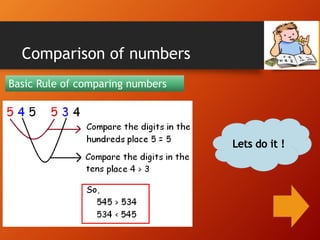
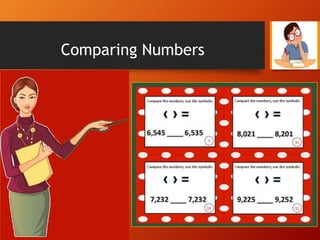
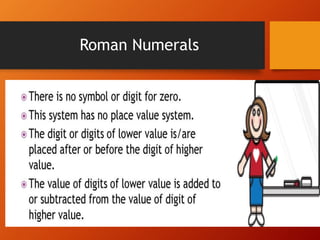
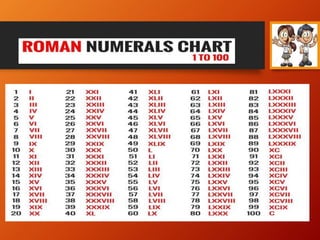
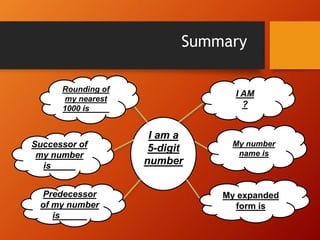
This document provides a lesson plan on place value and numbers for 4th grade mathematics. It introduces 5-digit and 6-digit numbers, place value, comparing numbers, and rounding numbers to the nearest 10, 100, and 1000. It also covers Roman numerals up to 100. The objectives are to understand place value with 4+ digit numbers and develop skills with expanded notation, comparing, forming, and rounding large numbers. Students will practice these concepts through examples and assignments rounding numbers and rewriting numbers with commas.