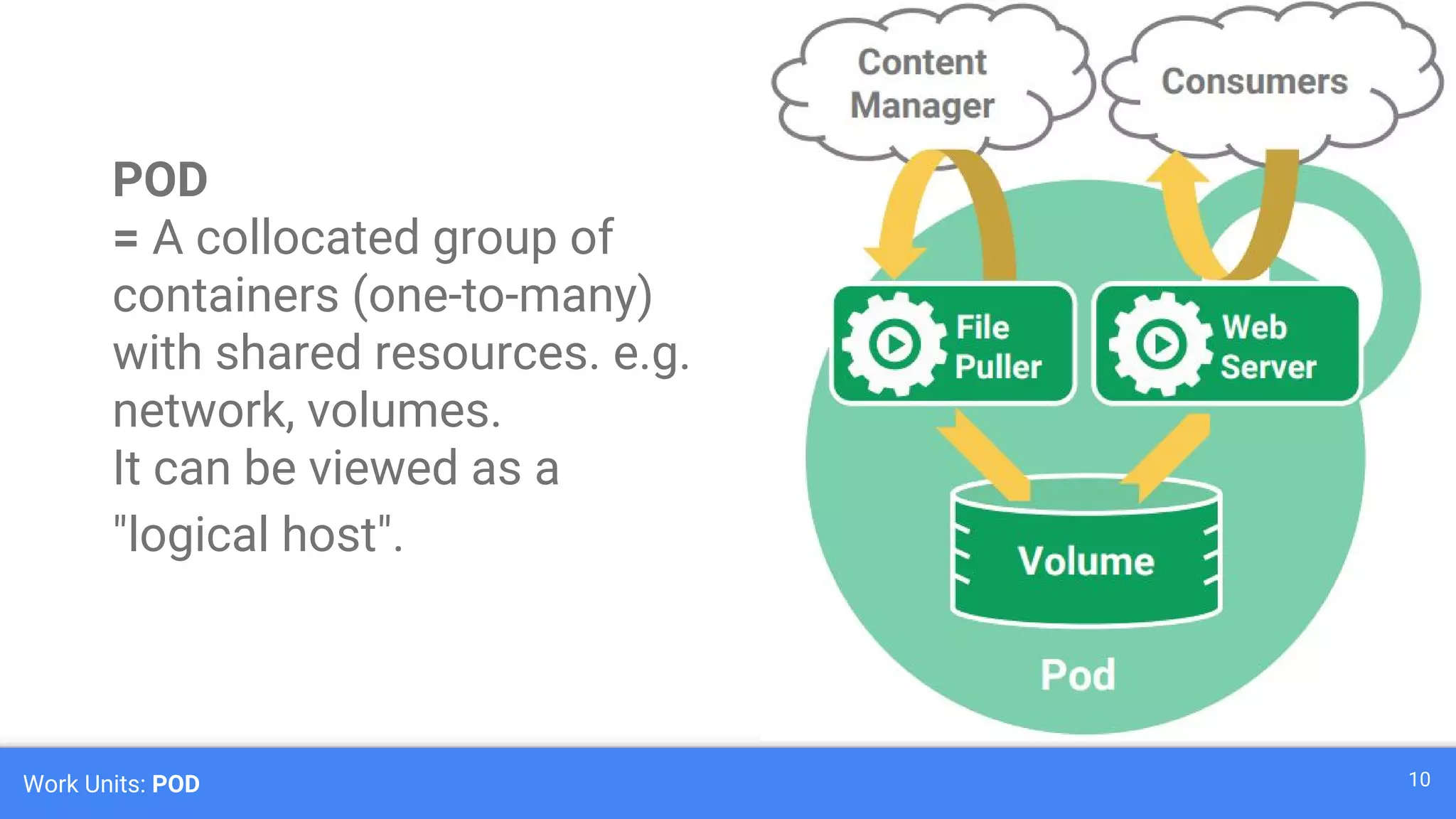
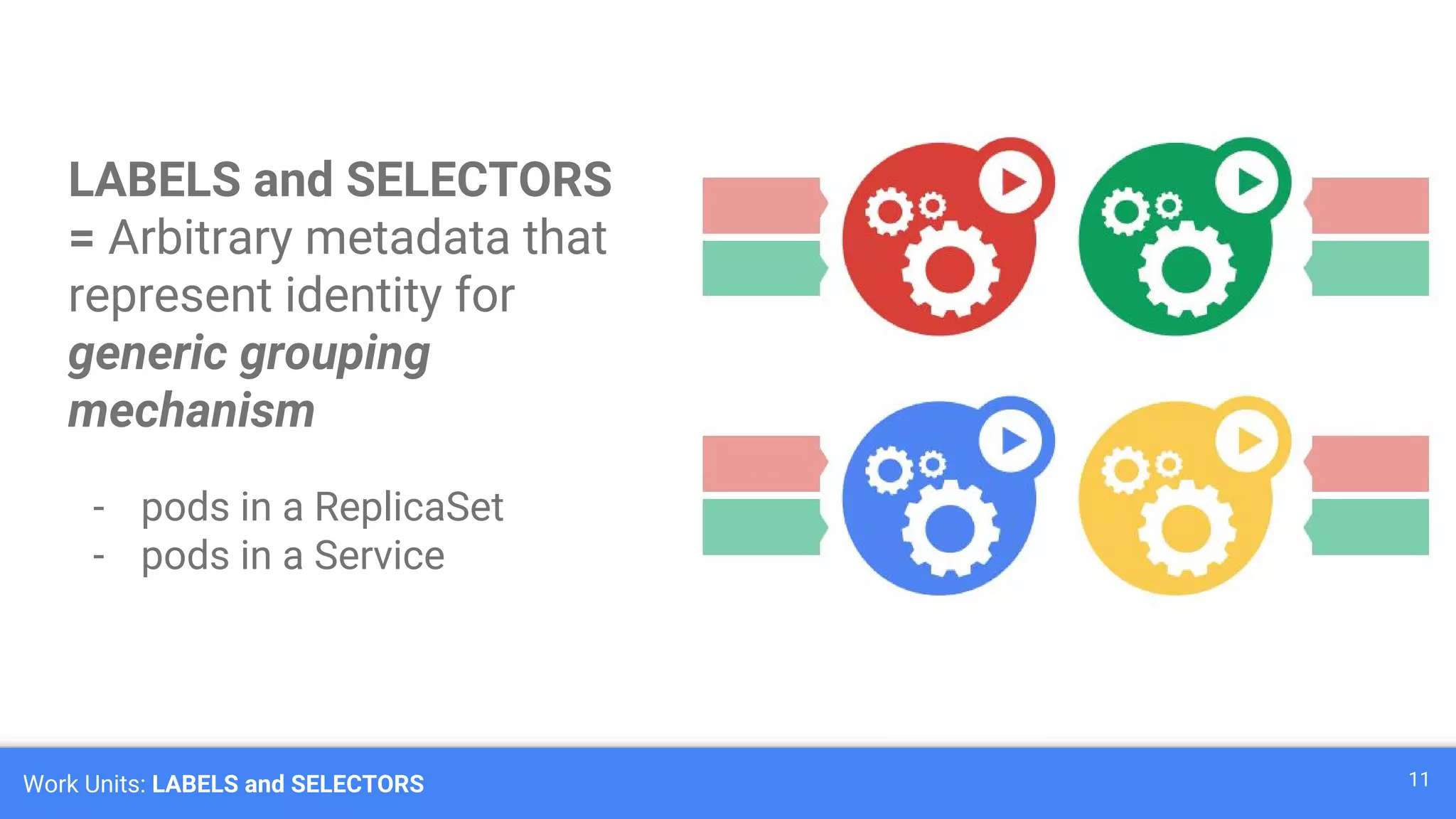
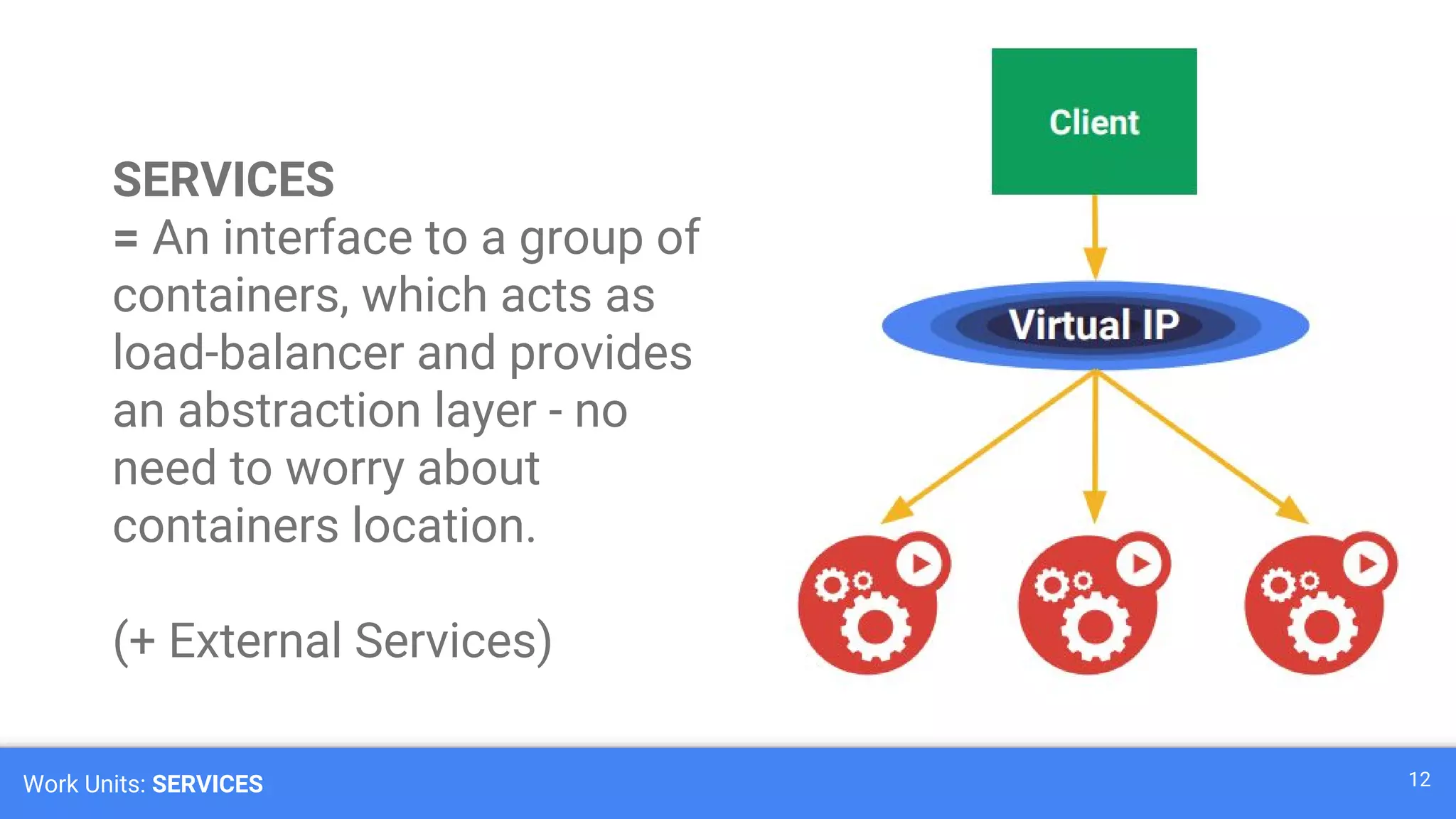
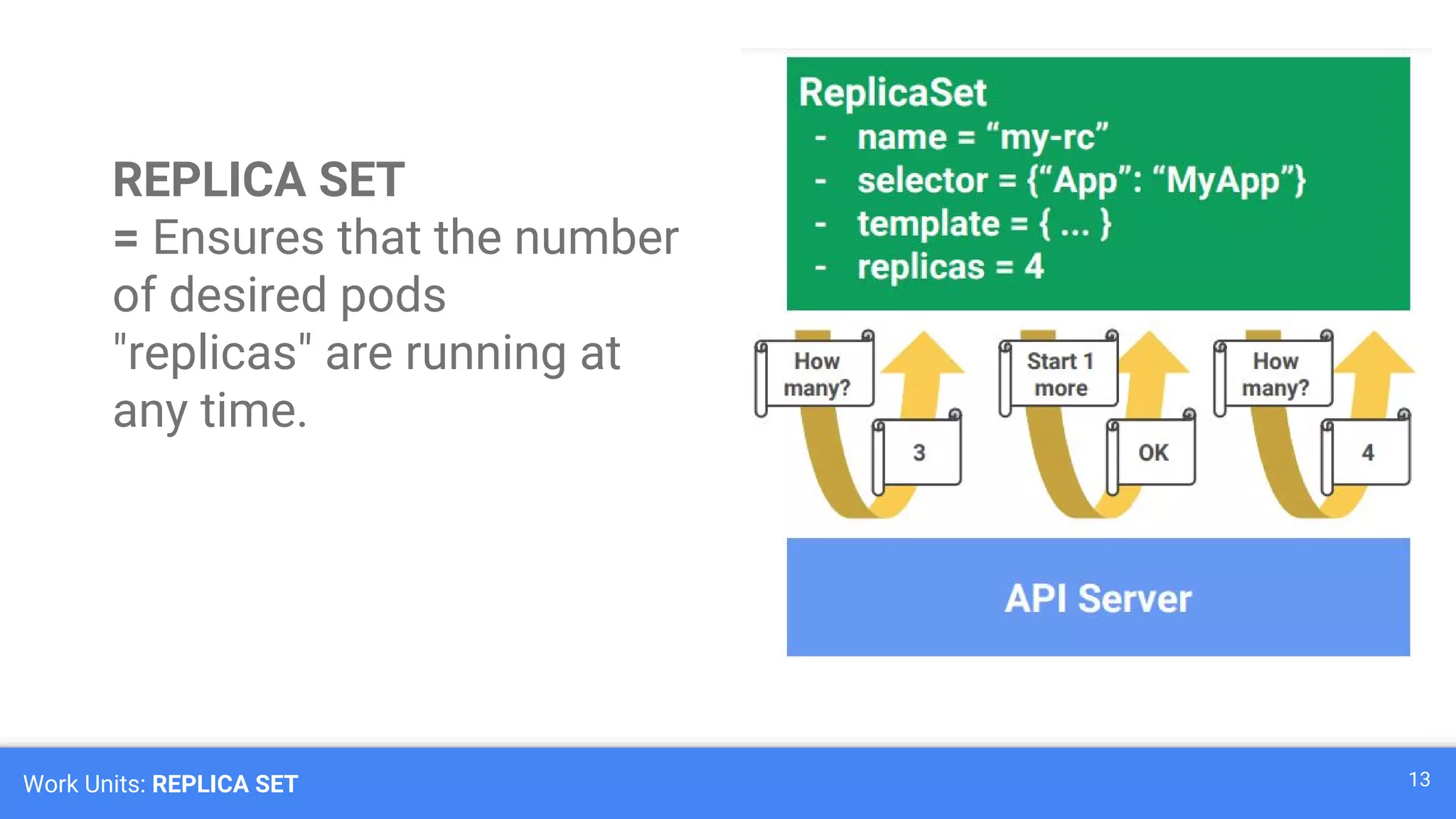
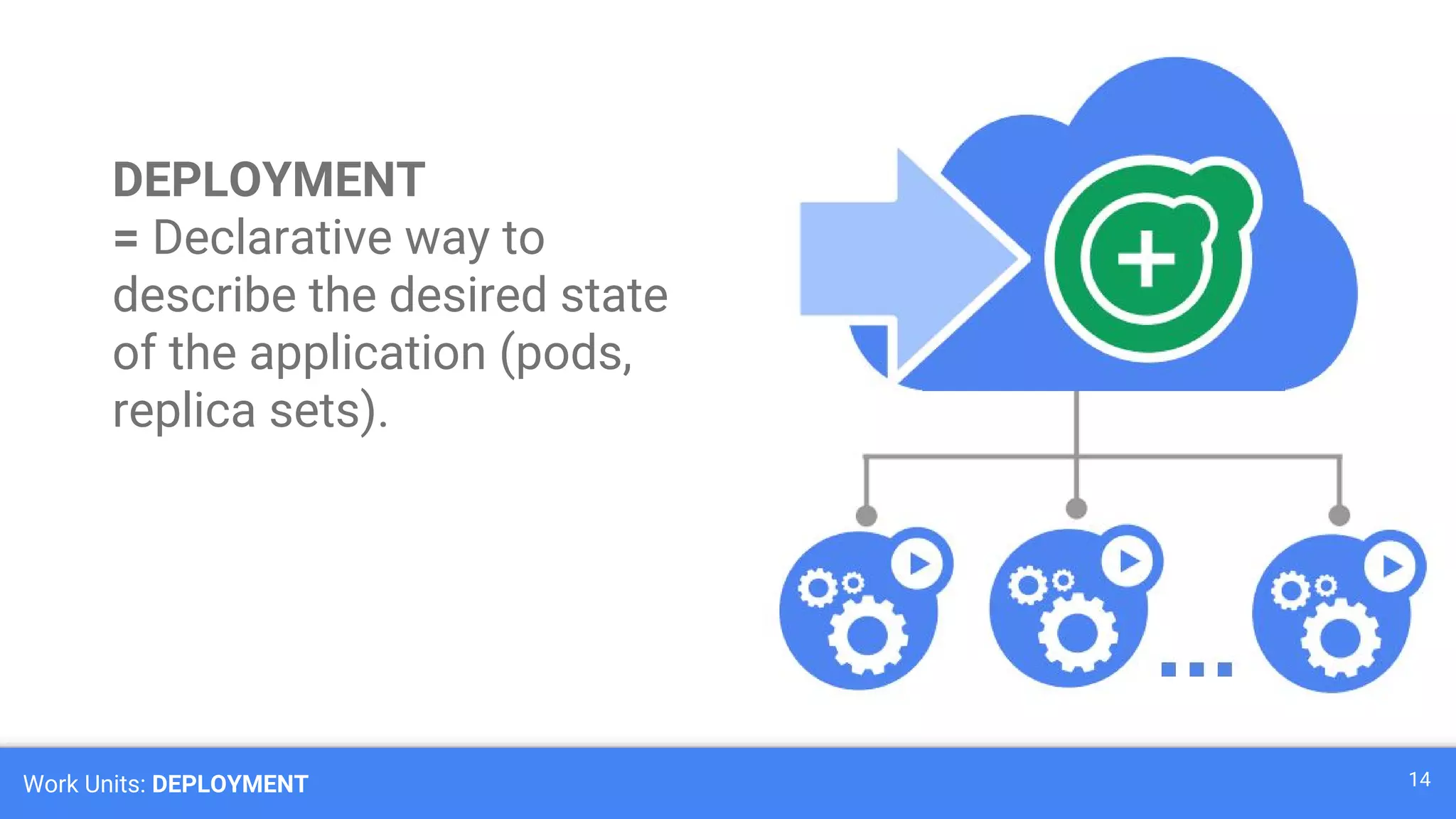
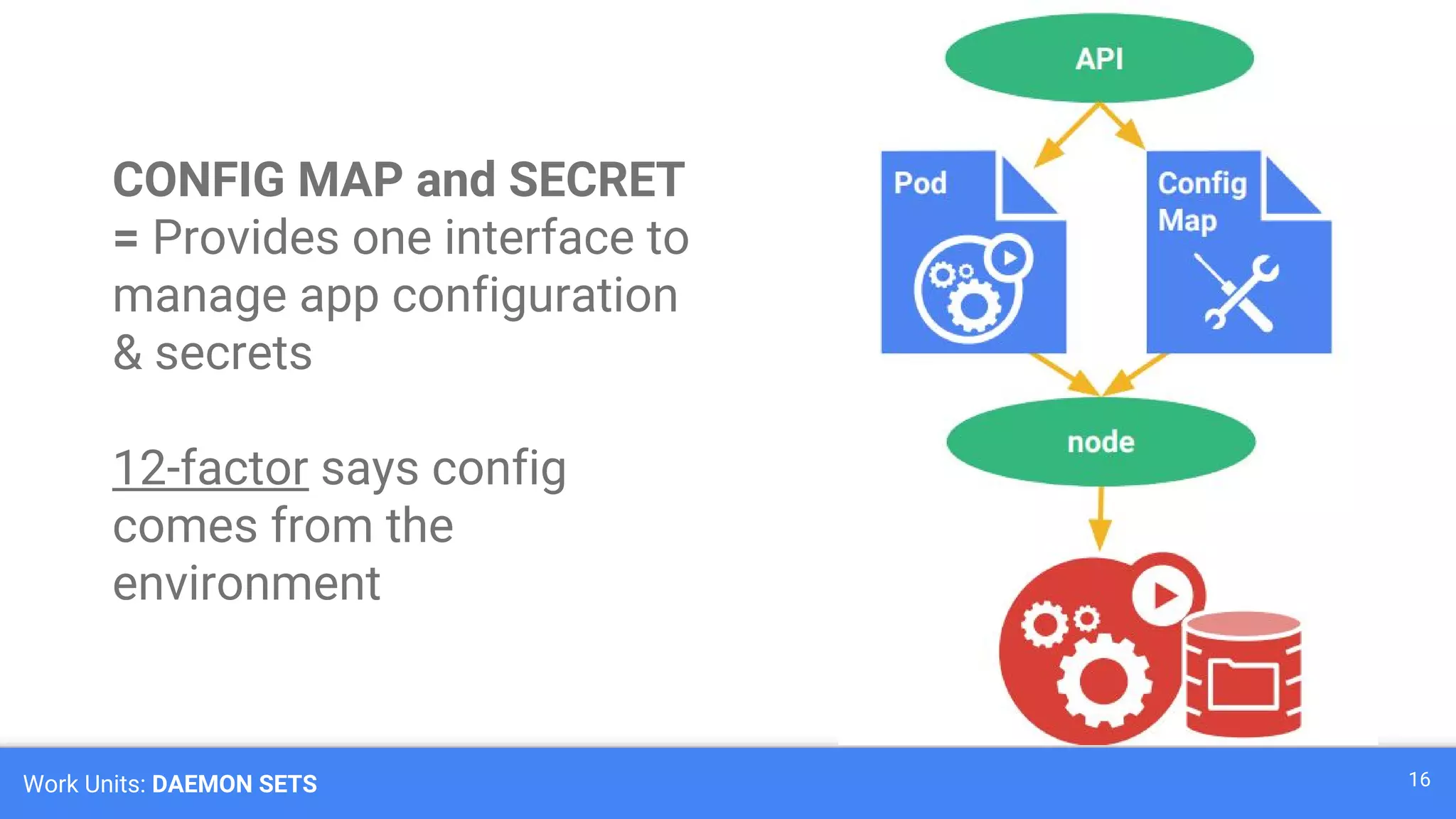
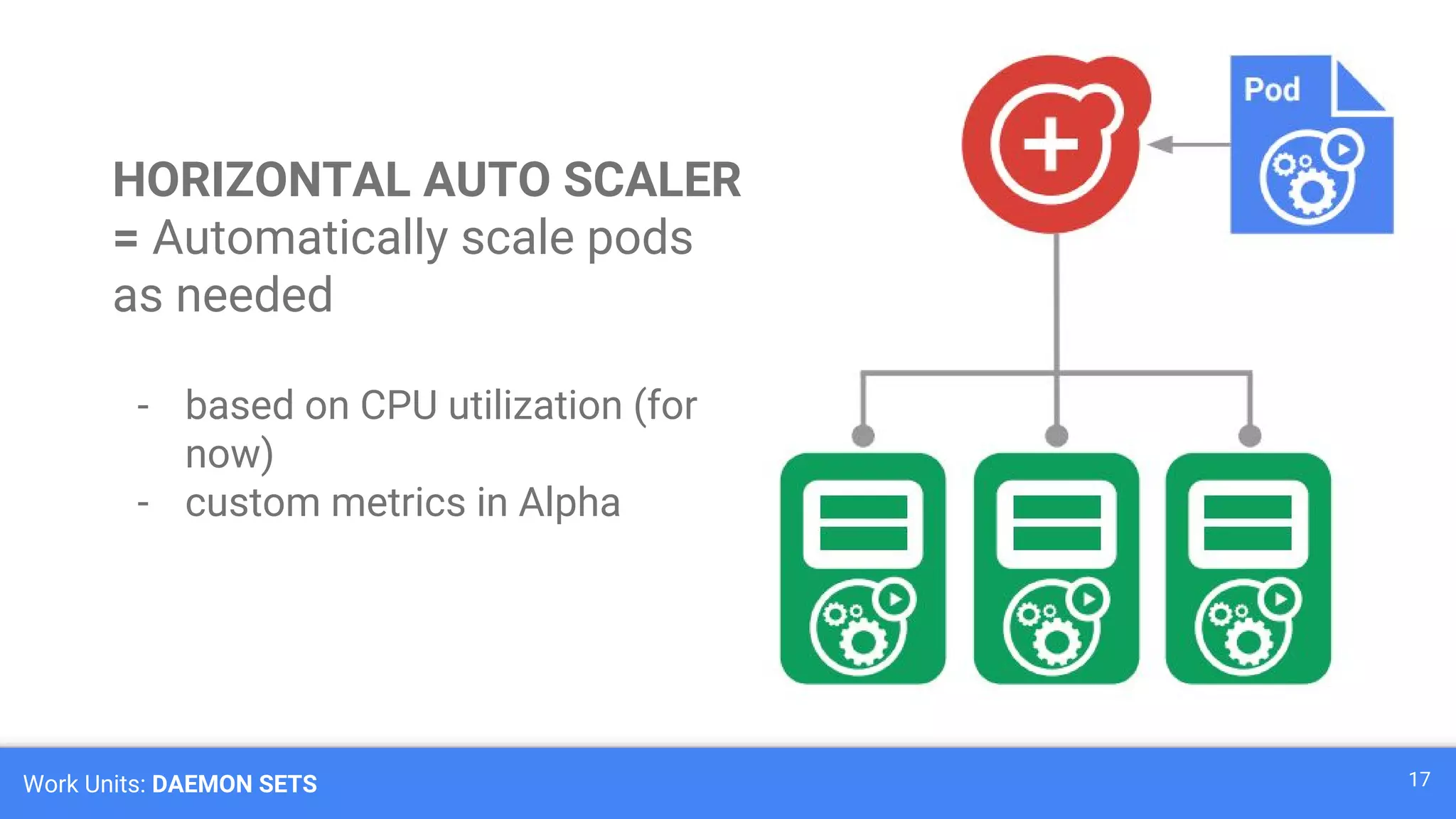
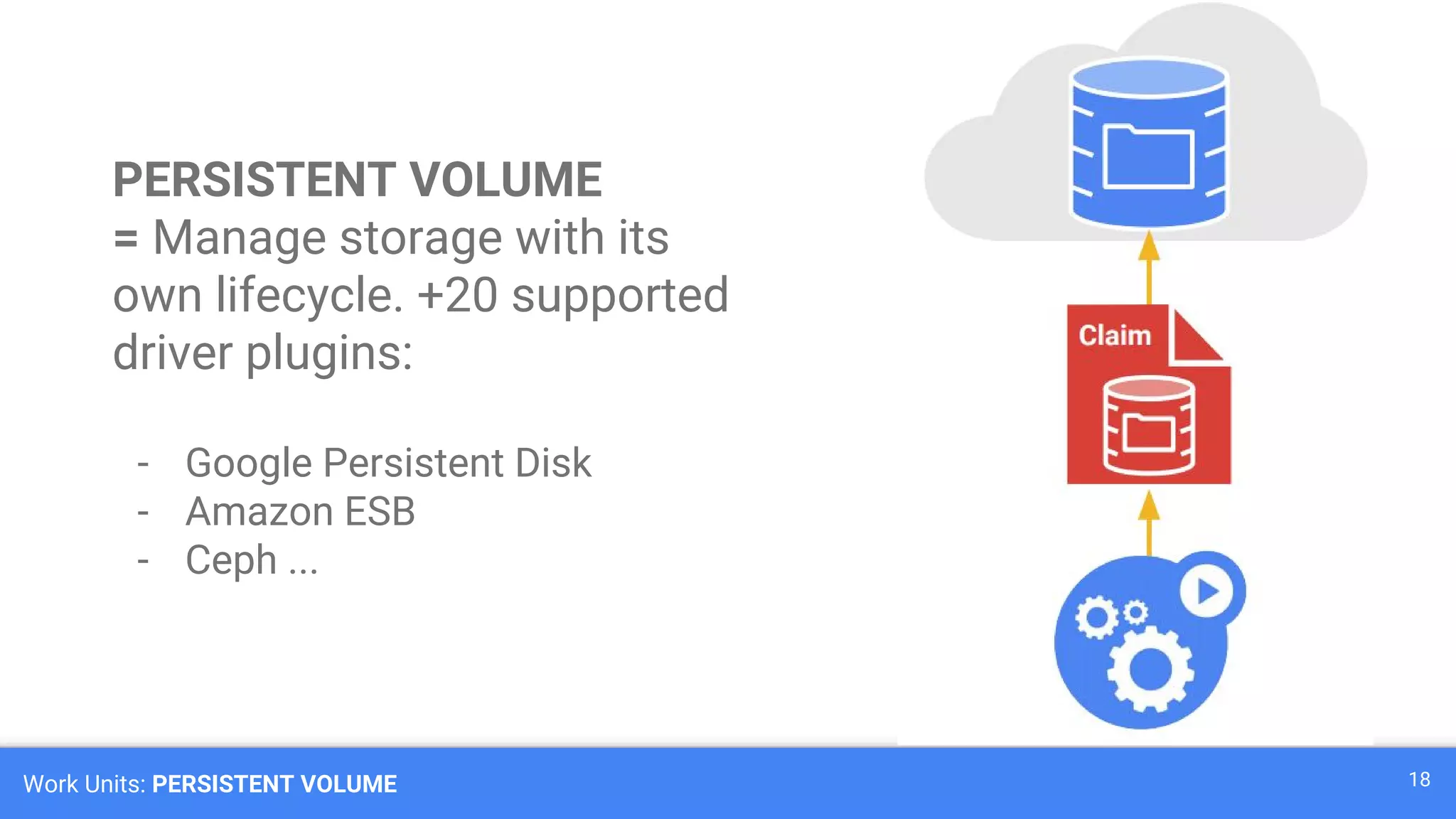
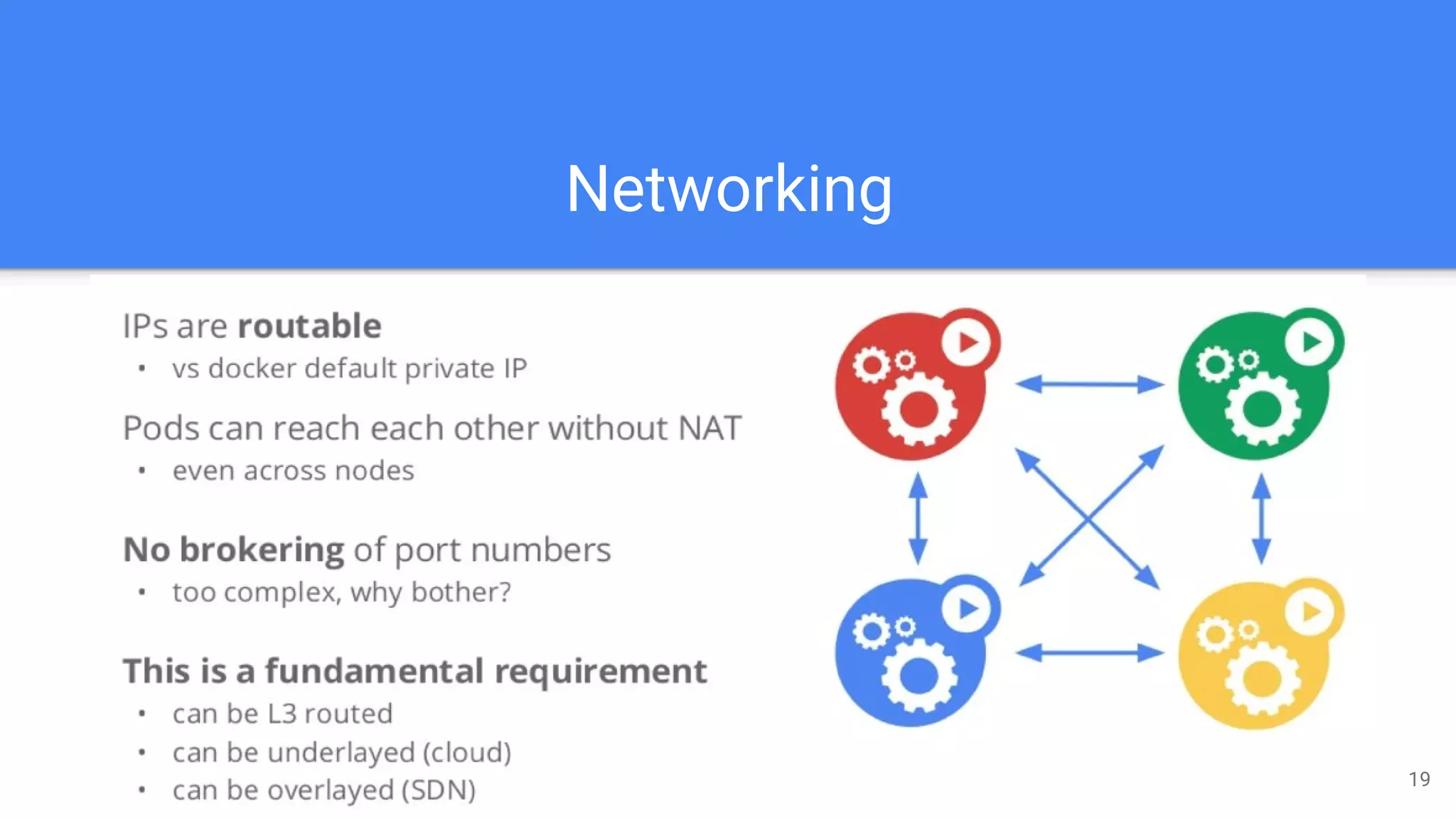
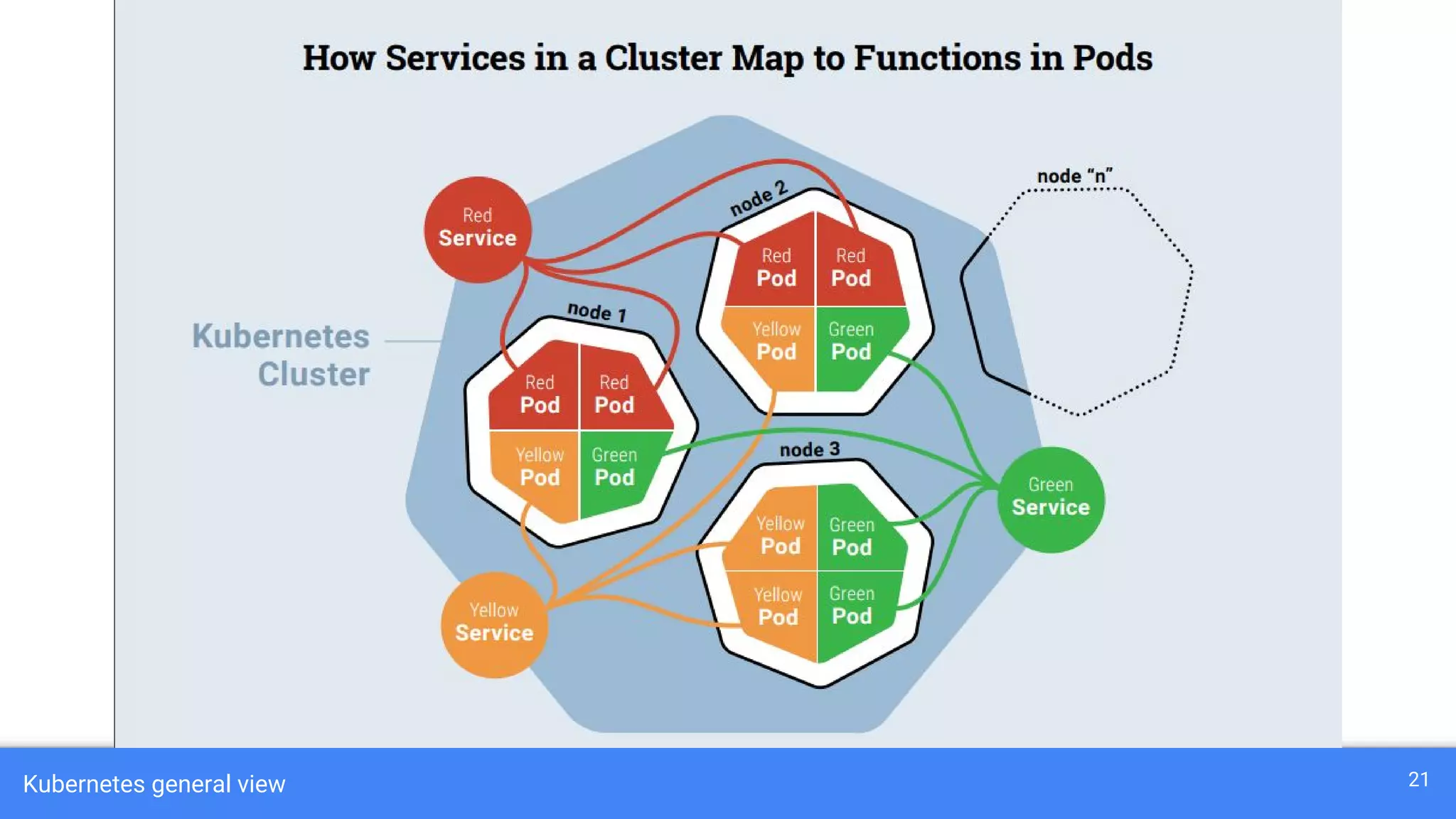
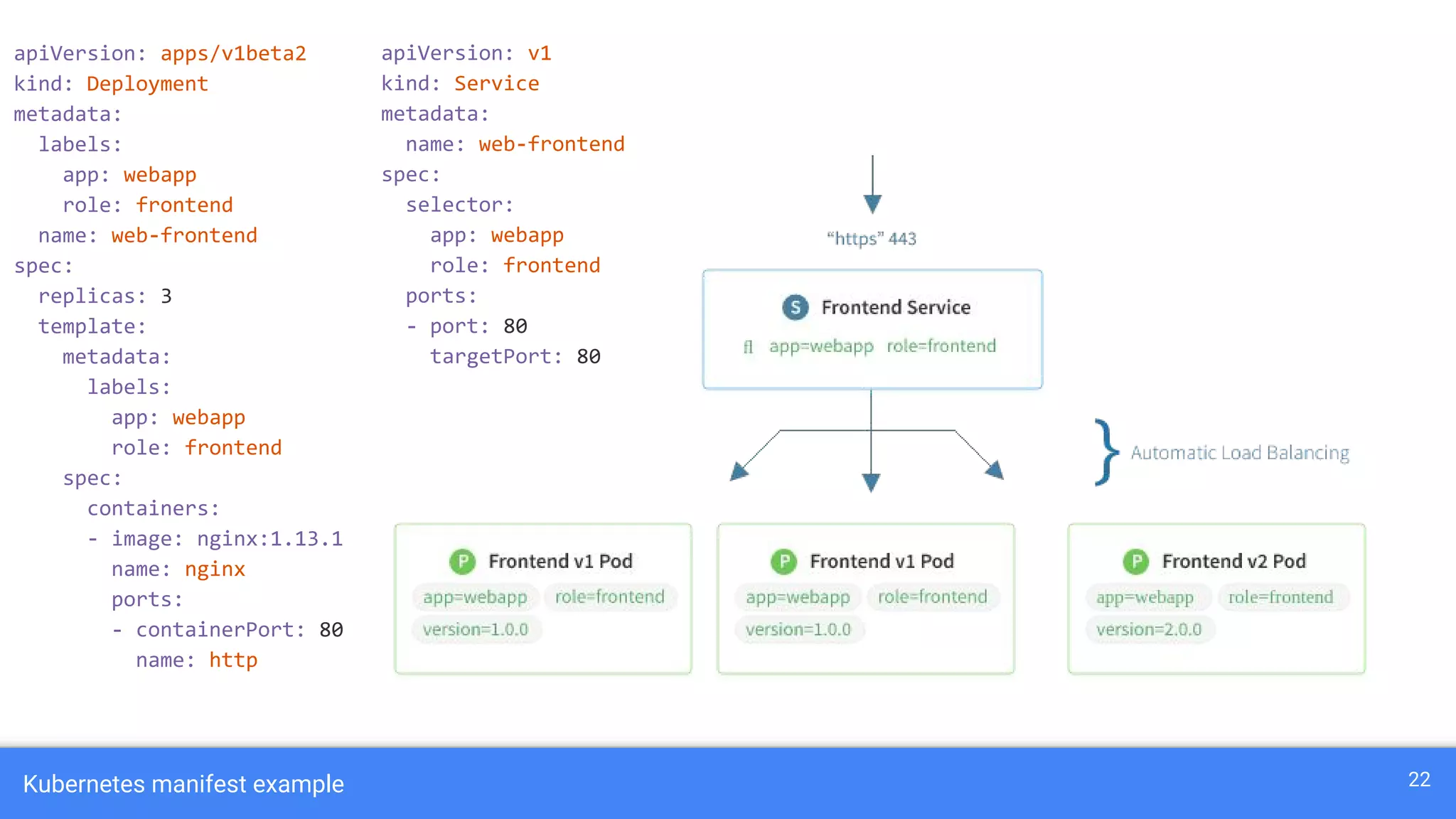
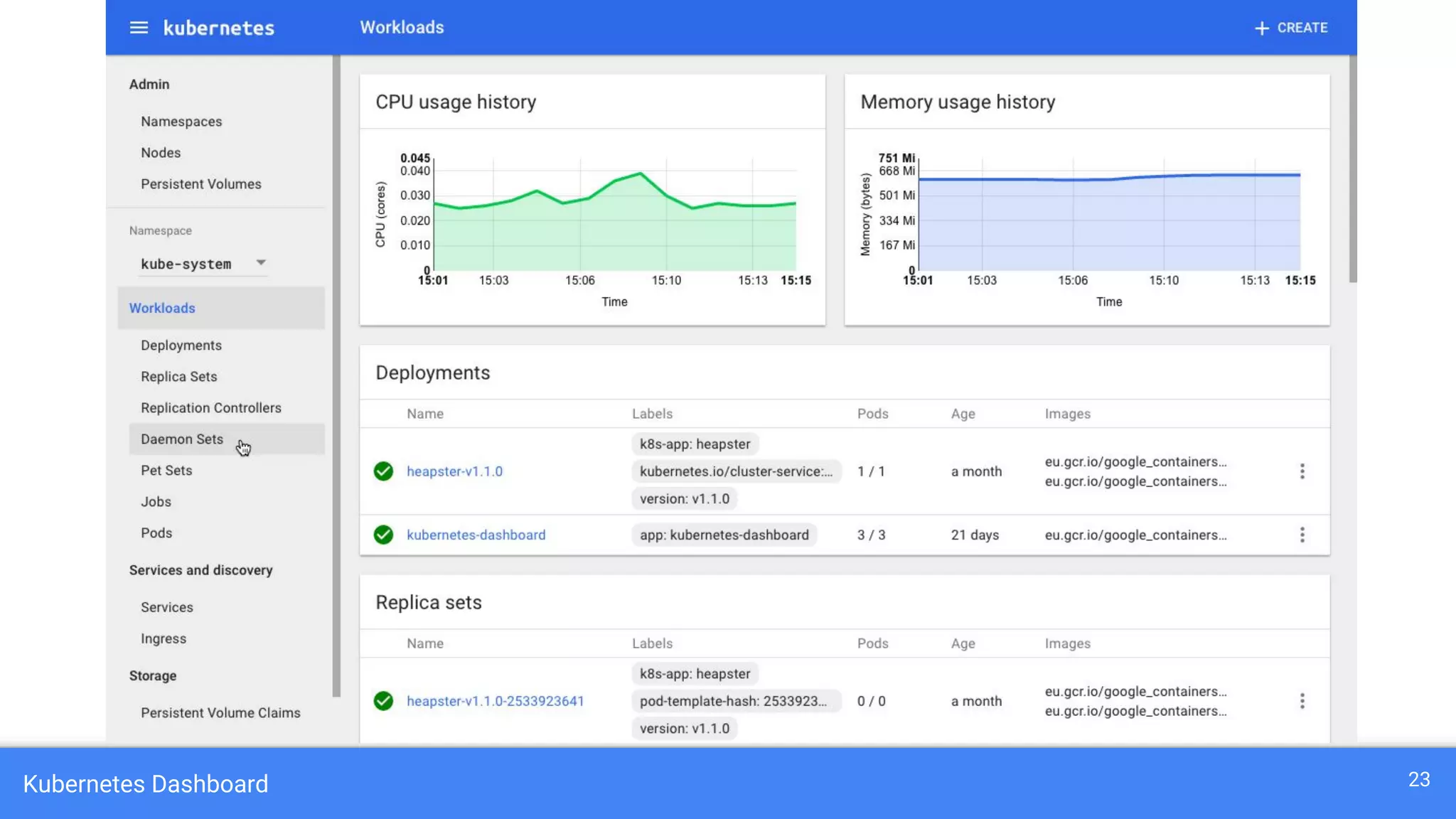
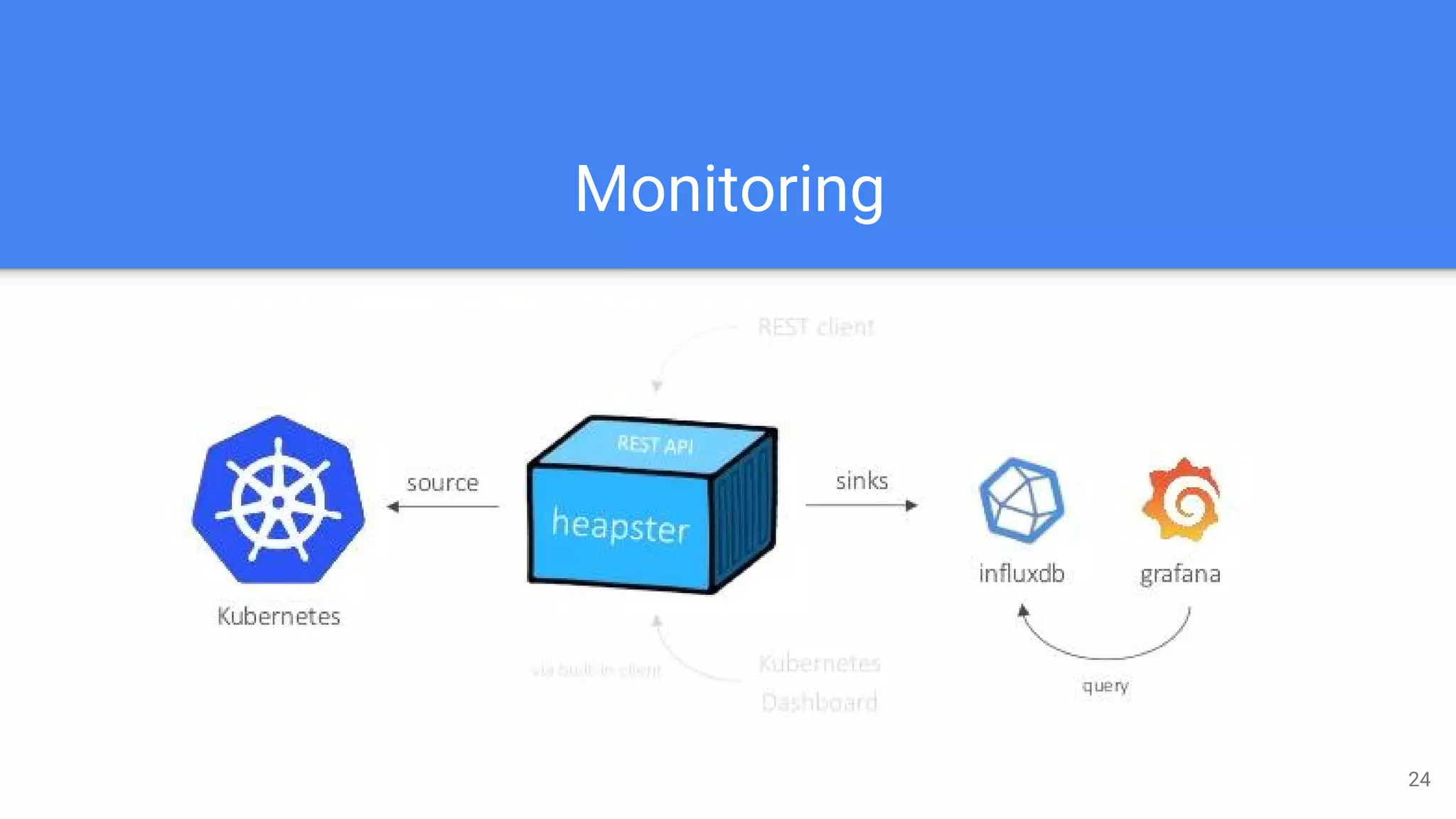
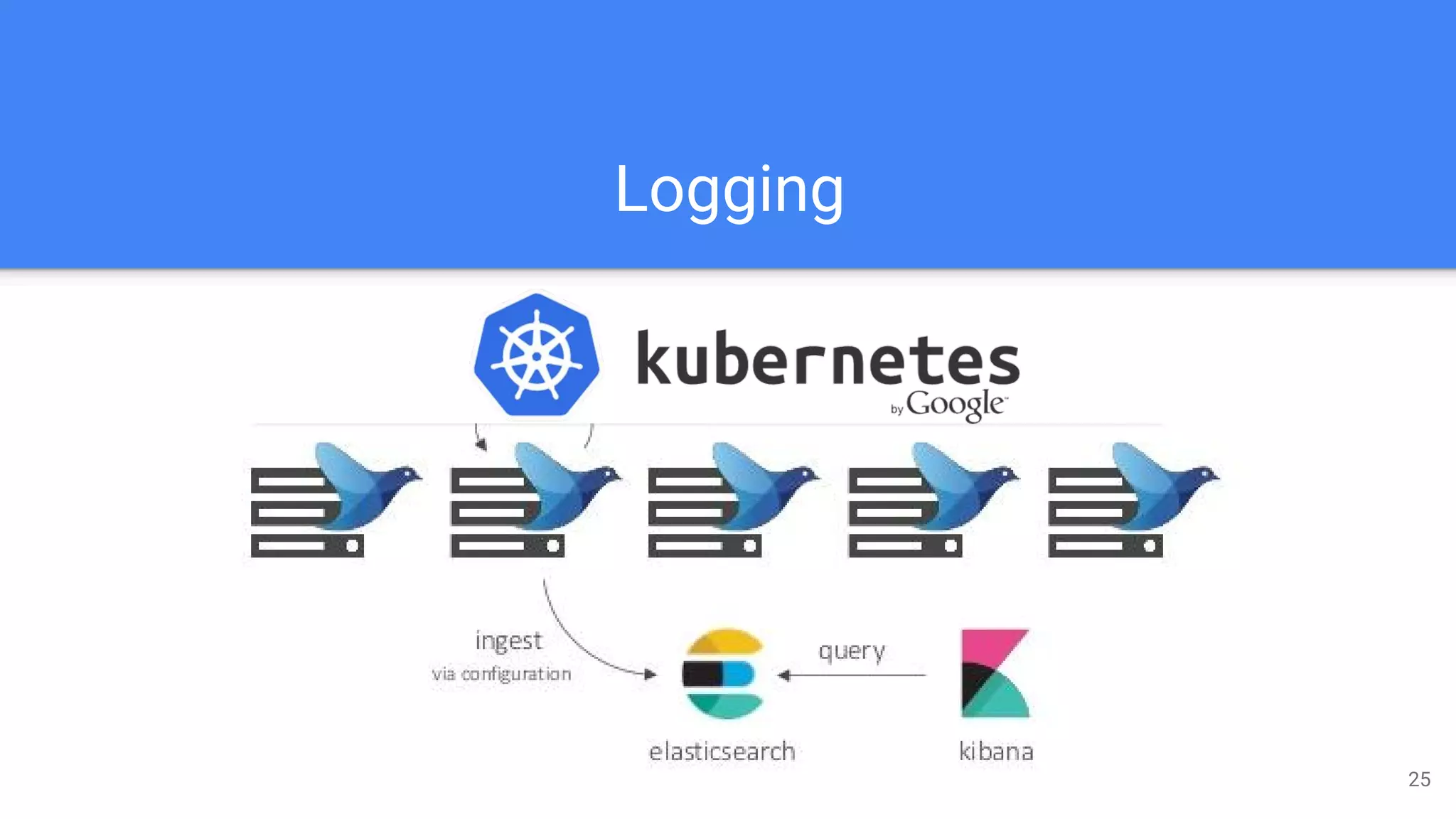
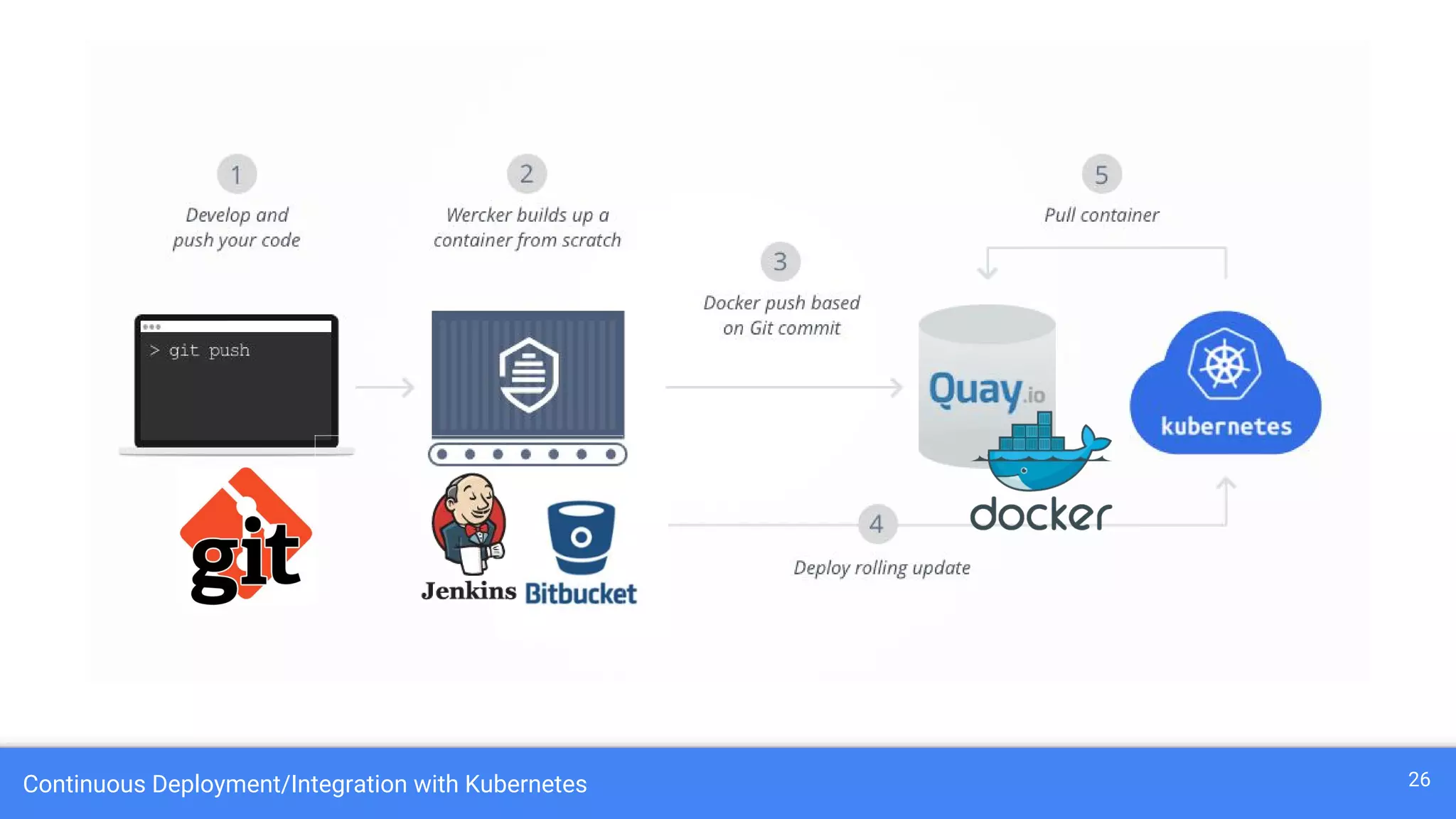
Kubernetes is a production-grade container orchestration system developed by Google, which abstracts hardware management to efficiently manage applications in a clustered environment. It provides features such as workload scheduling, load balancing, and scaling through concepts like pods, services, and replica sets. Since its inception in 2014, Kubernetes has seen continuous development and growing popularity, becoming a critical tool for managing containerized applications.