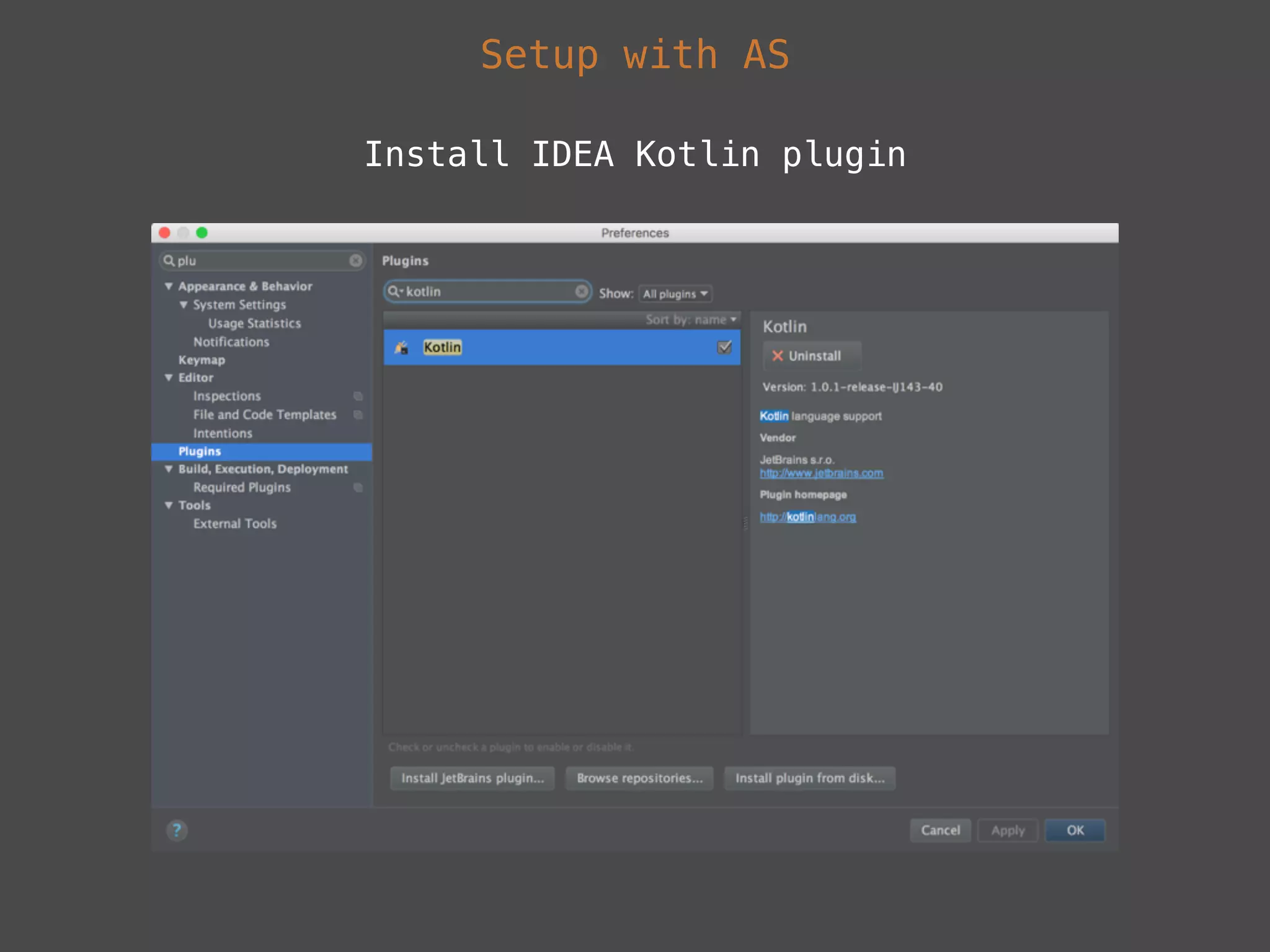
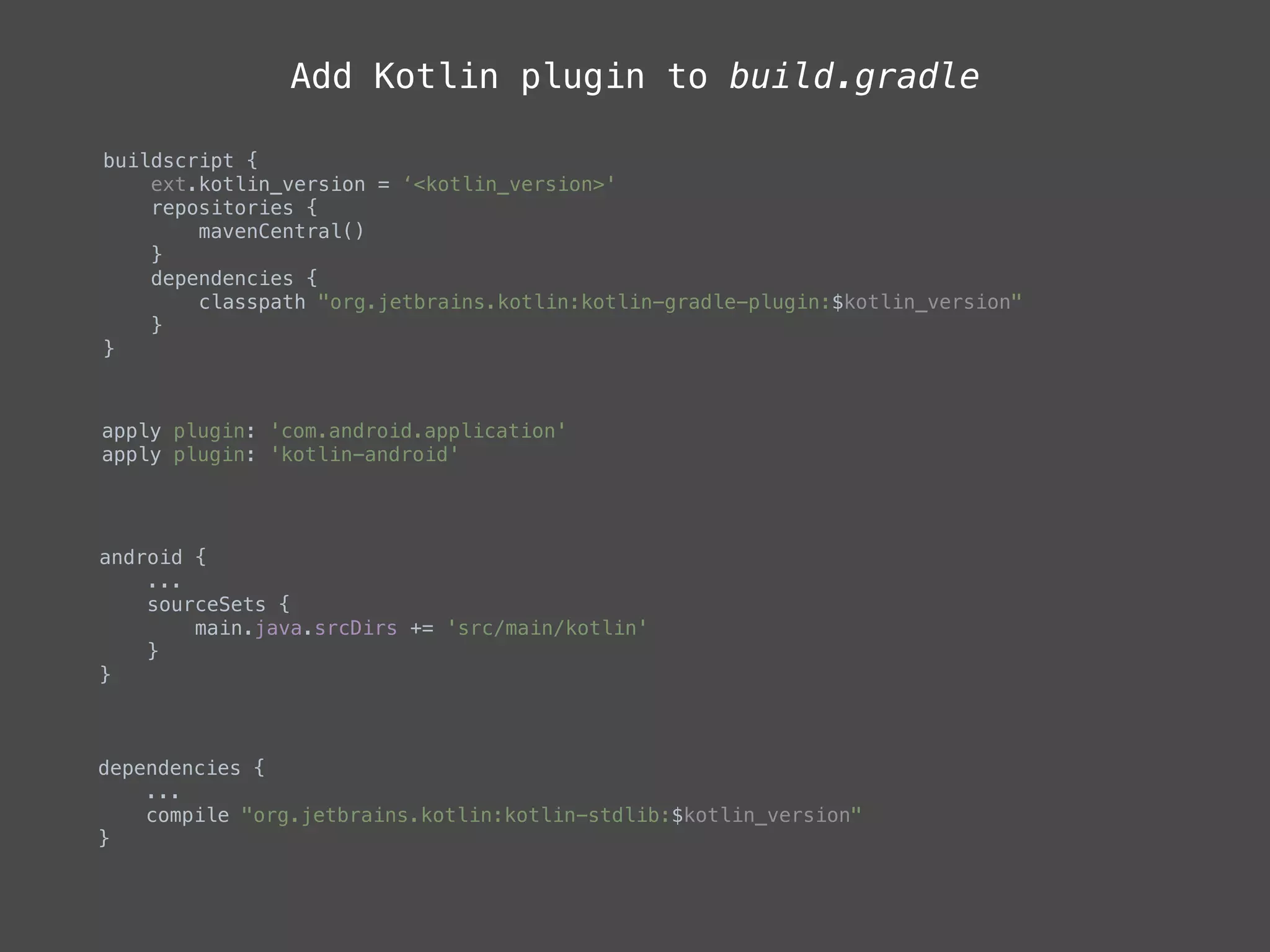
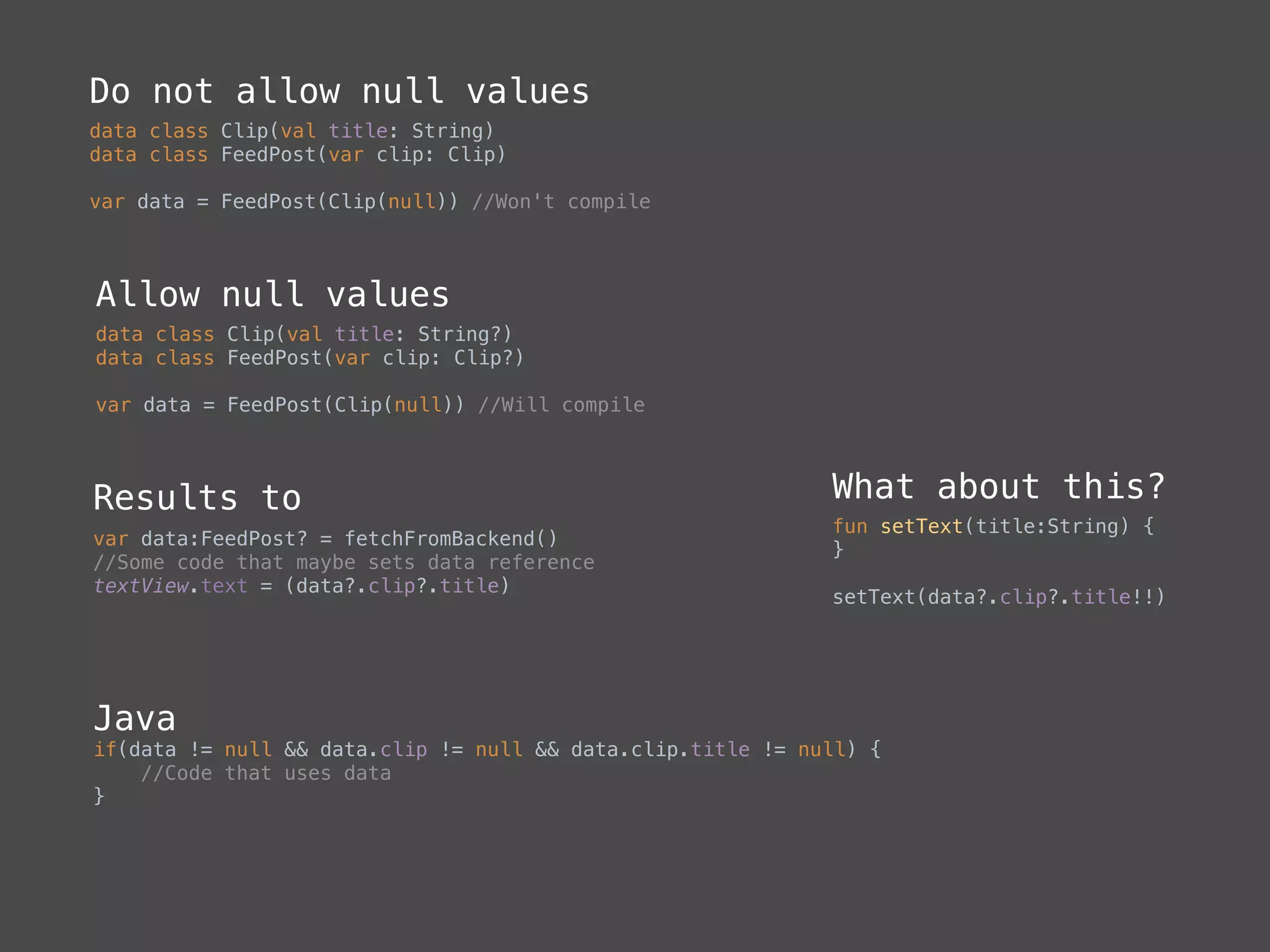
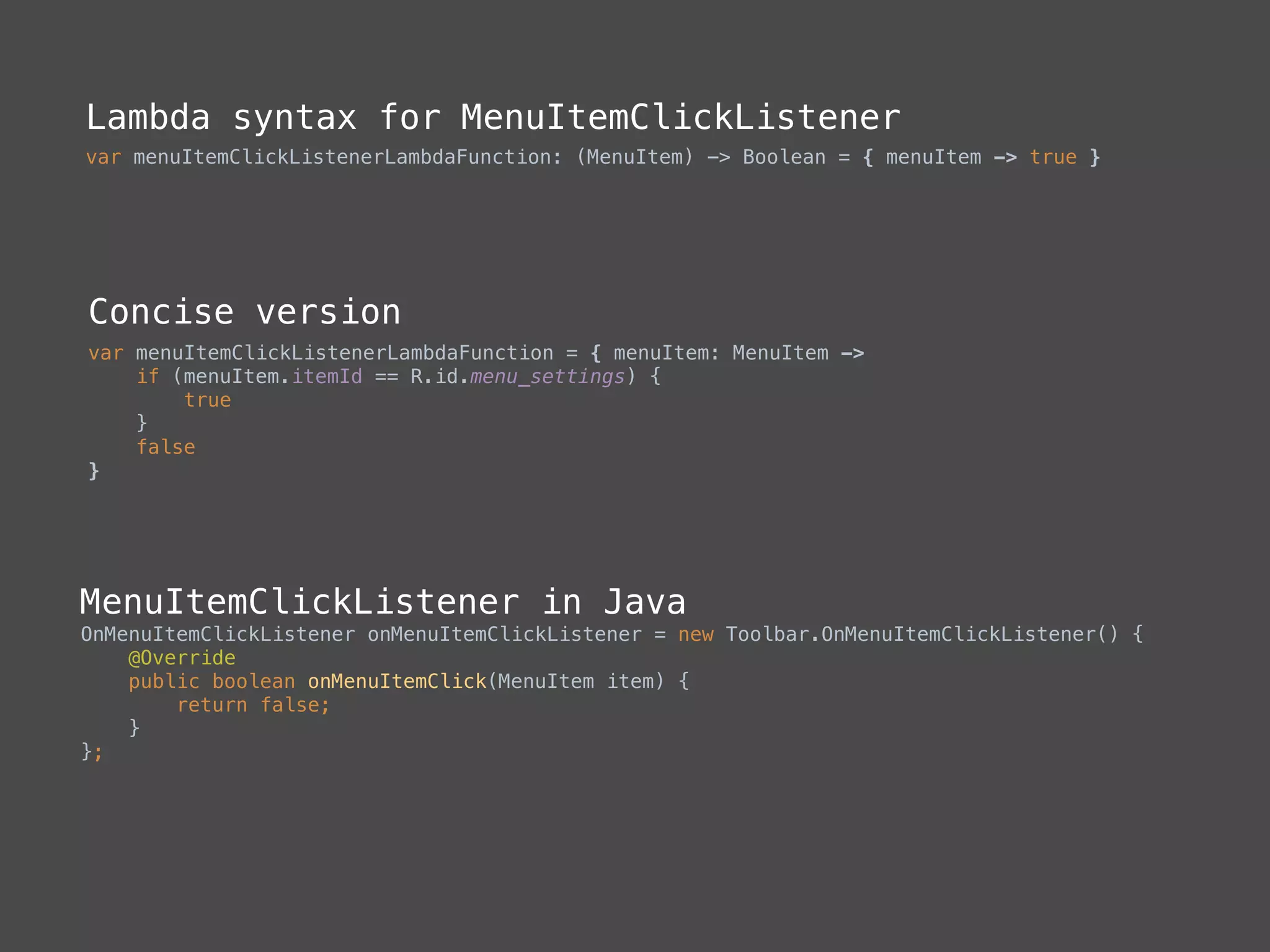
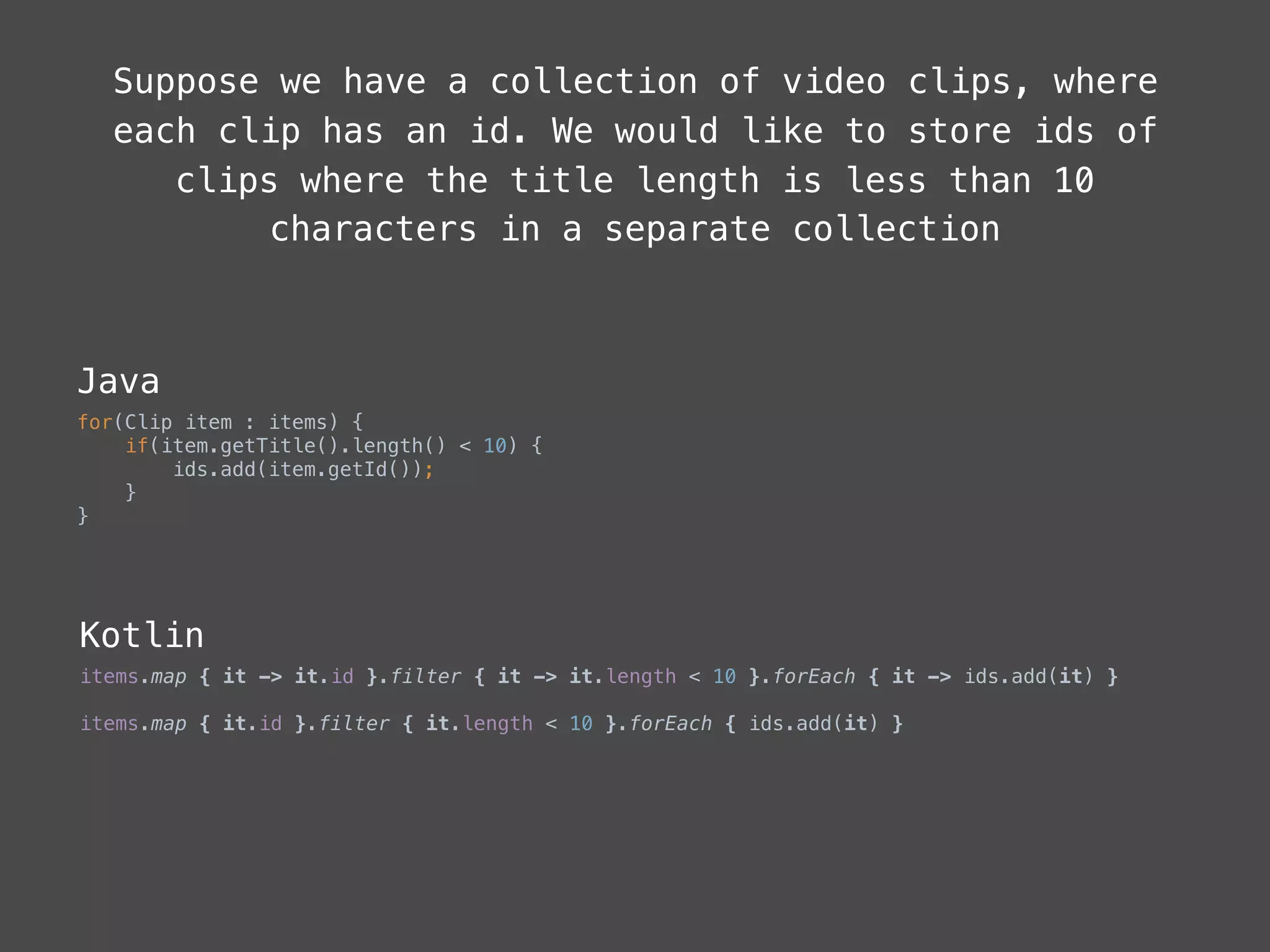
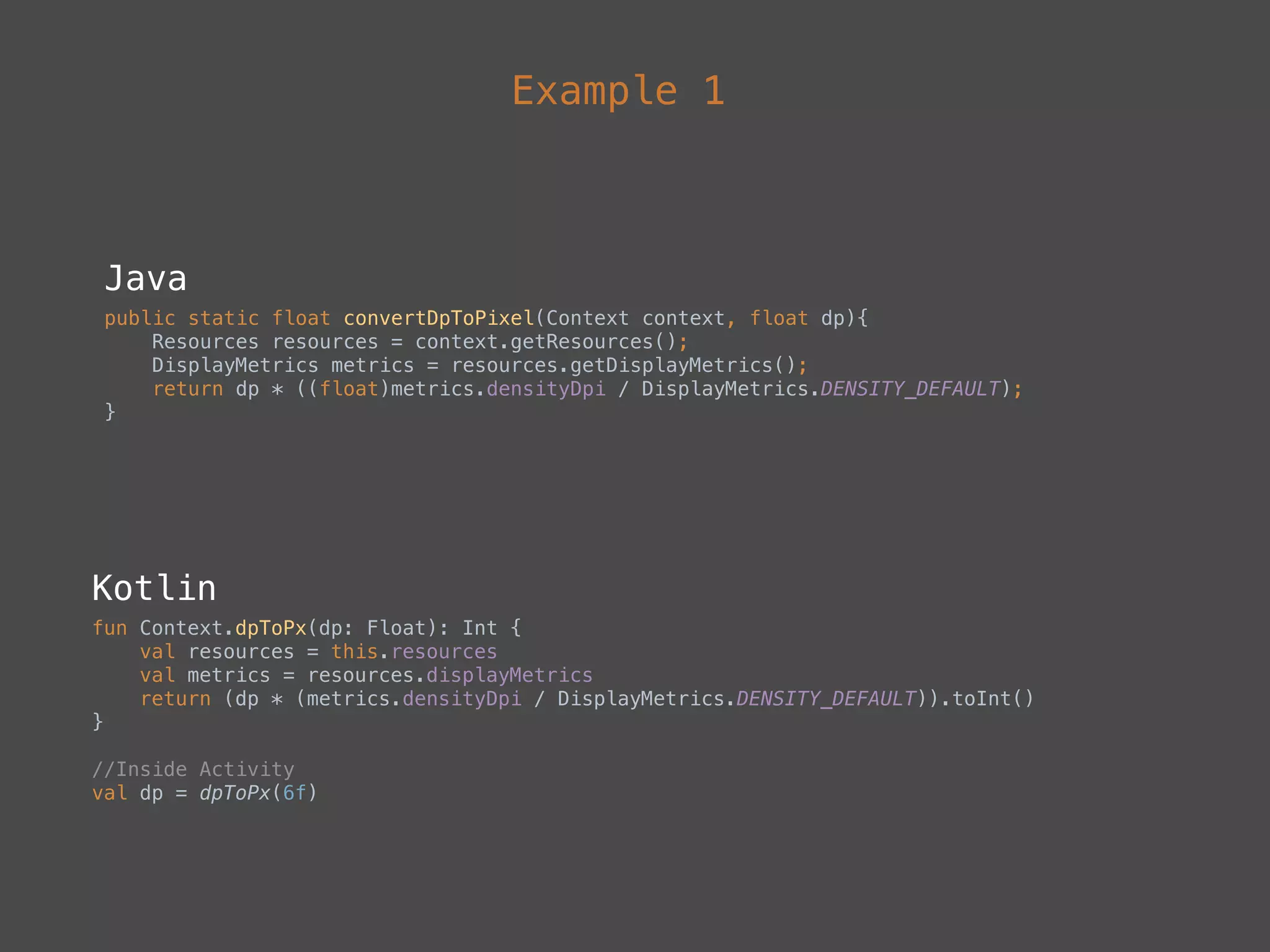
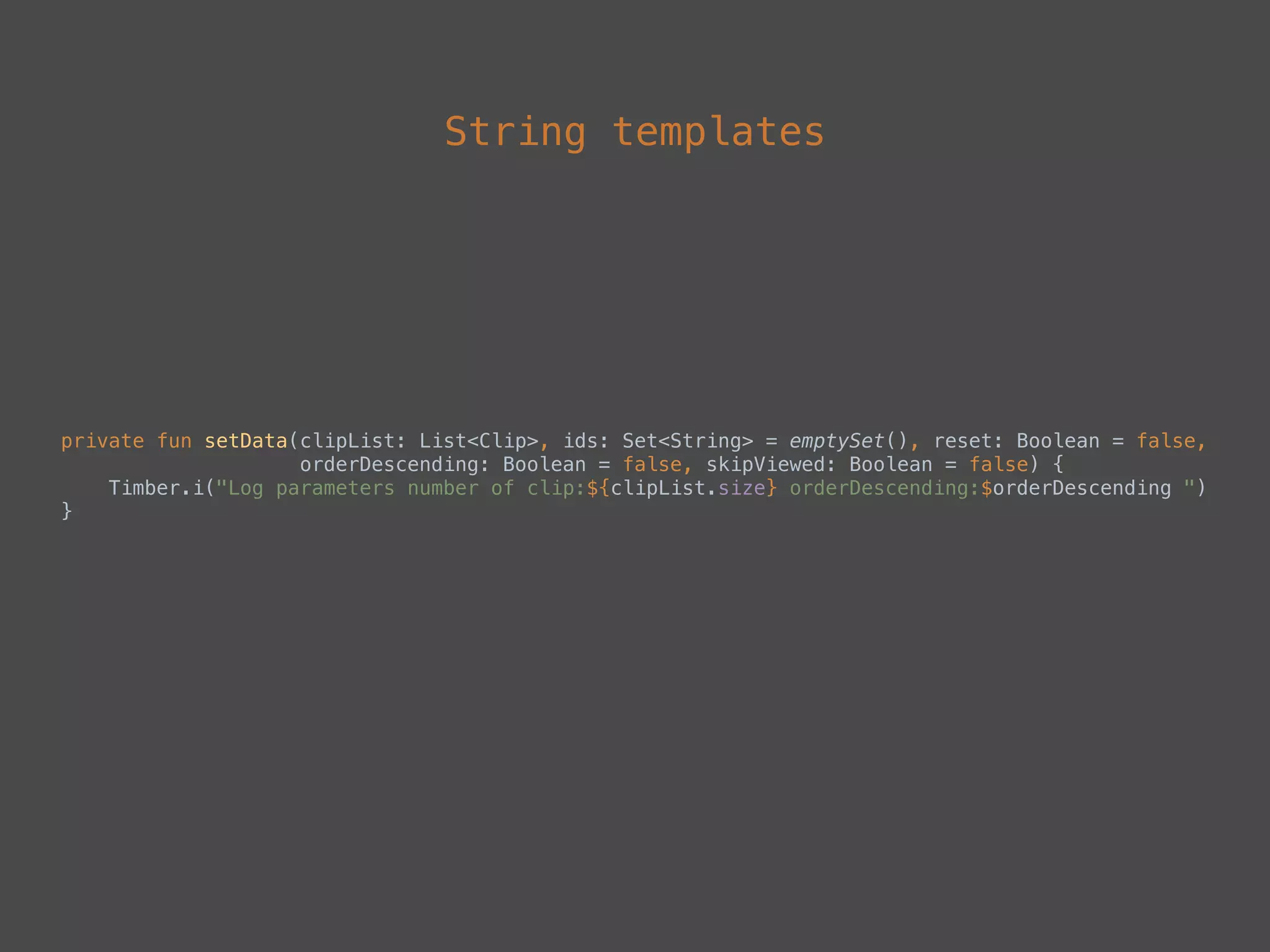
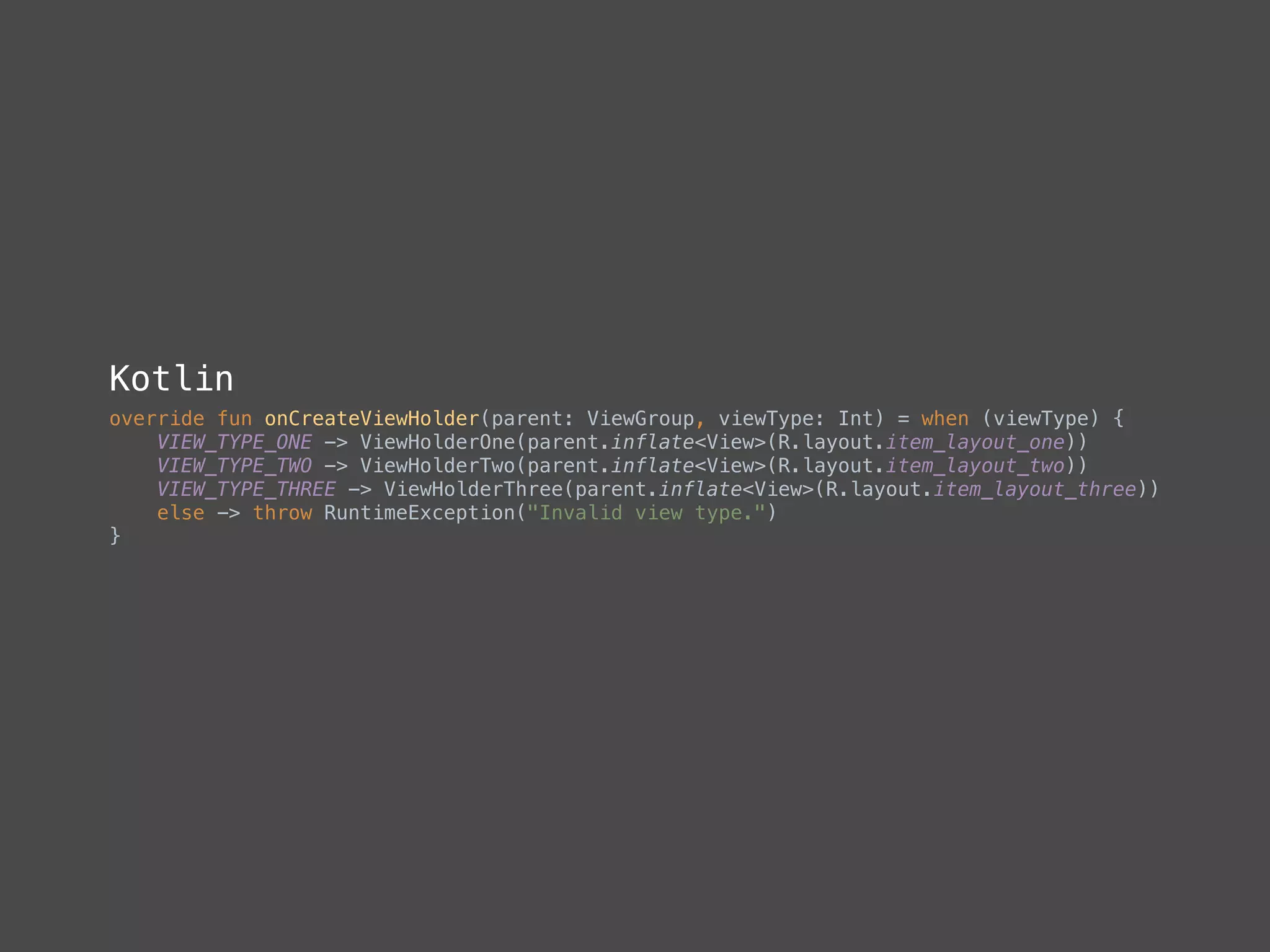
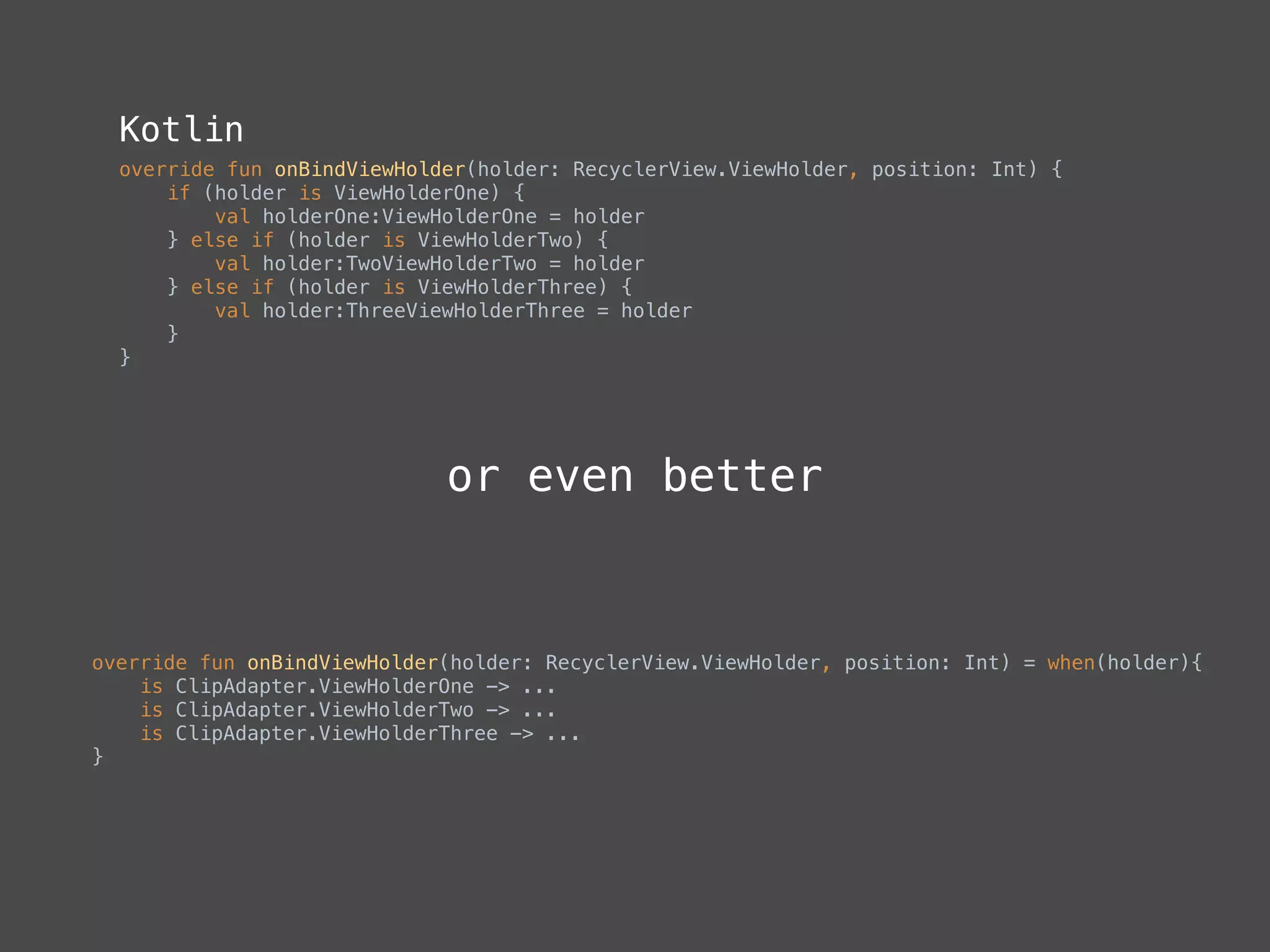
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Kotlin, a statically-typed programming language designed and developed by JetBrains, including its main features such as null safety, extensions, and data classes. It offers detailed guidance on setting up Kotlin in Android, utilizing its unique functionalities like higher-order functions, smart casts, and extension functions. Additionally, it highlights Kotlin's compatibility with Java and the advantages of using Kotlin in modern application development.