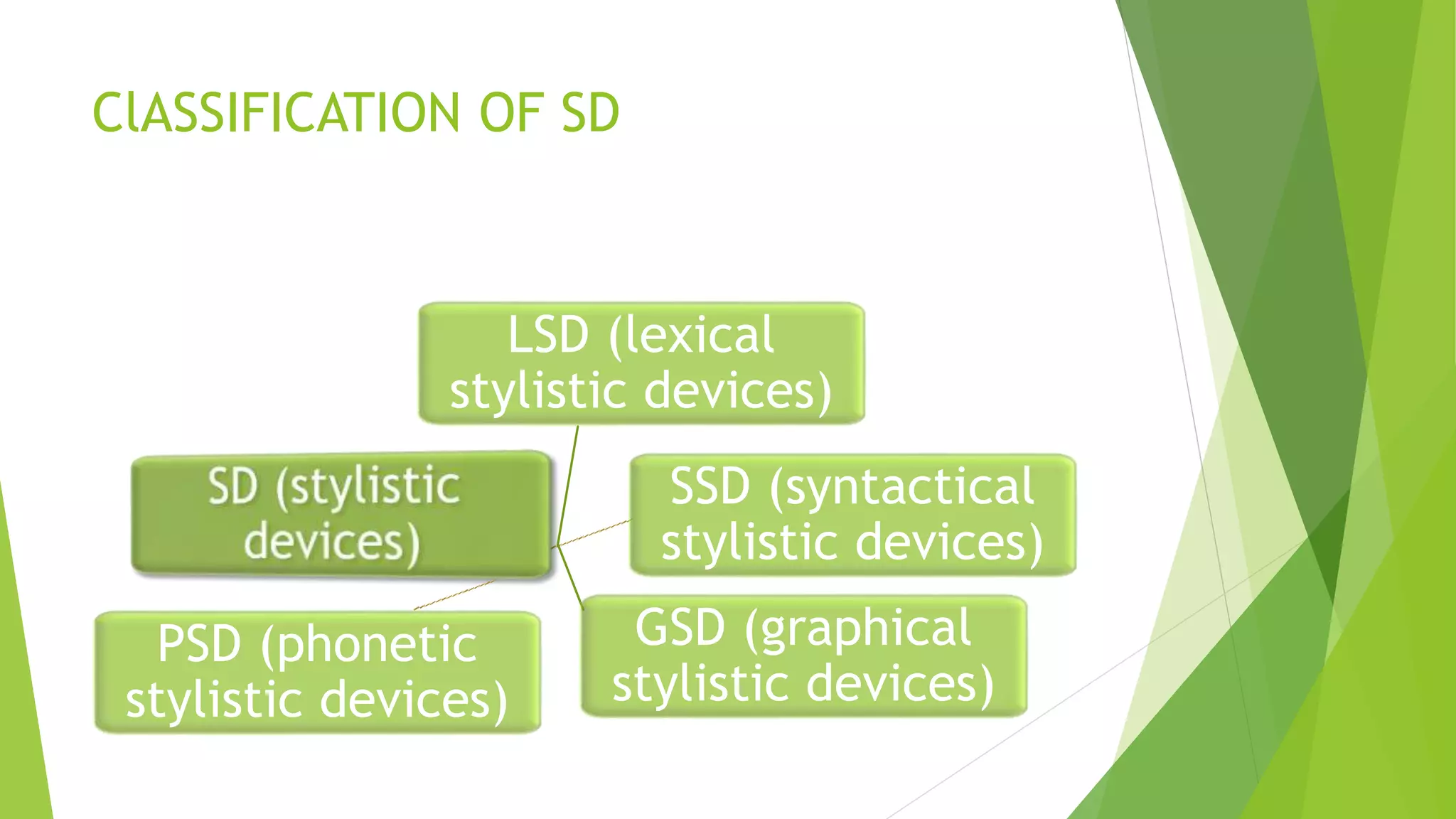
This document provides an overview of different types of lexical stylistic devices, including zeugma, pun, metonymy, irony, oxymoron, antonomasia, metaphor, epithet, personification, simile, hyperbole, periphrasis, cliche, proverb, allusion, and quotation. Each device is defined and an example is given to illustrate how it works. The document categorizes these devices based on how they interact with meanings and intensify features of things or phenomena for stylistic purposes.