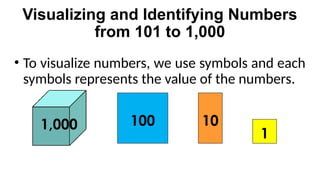
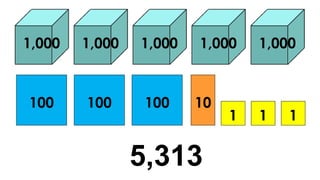
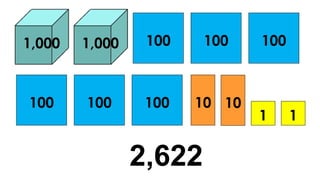
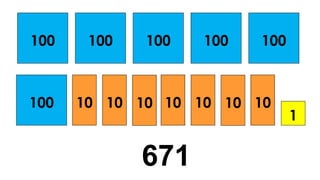
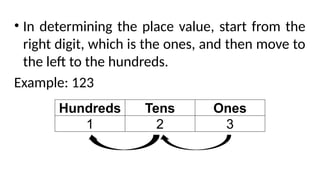
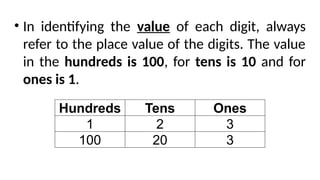
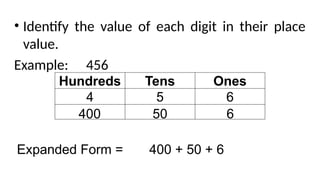
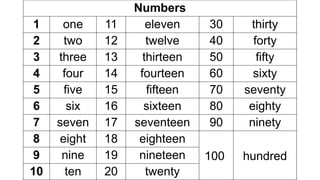
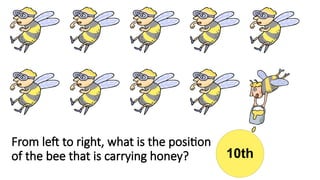
The document reviews concepts of visualizing and identifying numbers from 101 to 1,000, emphasizing place value, expanded form, and representation in both symbols and words. It explains methods for comparing, ordering, and determining the position of numbers, including steps to compare and arrange them correctly from greatest to least and least to greatest. Additionally, it introduces ordinal numbers and guidelines for identifying their positions based on a point of reference.