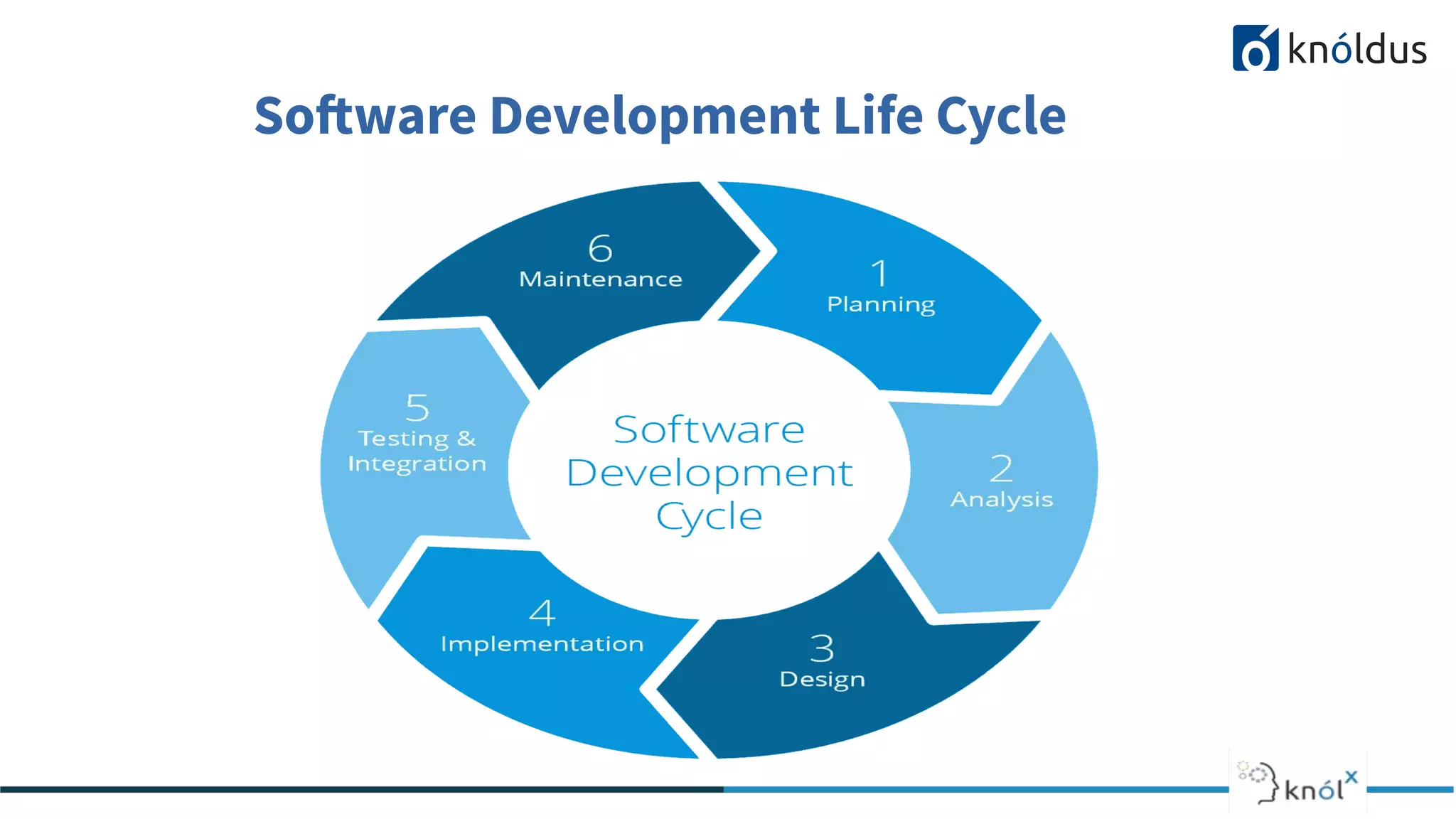
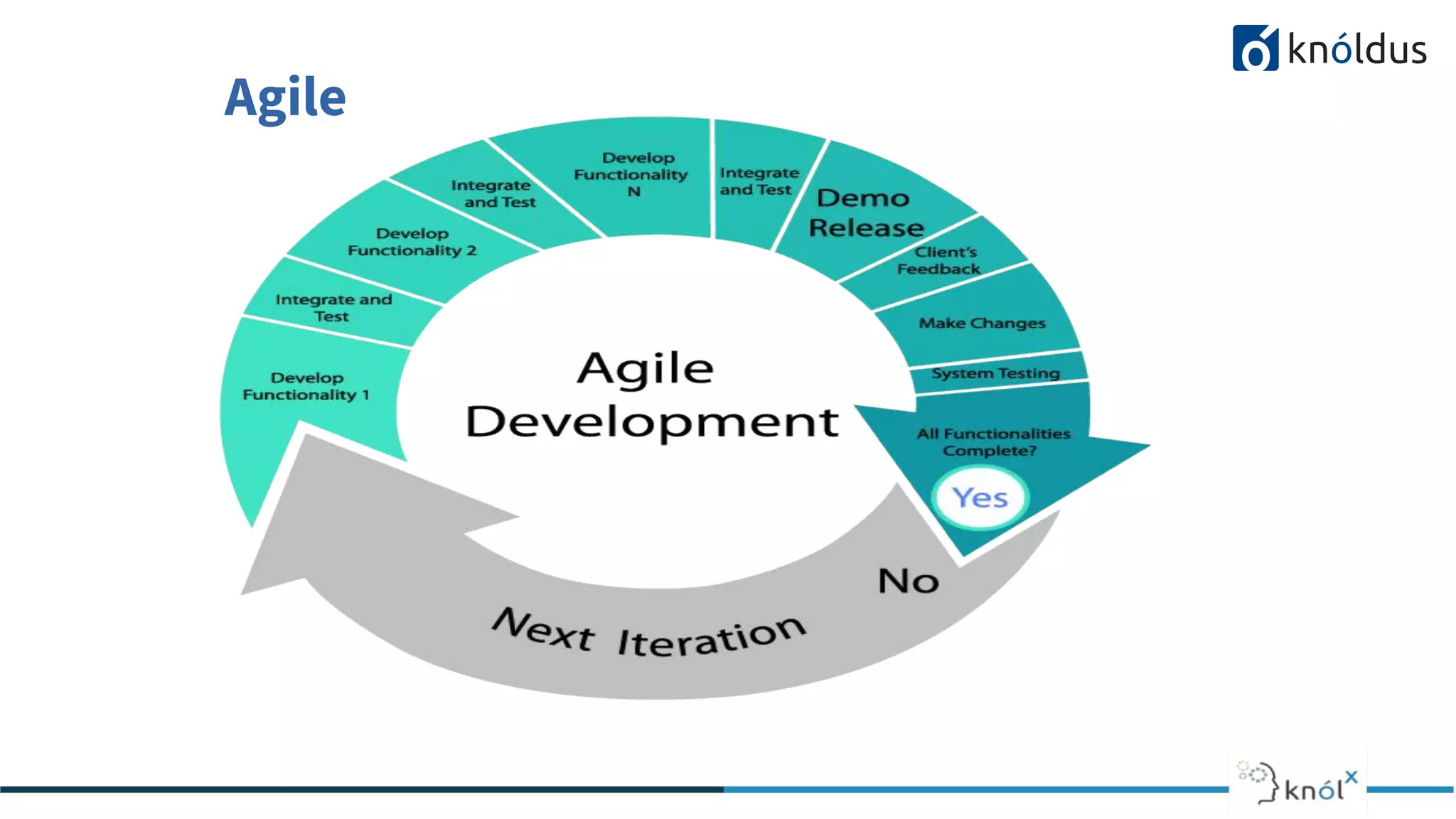
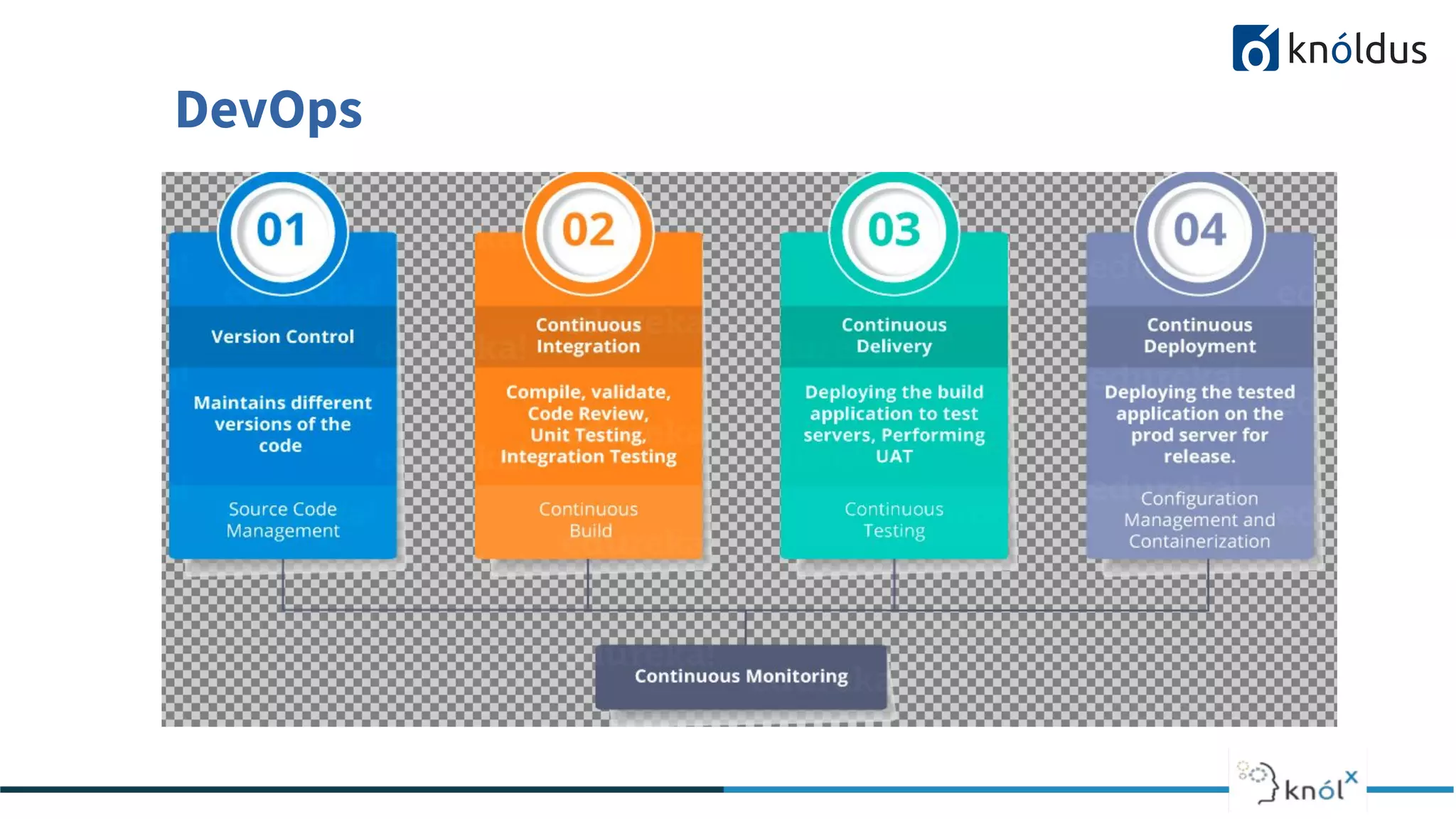
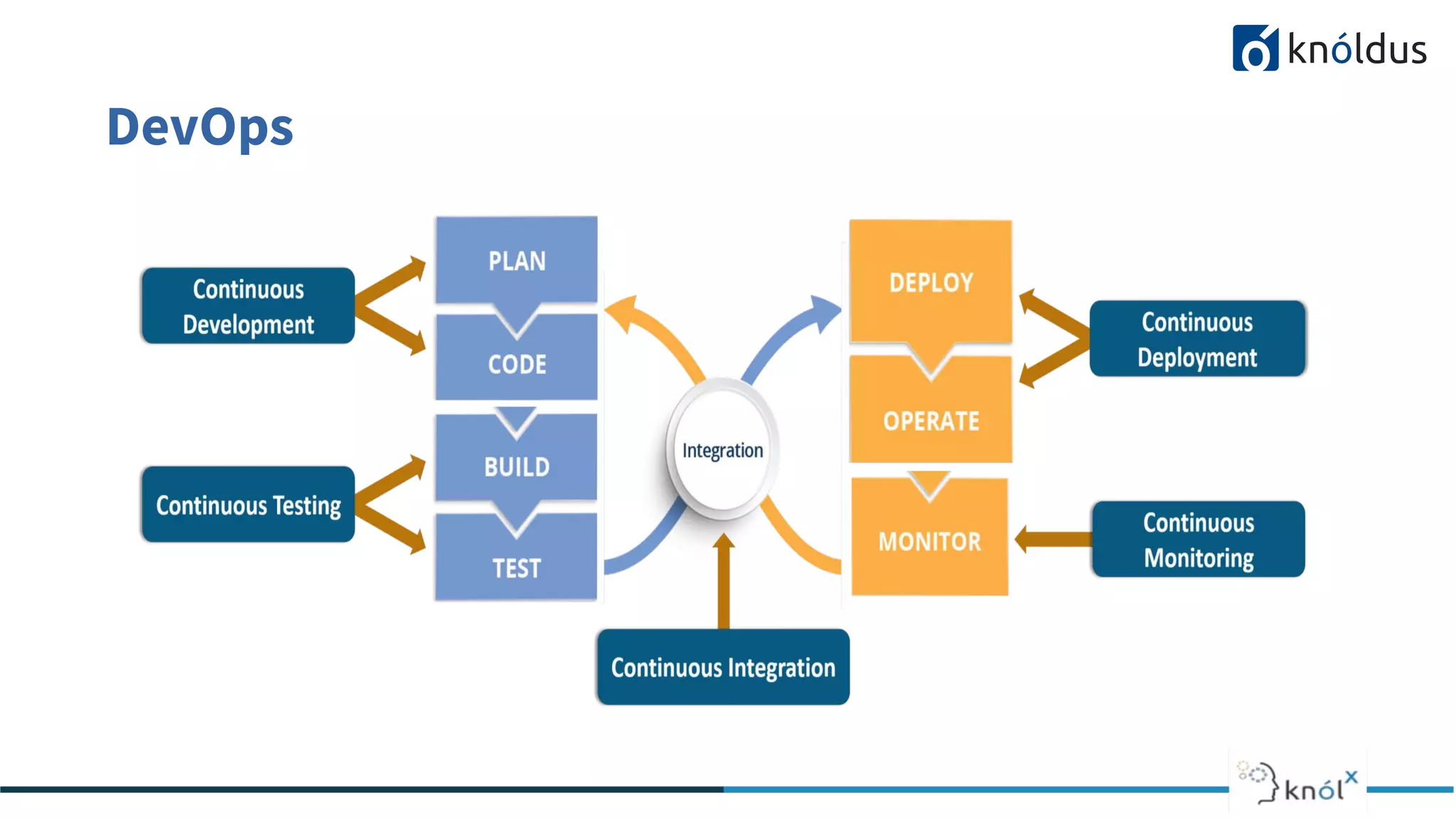
The document provides an overview of the software development life cycle (SDLC) including its phases and common methodologies. It discusses the SDLC phases of planning/initiation, constant development, and gateway. Common methodologies covered are waterfall, iterative, agile, and DevOps. Waterfall follows sequential tasks while iterative allows learning from iterations. Agile advocates adaptive planning and evolution. DevOps enables continuous development, testing, integration, deployment and monitoring throughout the development cycle. The presentation concludes with a Q&A section.



















![DevOps Tools
Continuous Development
Tools : Git, SVN, CVS, Mercurial
CI [ Continuous Integration ]
Tools : Jenkins, TeamCity, Travis
Continuous Testing
Tools : Jenkins , Selenium , TestNG , JUnit
CD [Continuous Deployment]
Tools: Configuration Management Tools – Chef, Puppet, Ansible and
Containerization – Docker, Vagrant
Continuous Montiroing
Tools: Splunk, ELK Stack, Nagios, New Relic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/knoldussdlcpracticestandards-210614152120/75/Knoldus-SDLC-Standard-Practices-26-2048.jpg)
