The document discusses heat treatment processes for engineering materials. It describes how heating and cooling can be used to alter the structure and properties of materials, primarily metals. Key points include:
1) Heat treatment involves controlled heating and cooling to change a material's microstructure and properties in a way that does not alter its overall shape.
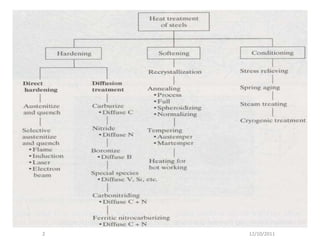
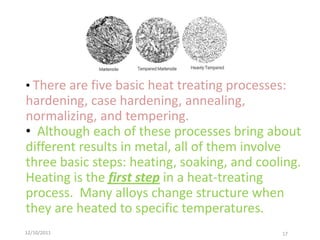
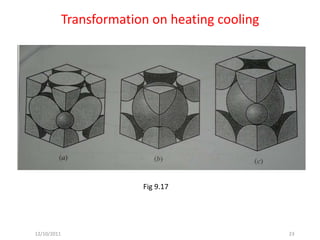
2) Common heat treatments include hardening, annealing, normalizing and tempering. All involve heating, holding, and cooling, which can result in phase transformations.
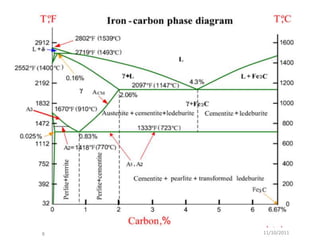
3) Phase transformations in steel depend on the alloy's carbon content and the heating/cooling rates. Rapid cooling can form martensite to increase hardness, while slower cooling forms pearlite or ferrite/