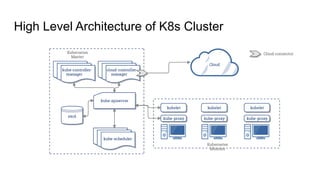
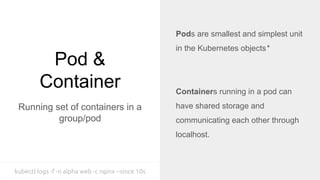
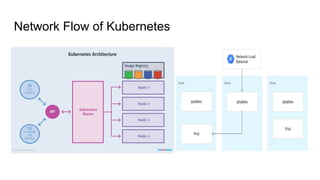
This document provides an overview of running Kubernetes and its key components. It describes where Kubernetes clusters can be run, such as on Amazon EKS, Google GKE, Azure AKS, or self-hosted. It also discusses tools for managing Kubernetes clusters like kops, and autoscaling options like Cluster Autoscaler and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler. Additionally, it covers Kubernetes concepts like pods, services, ingress, jobs, cronjobs, and using Helm to manage Kubernetes applications.