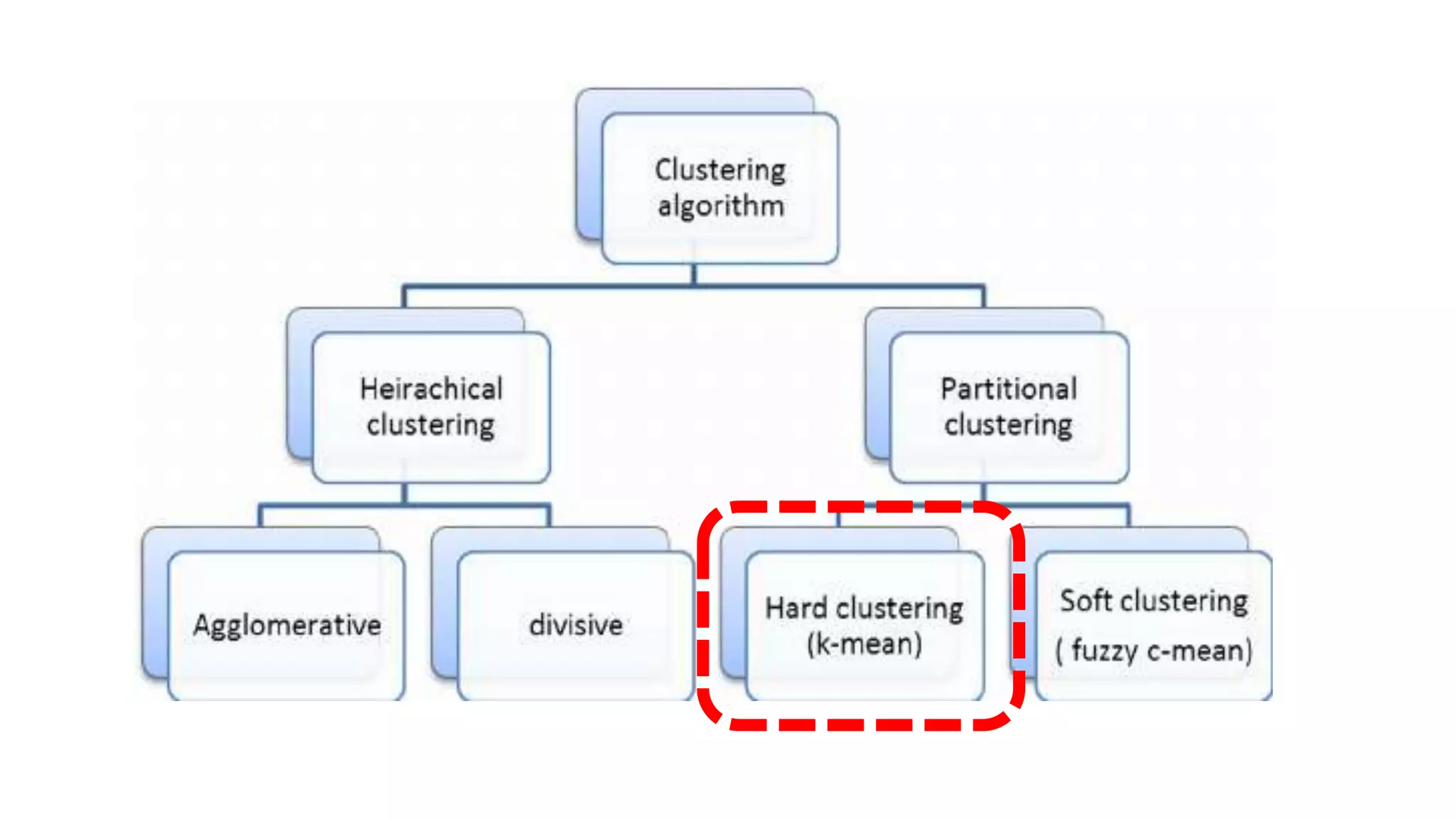
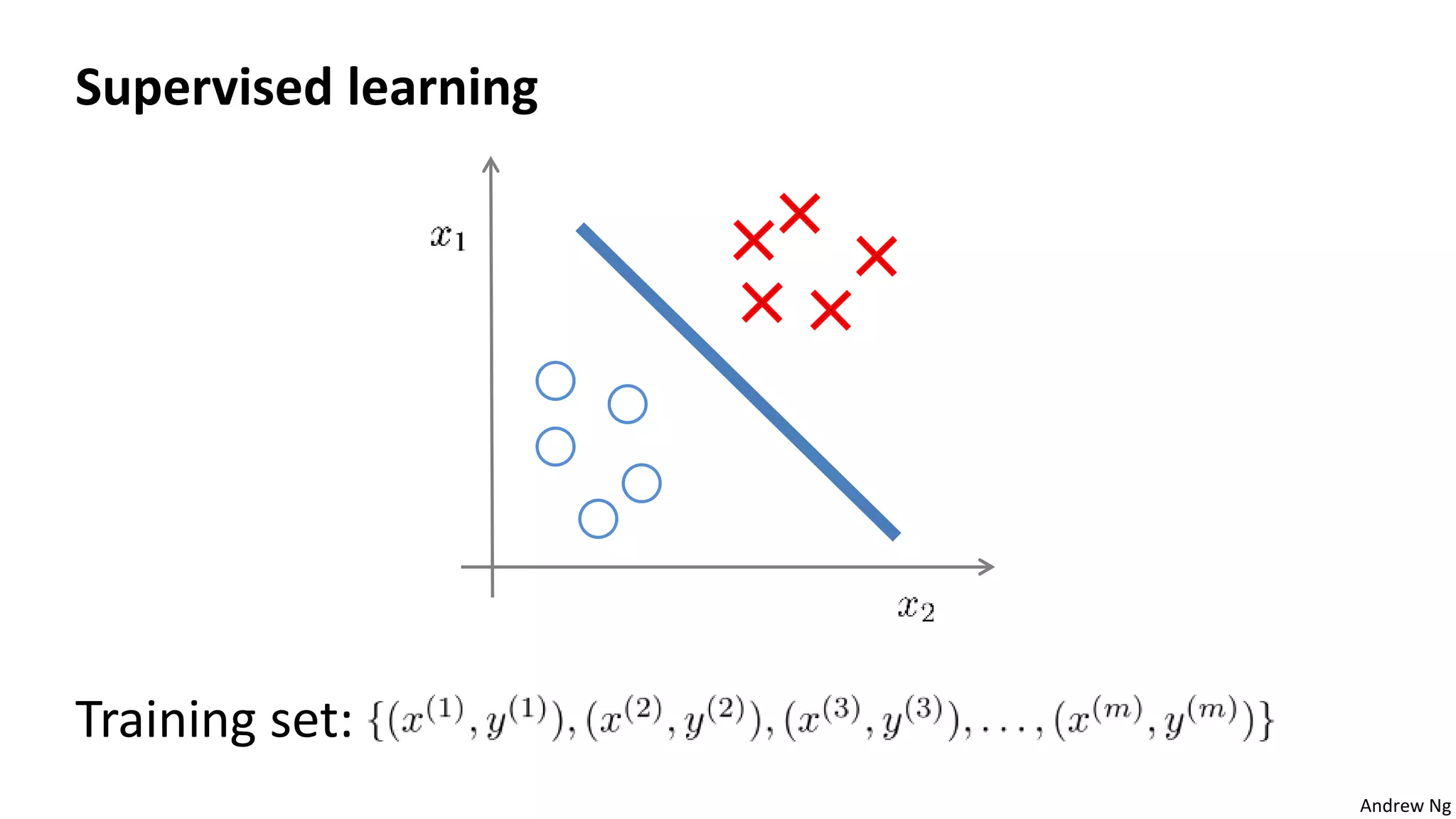
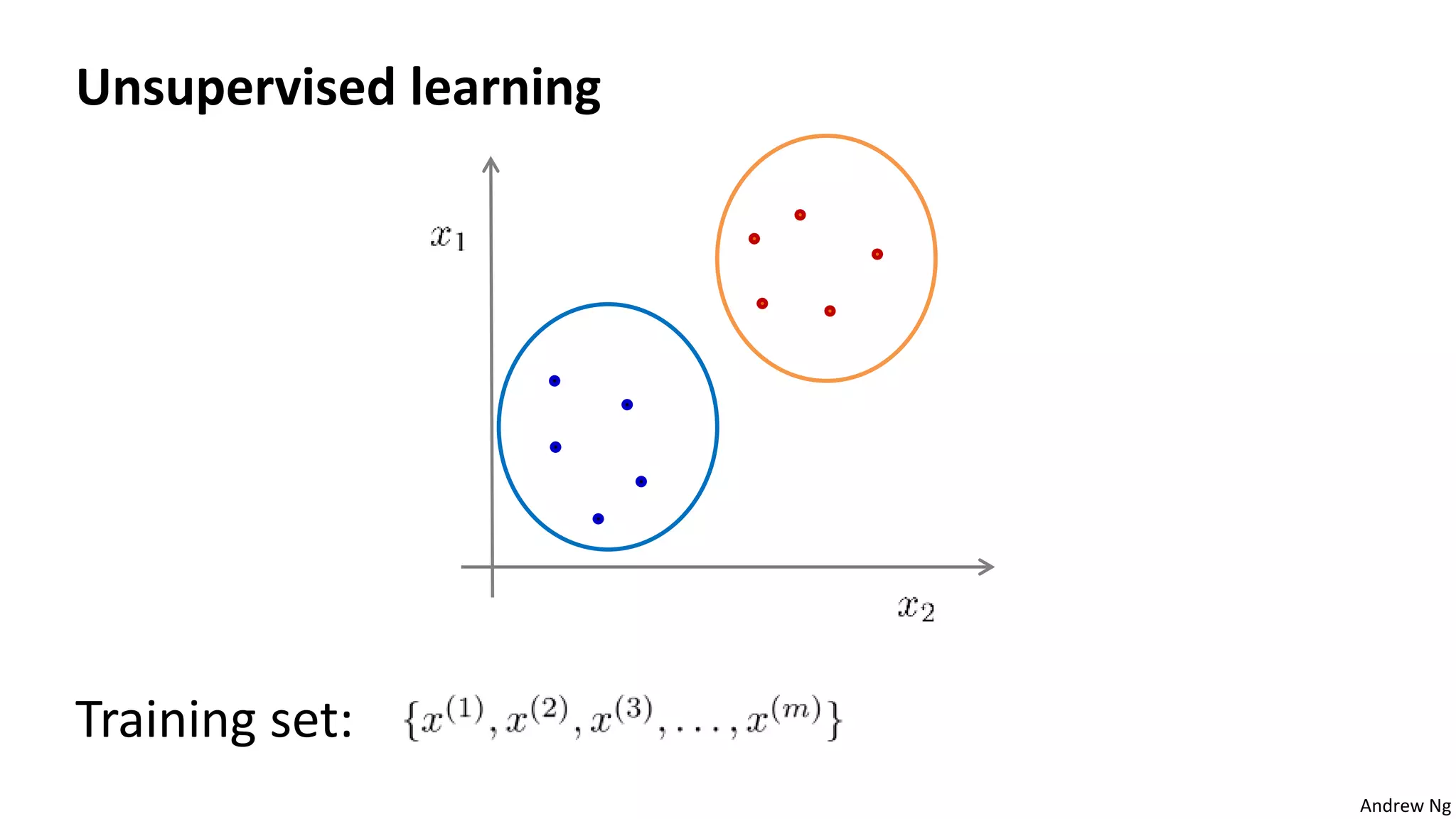
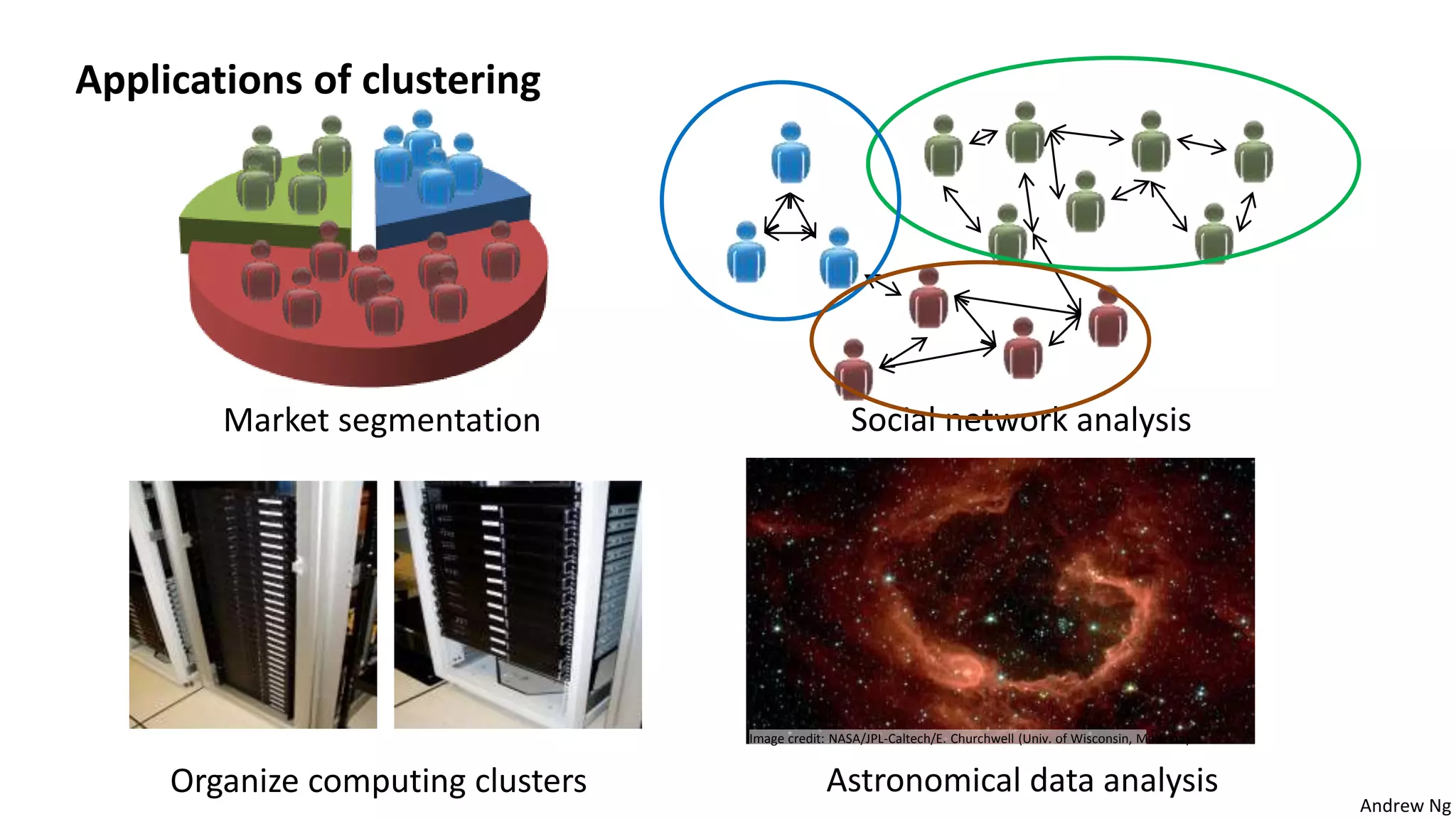
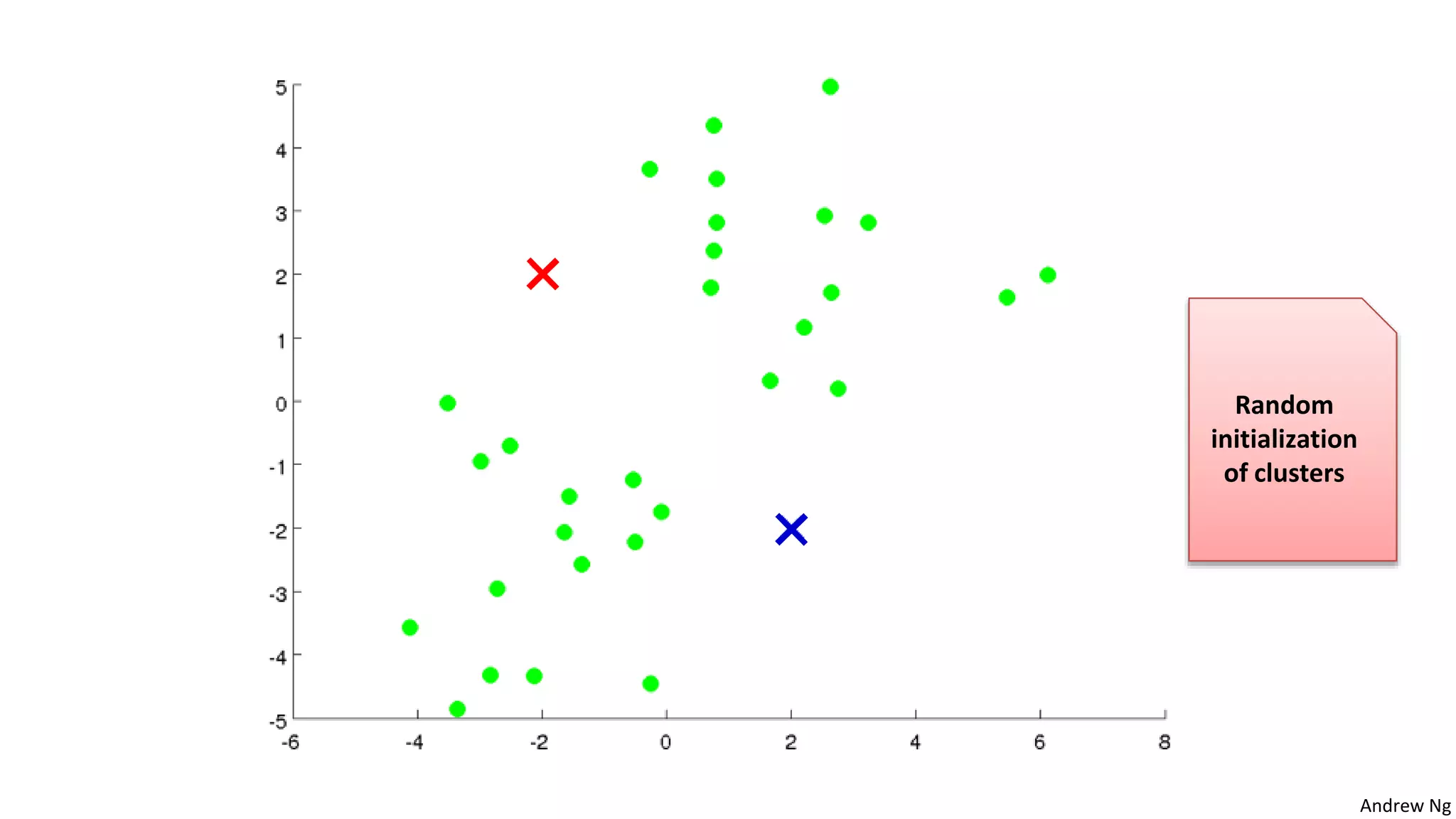
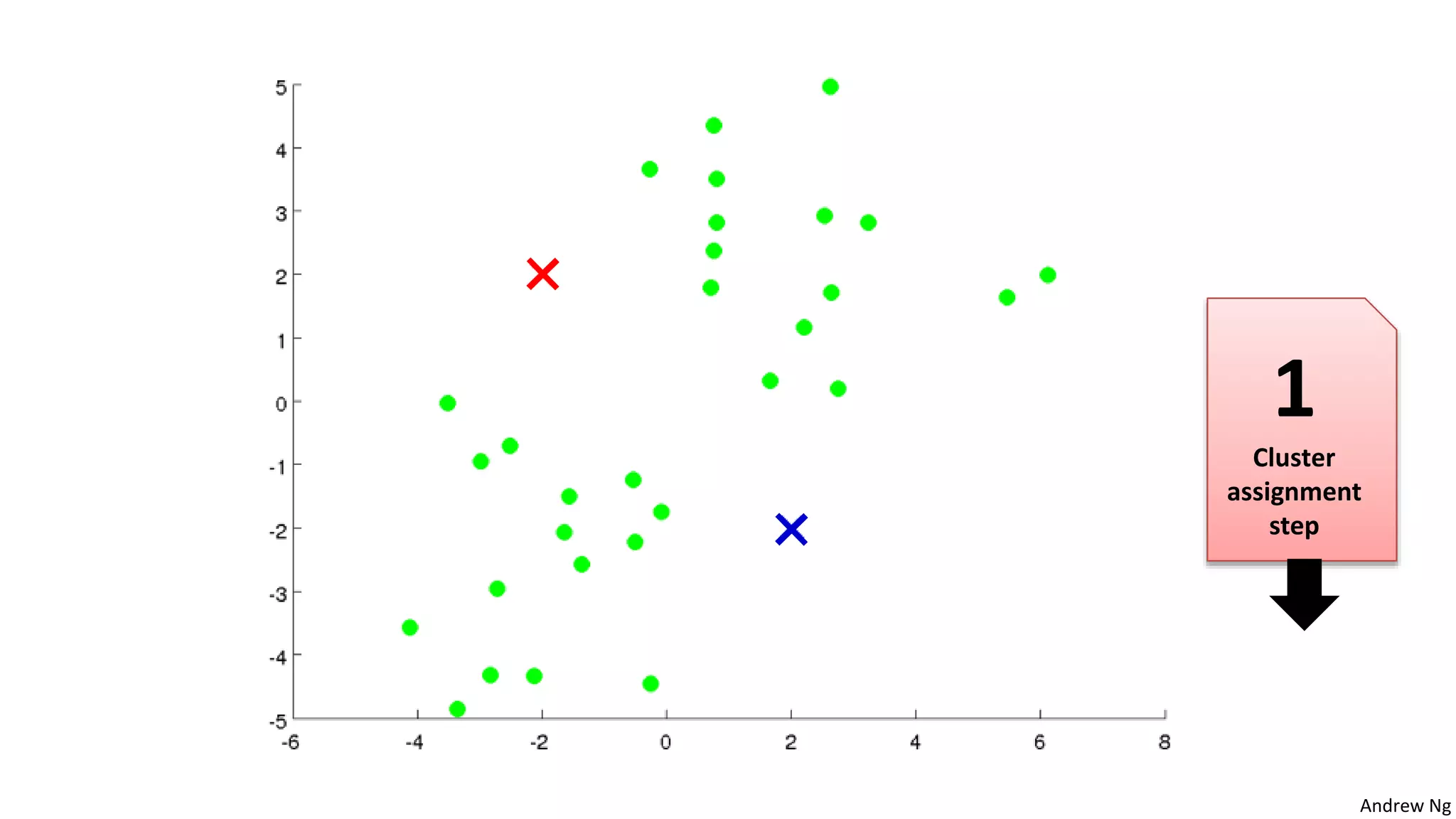
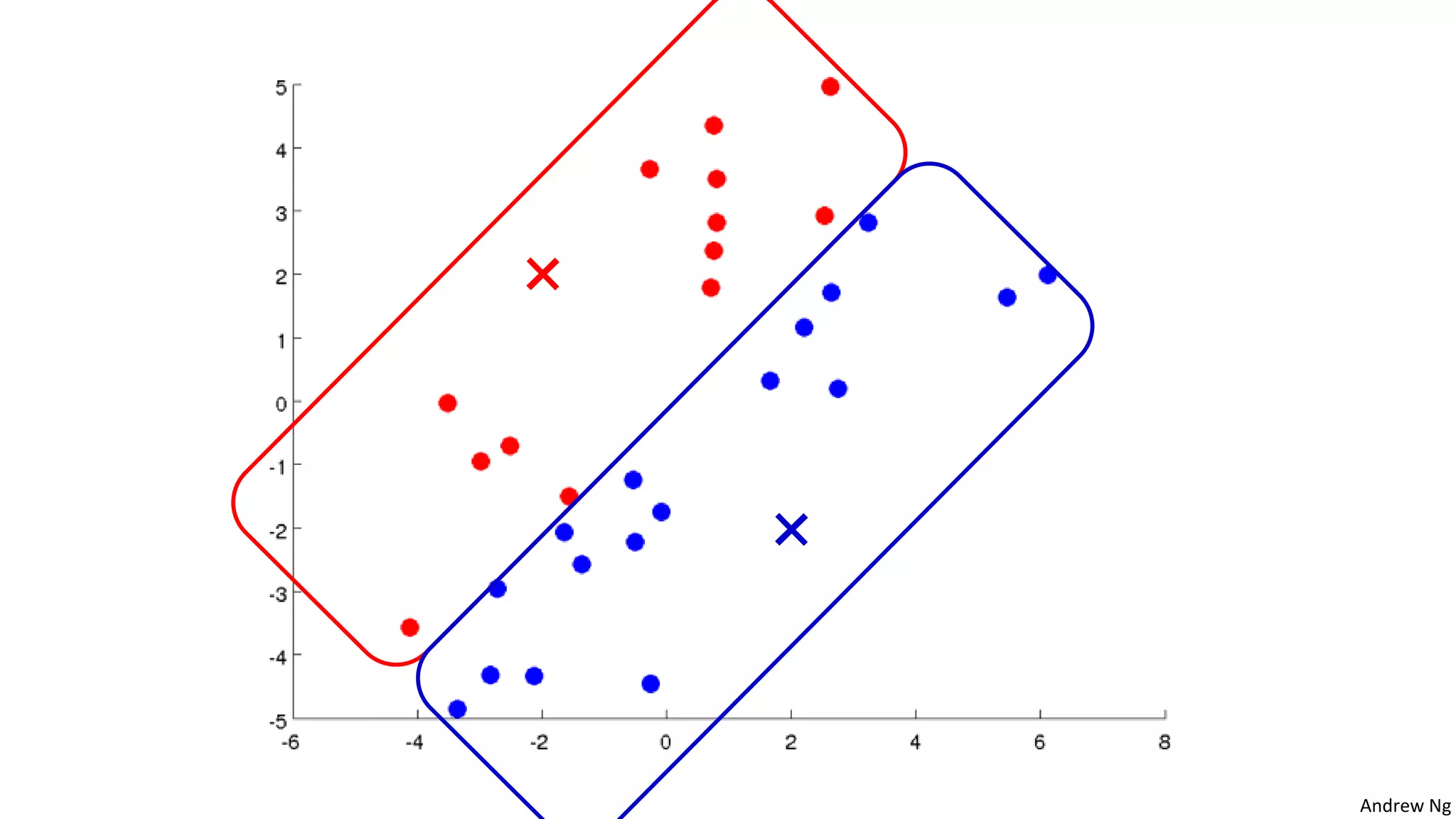
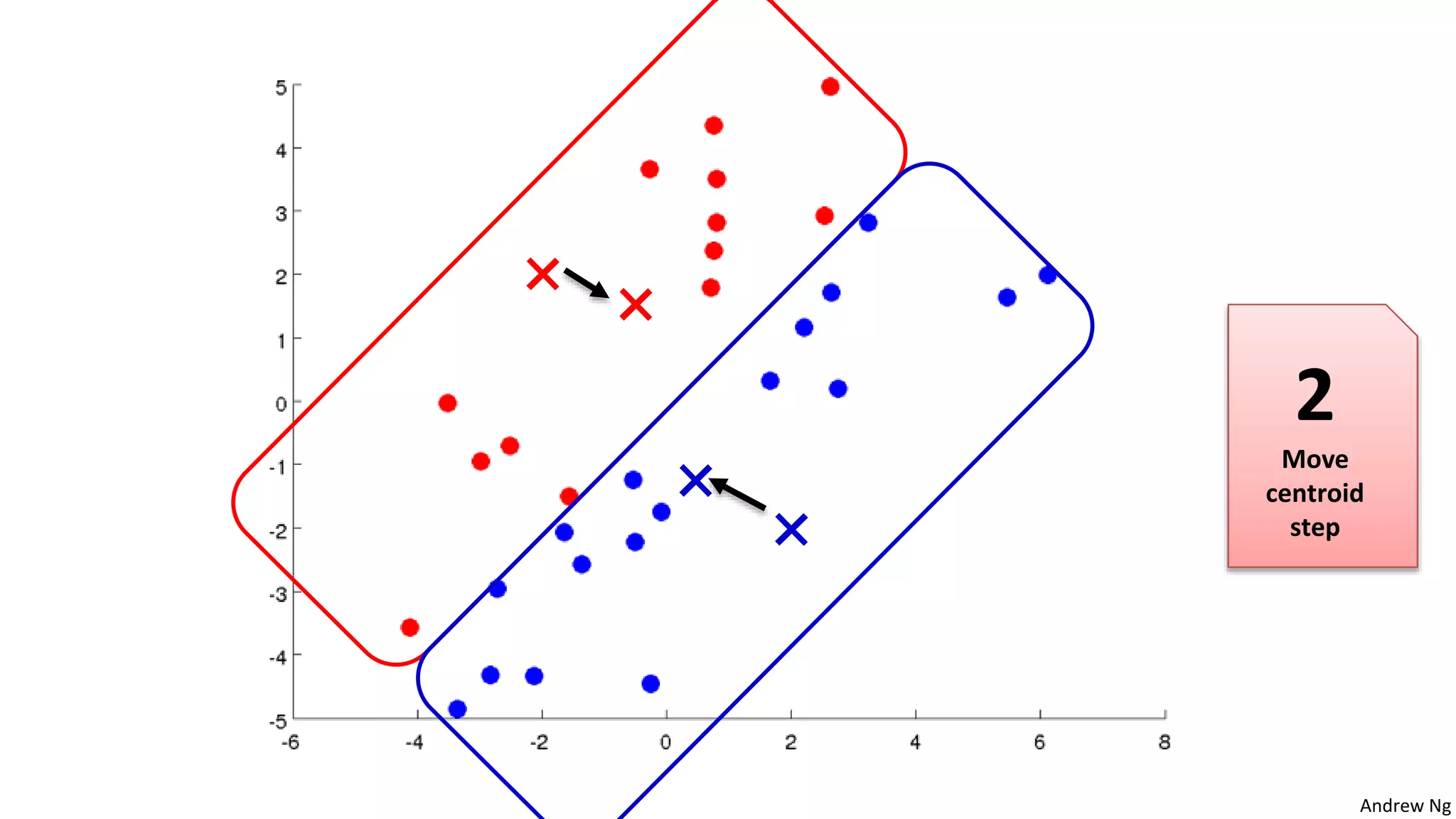
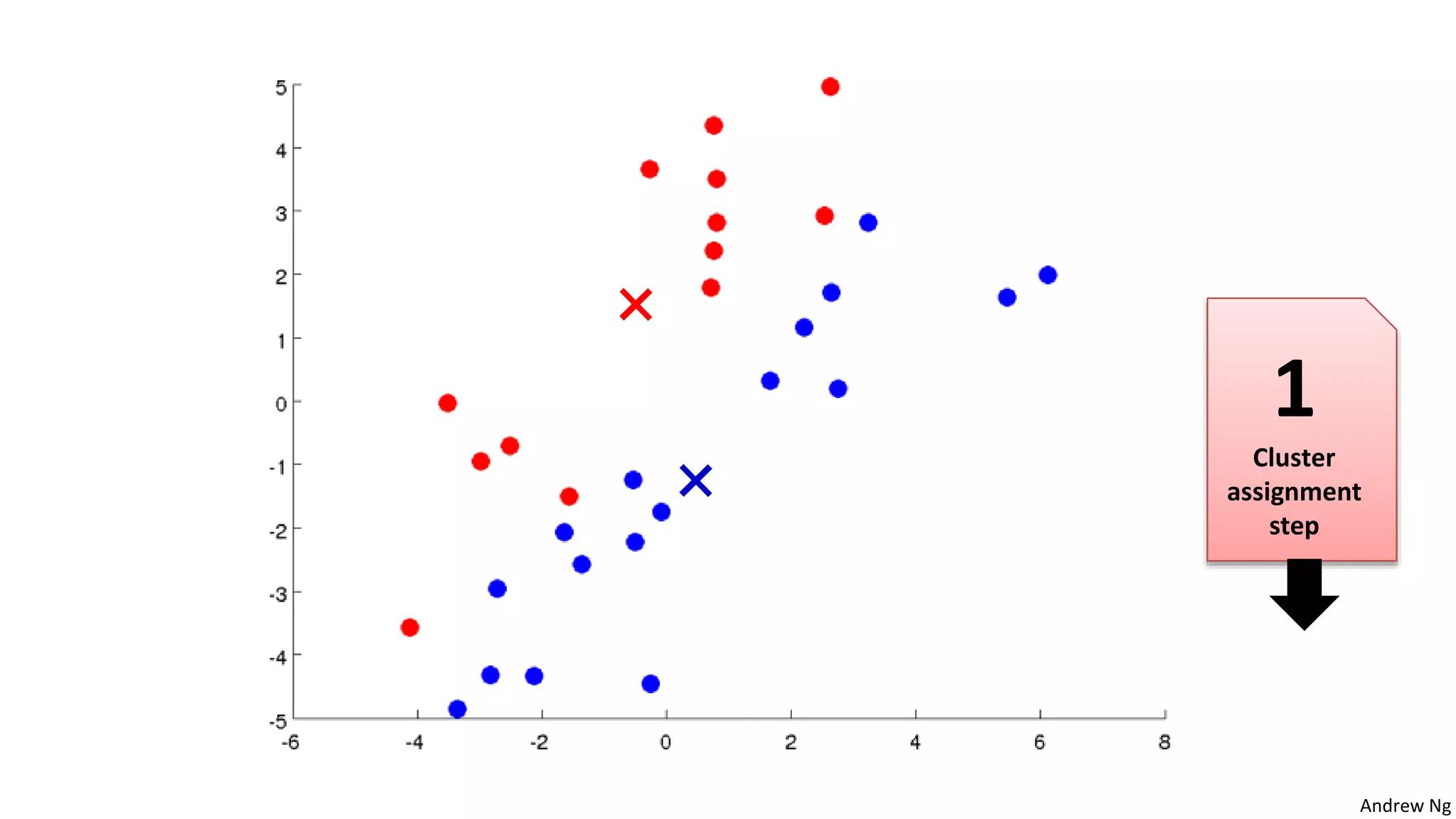
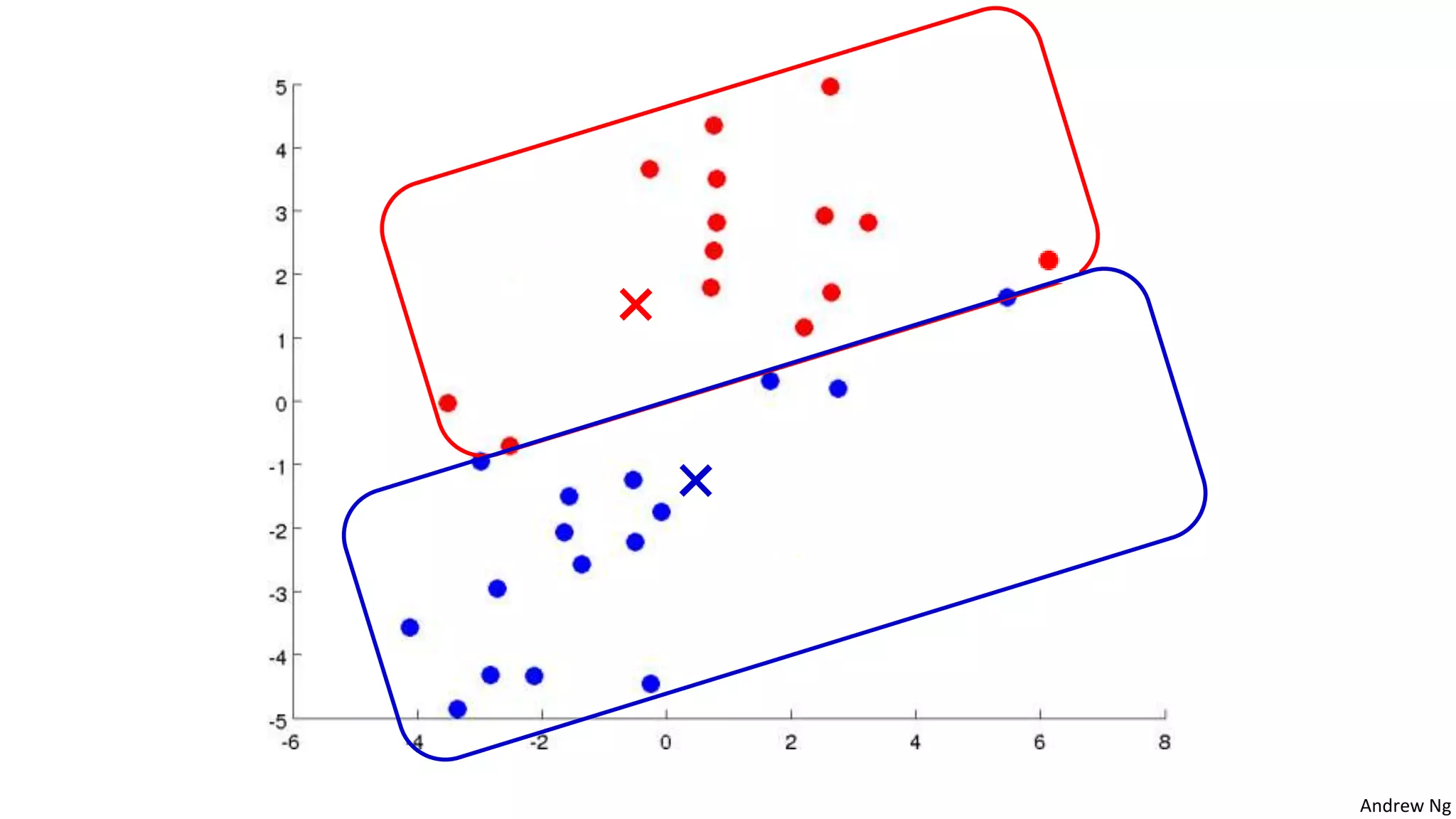
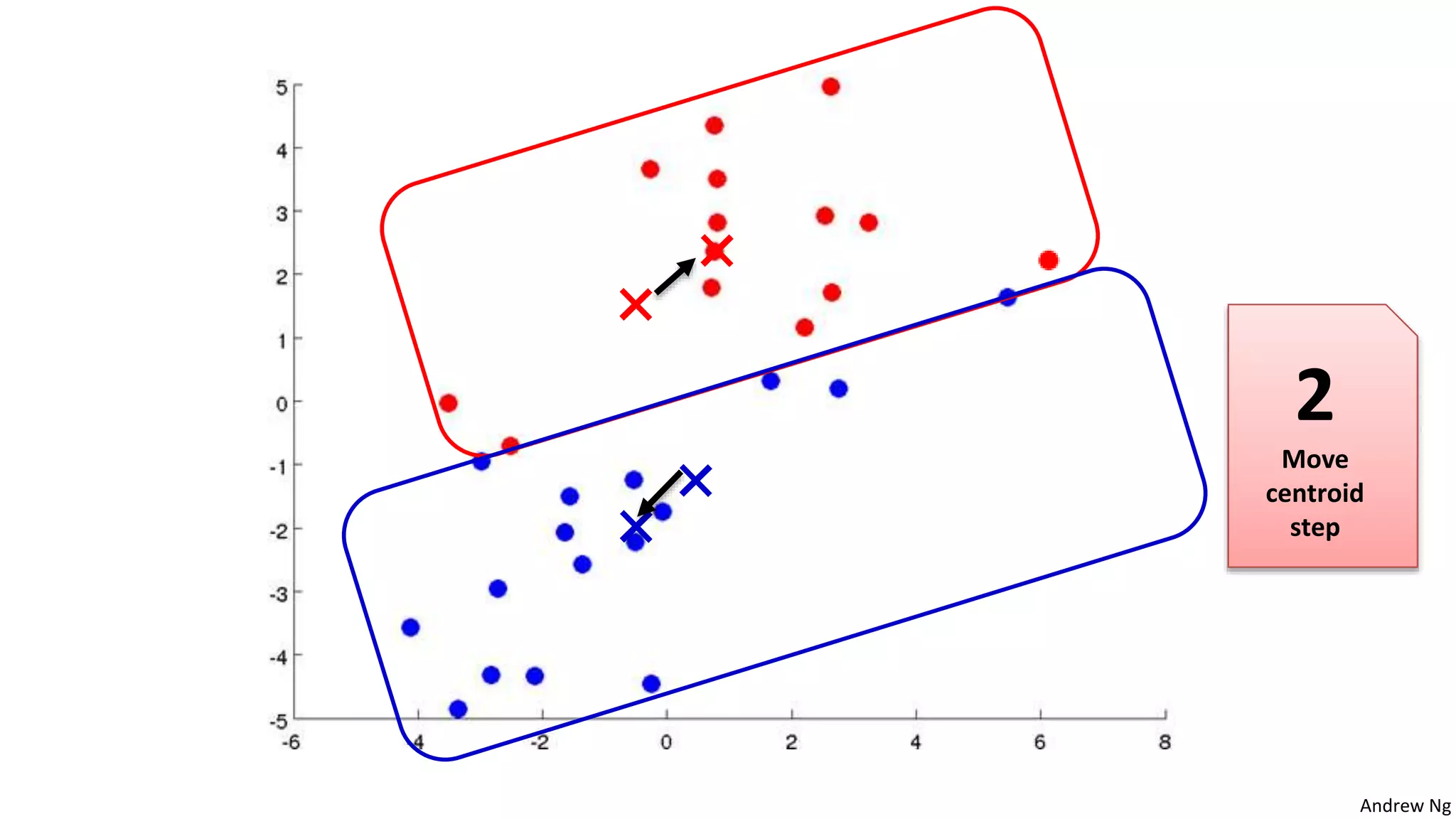
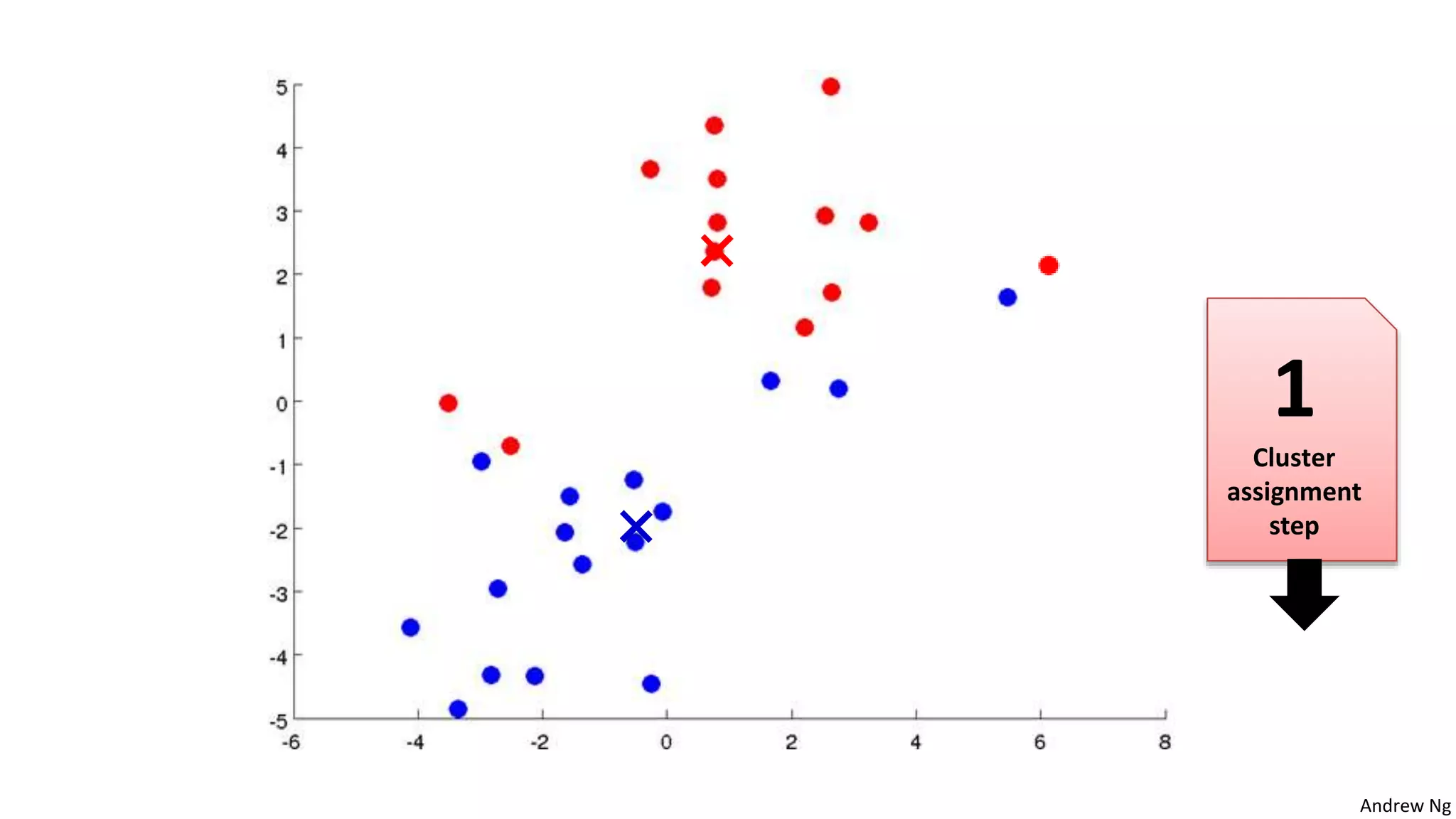
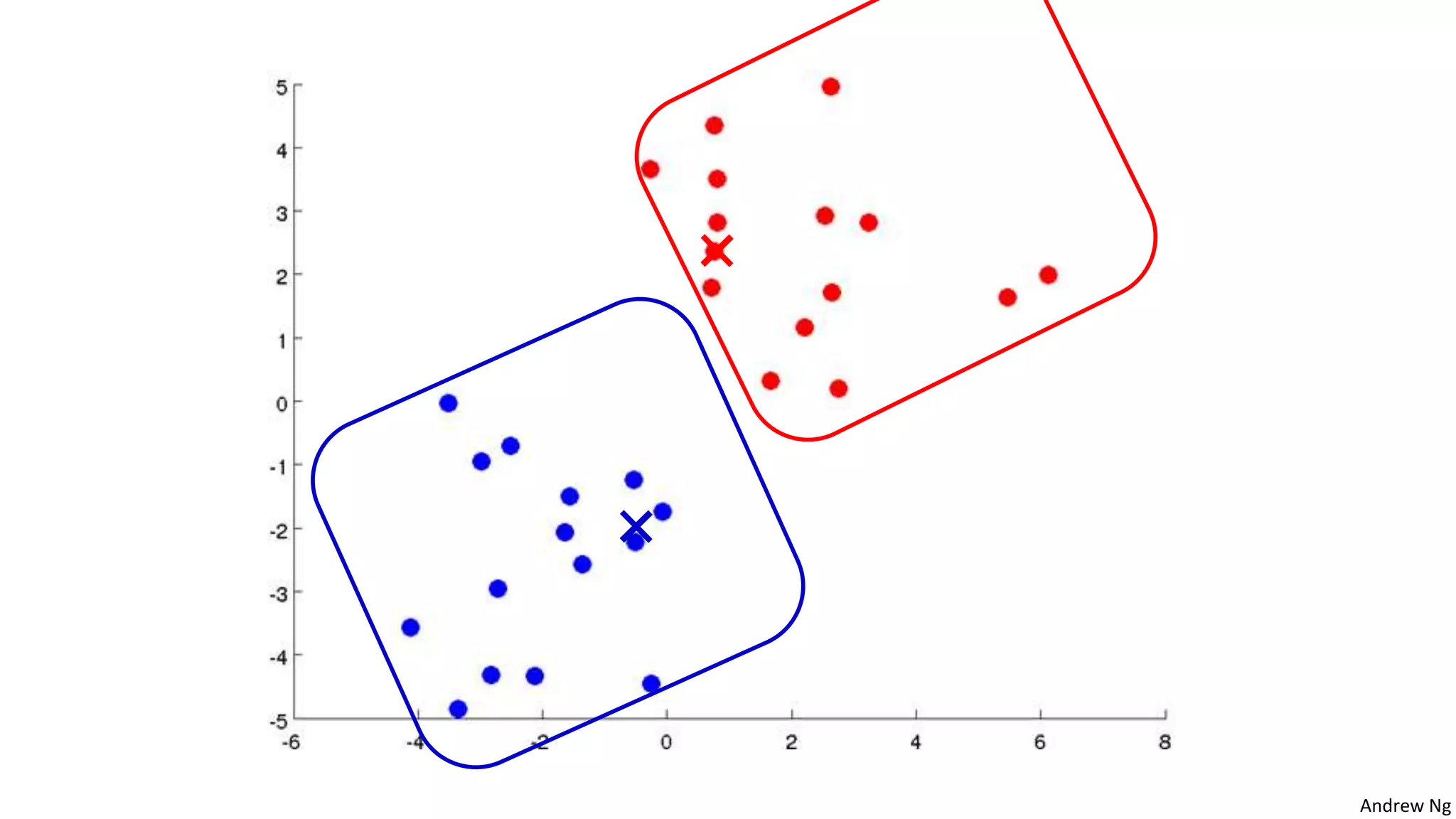
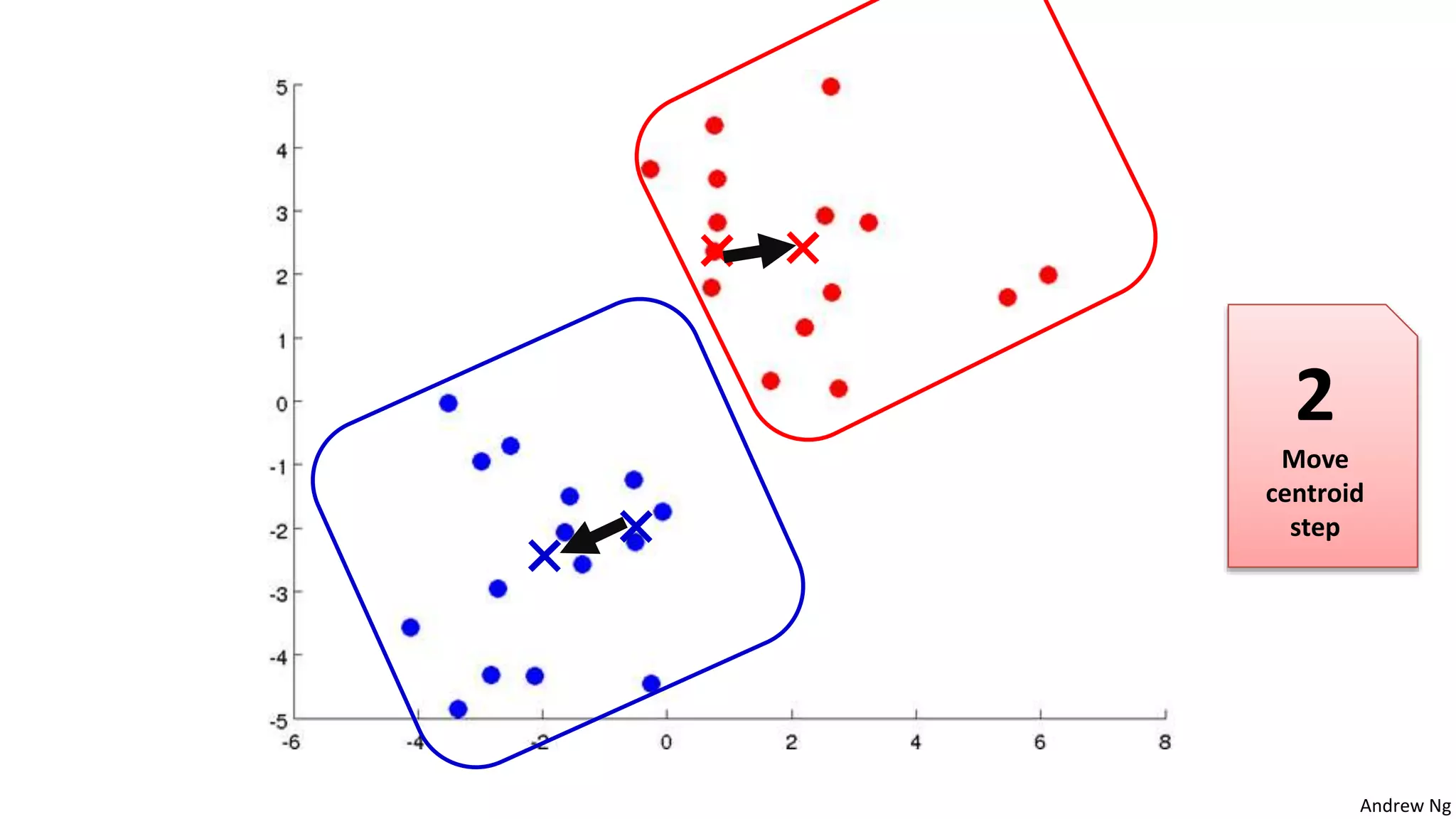
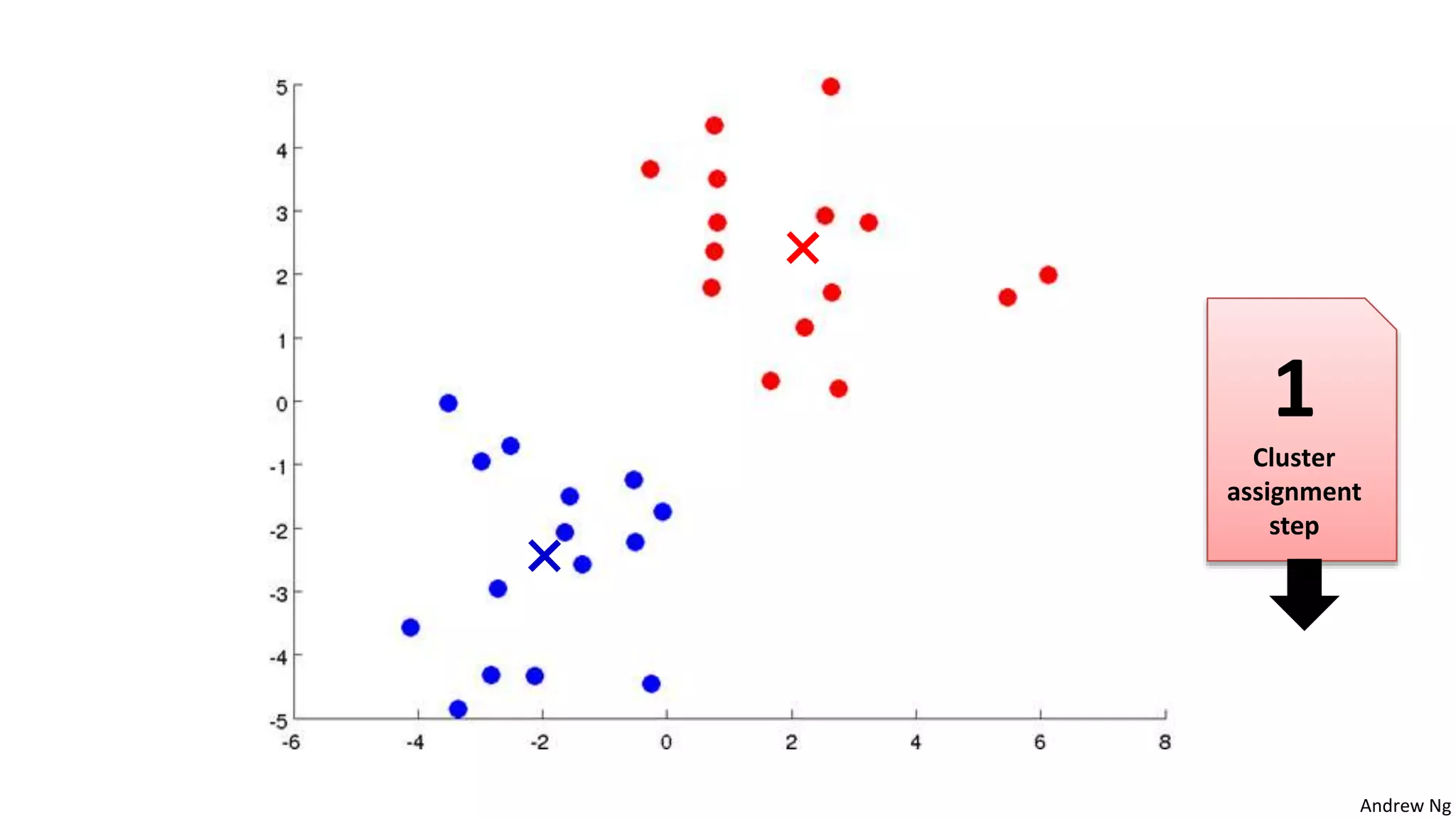
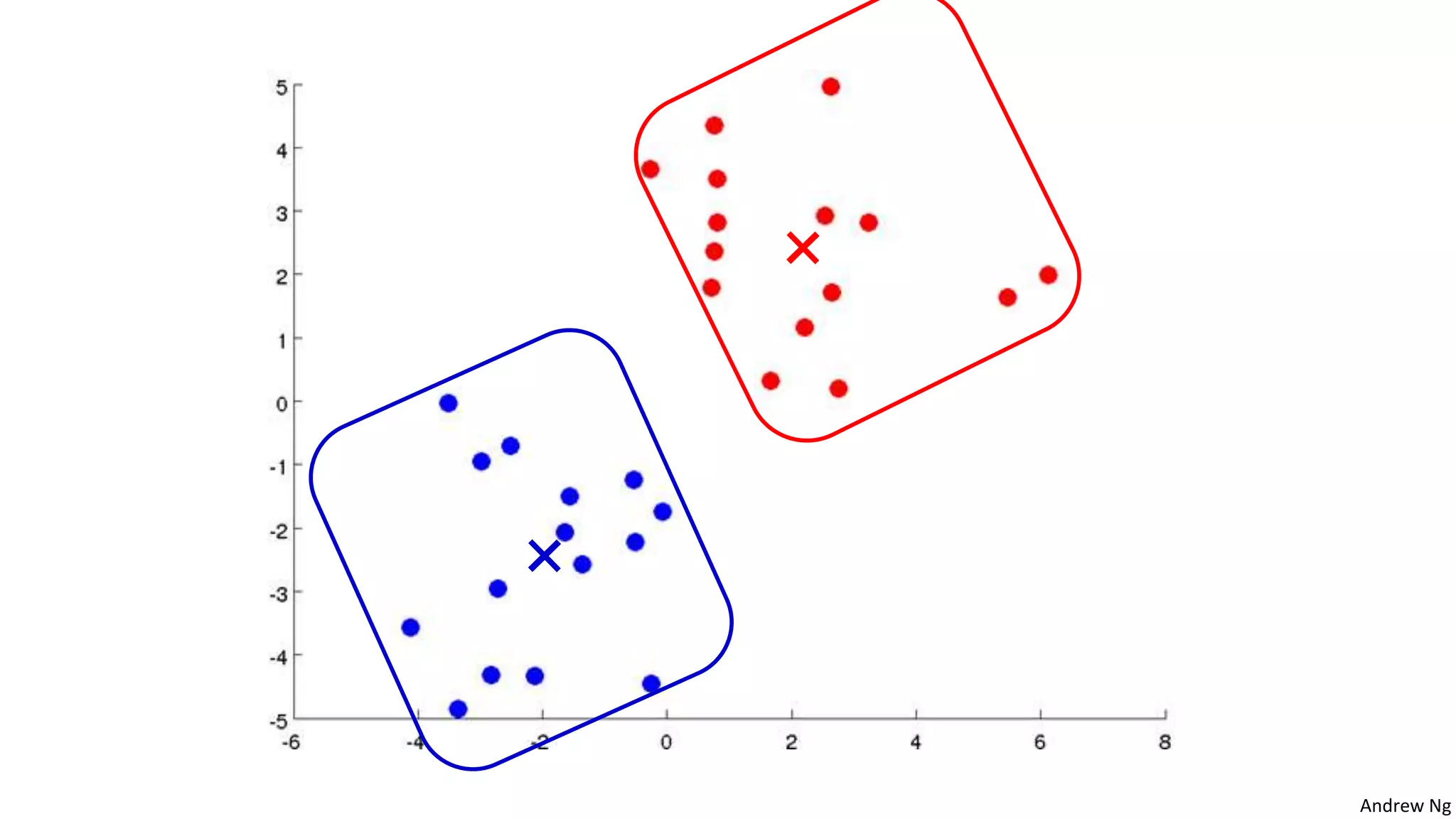
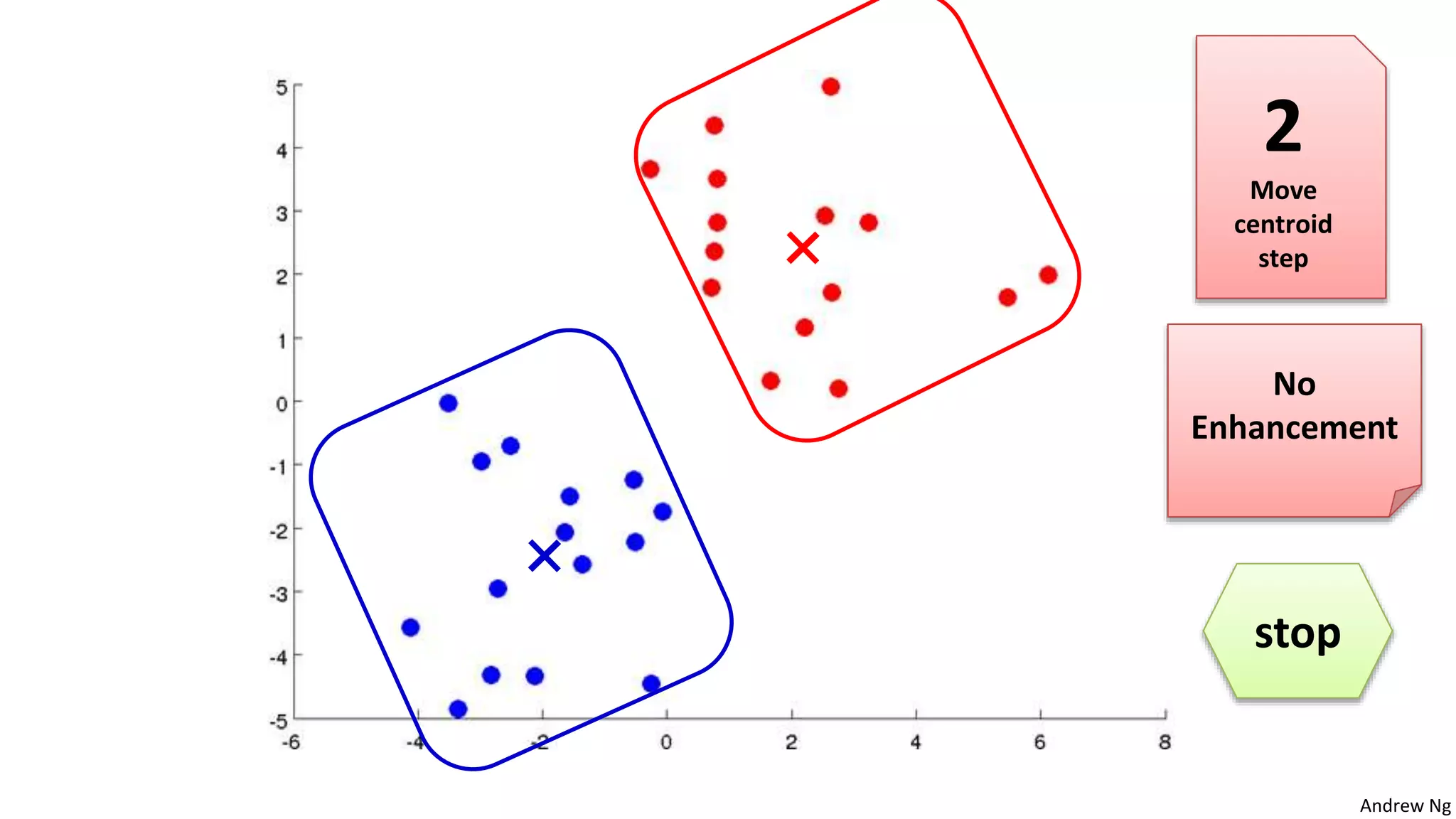
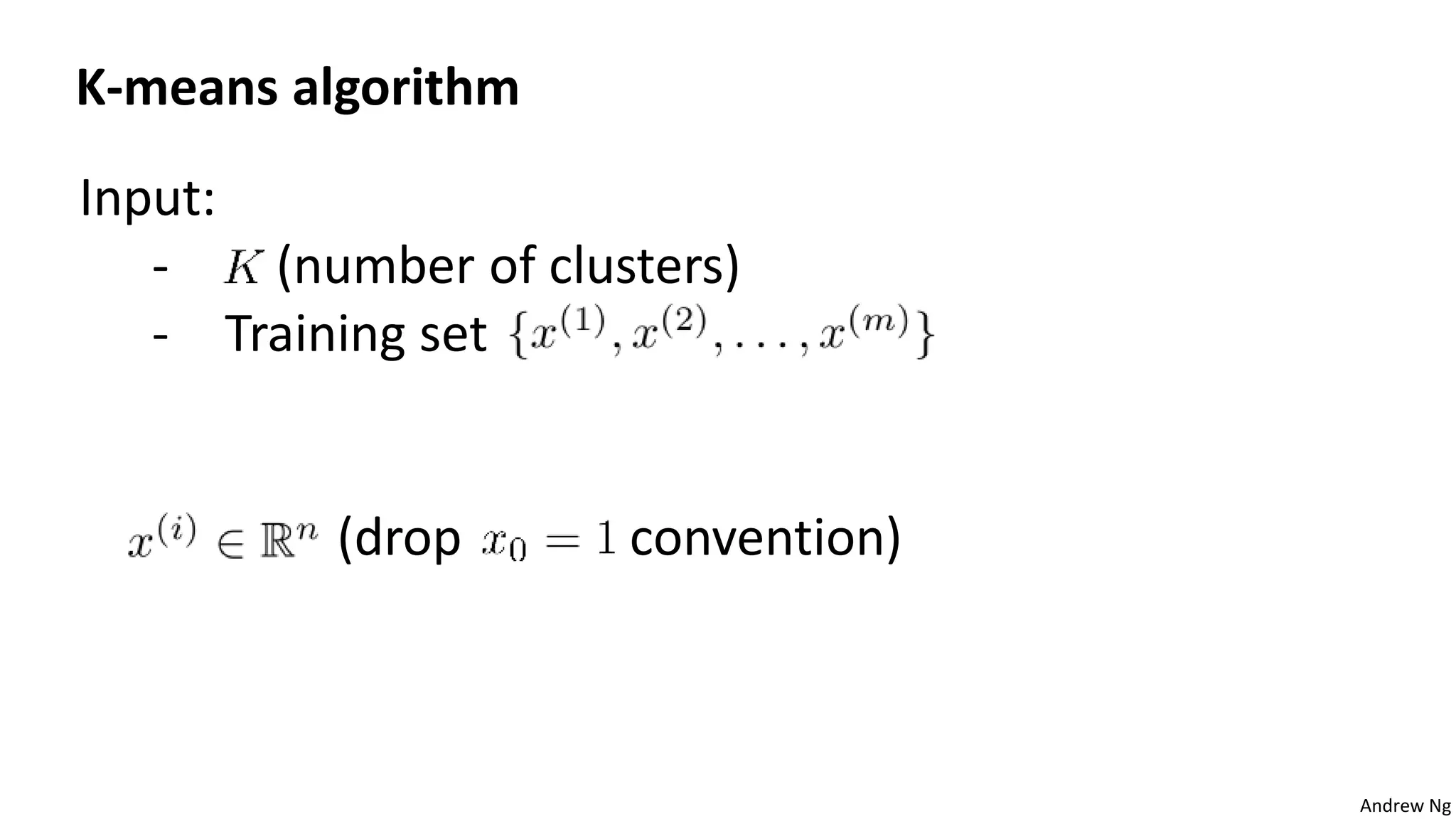
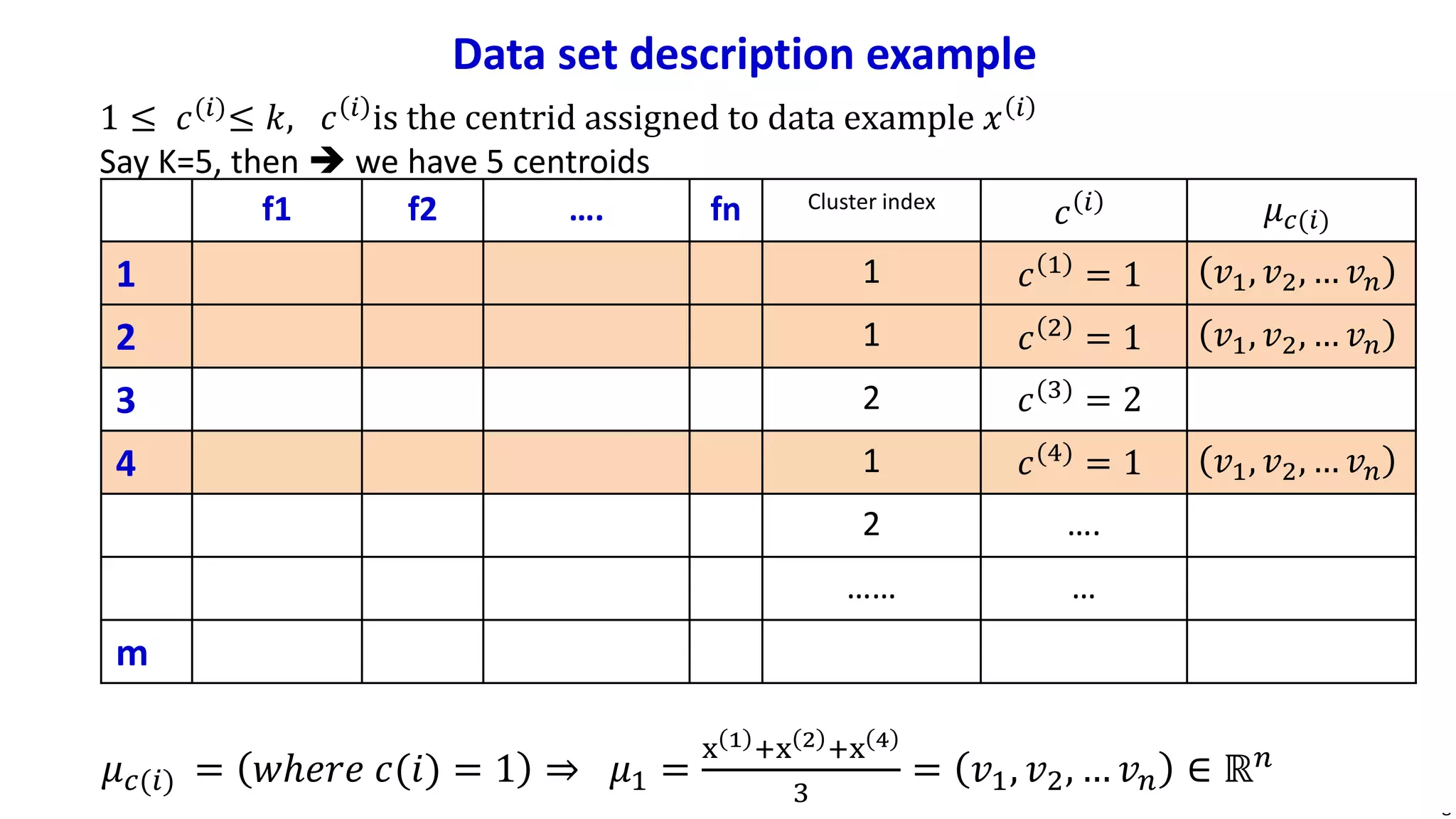
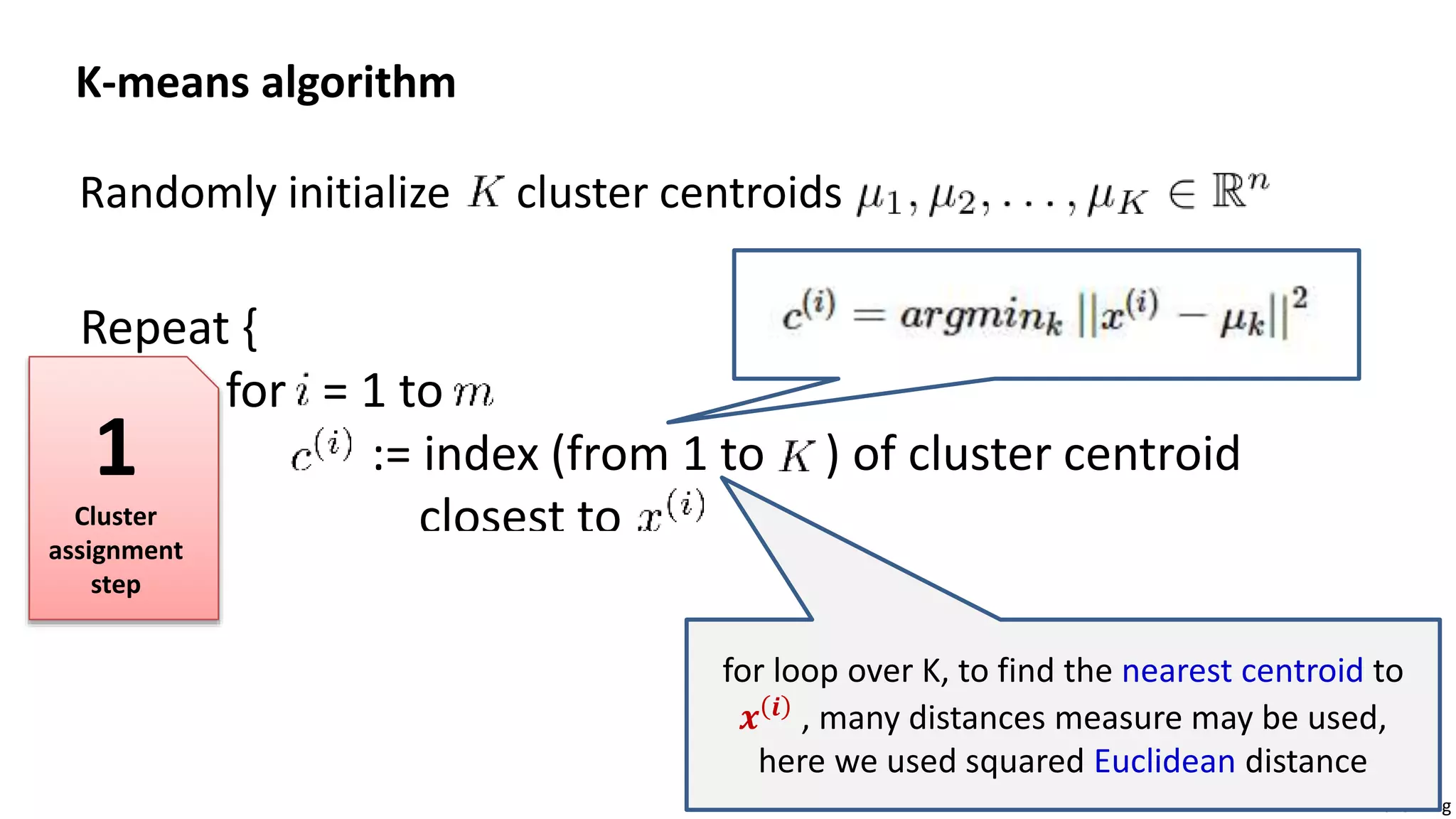
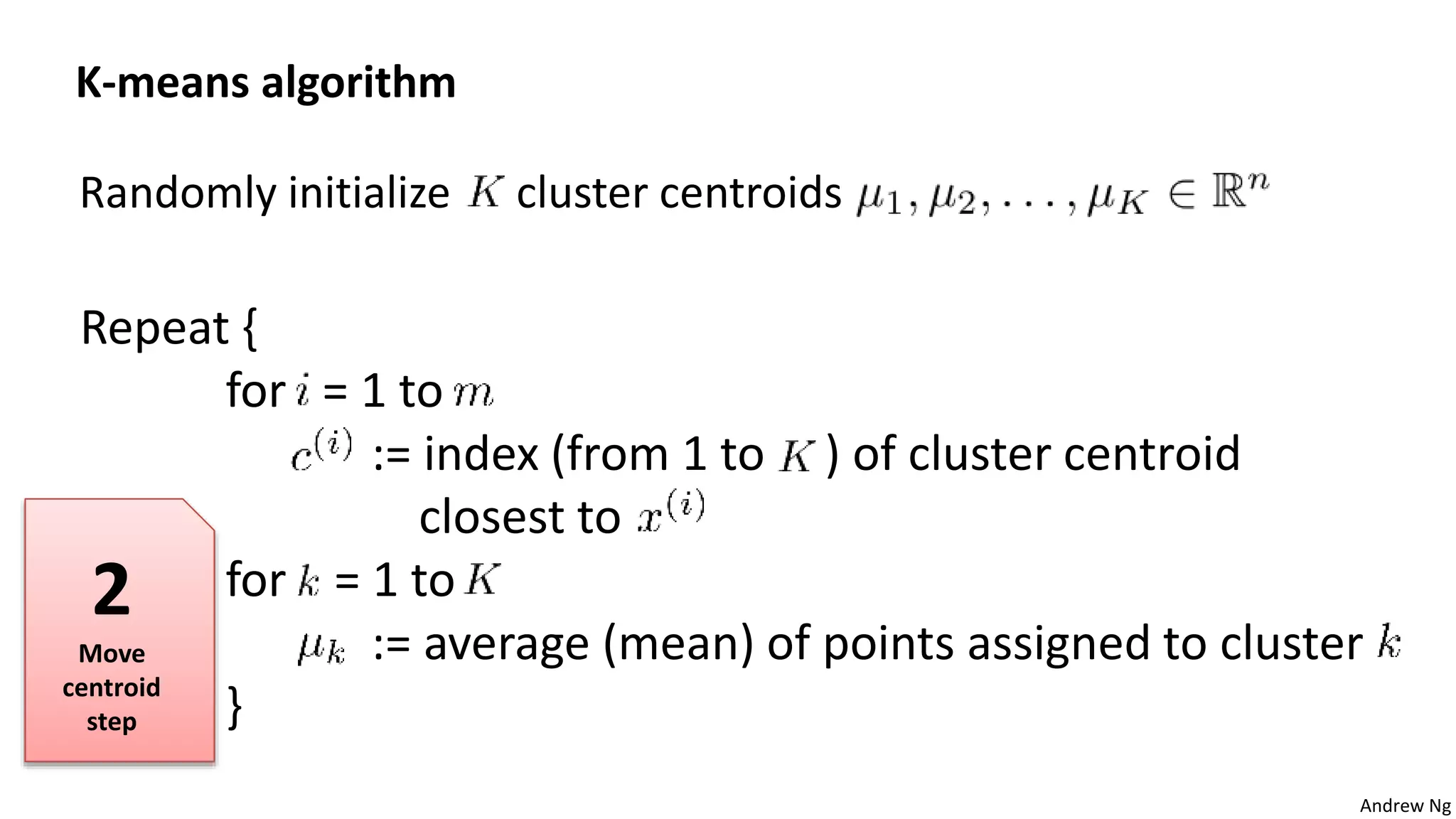
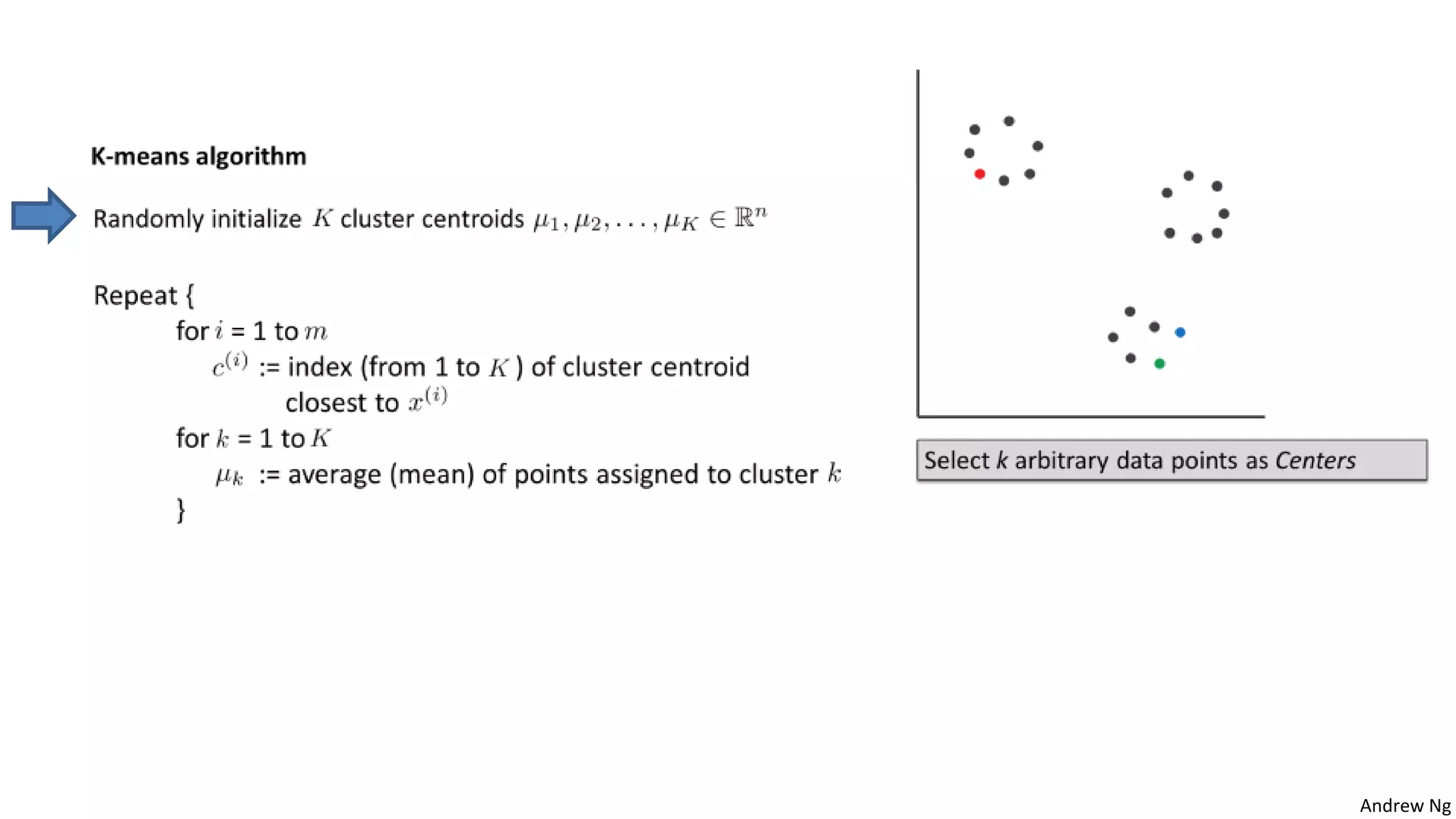
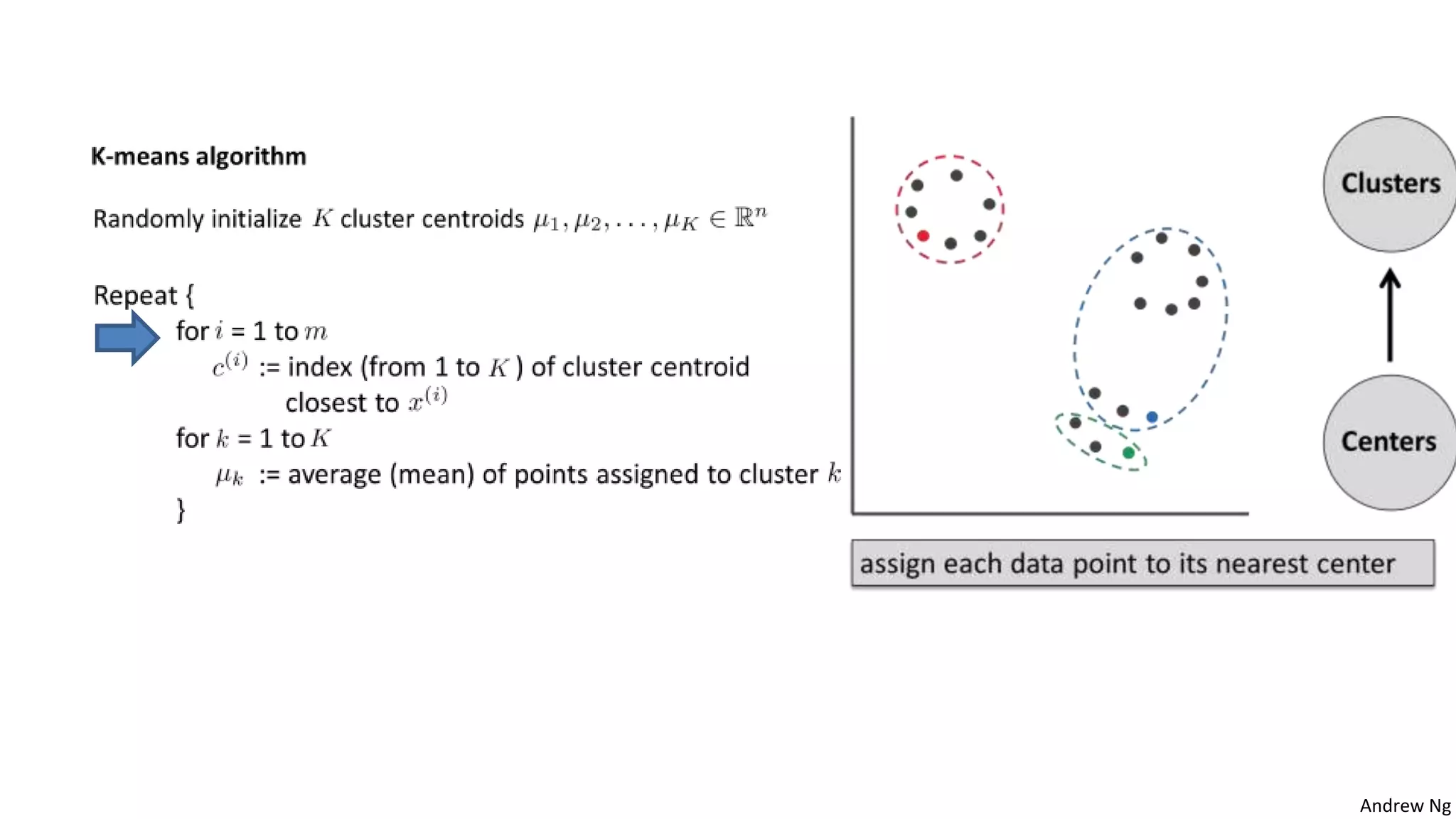
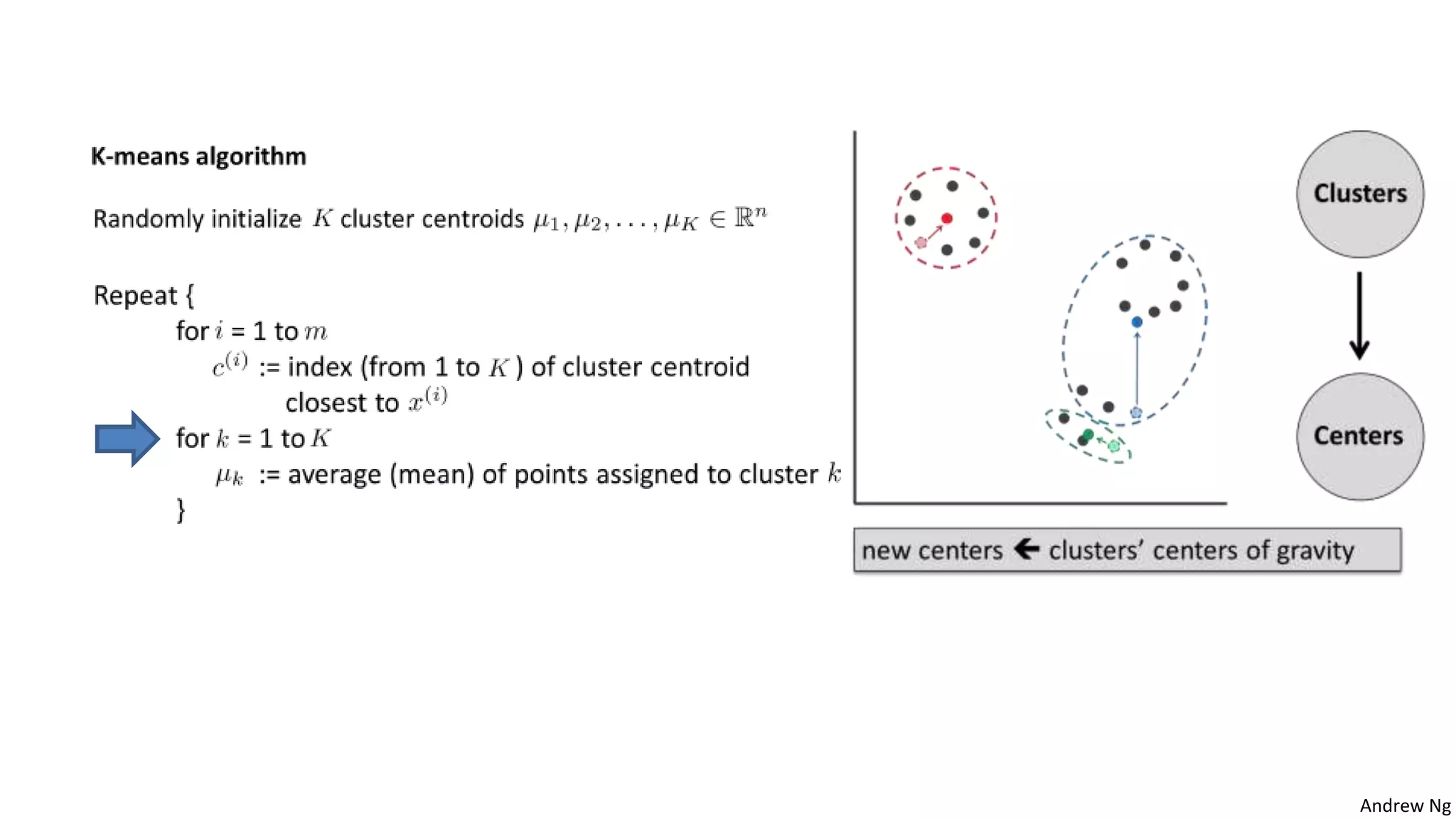
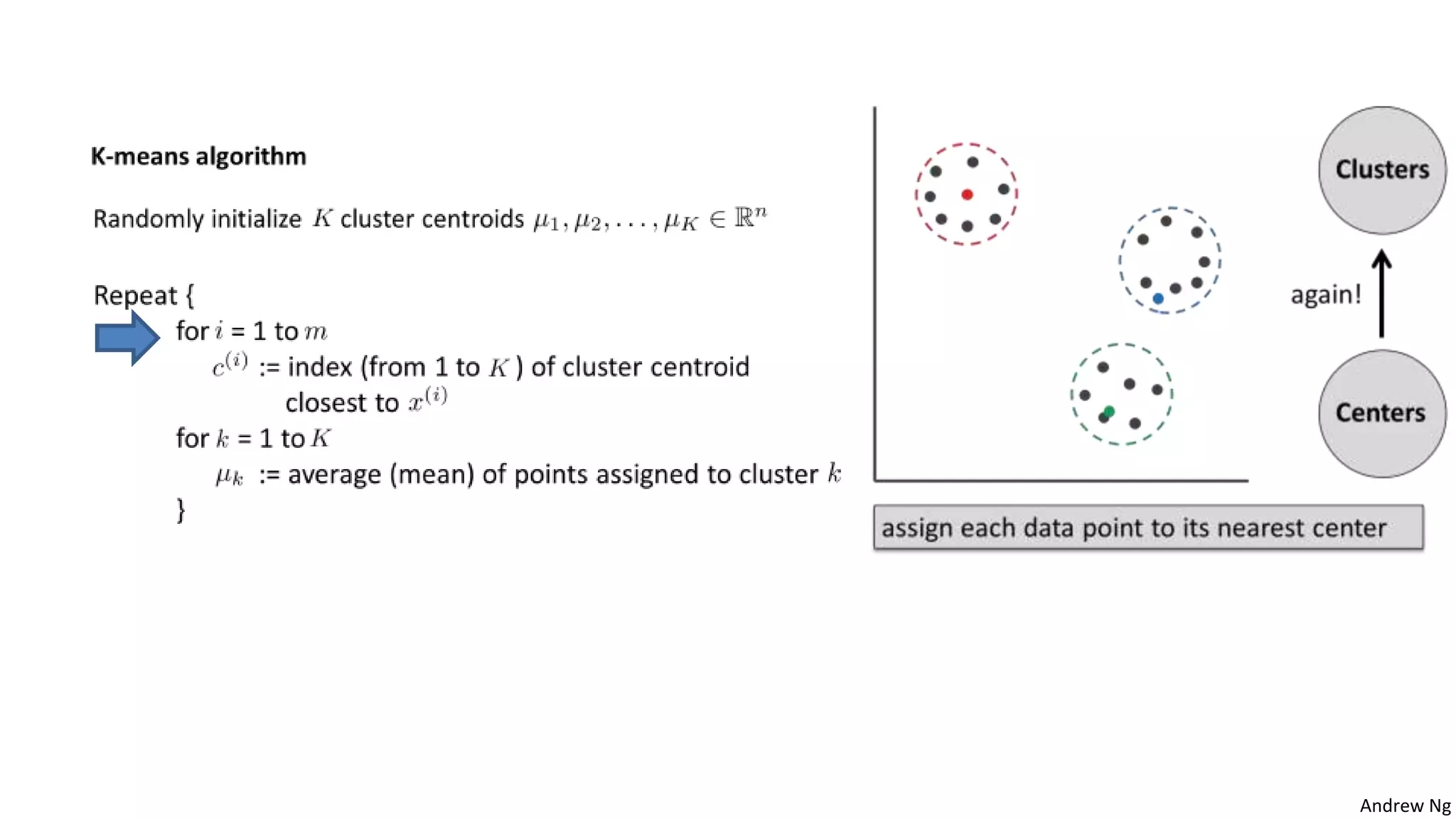
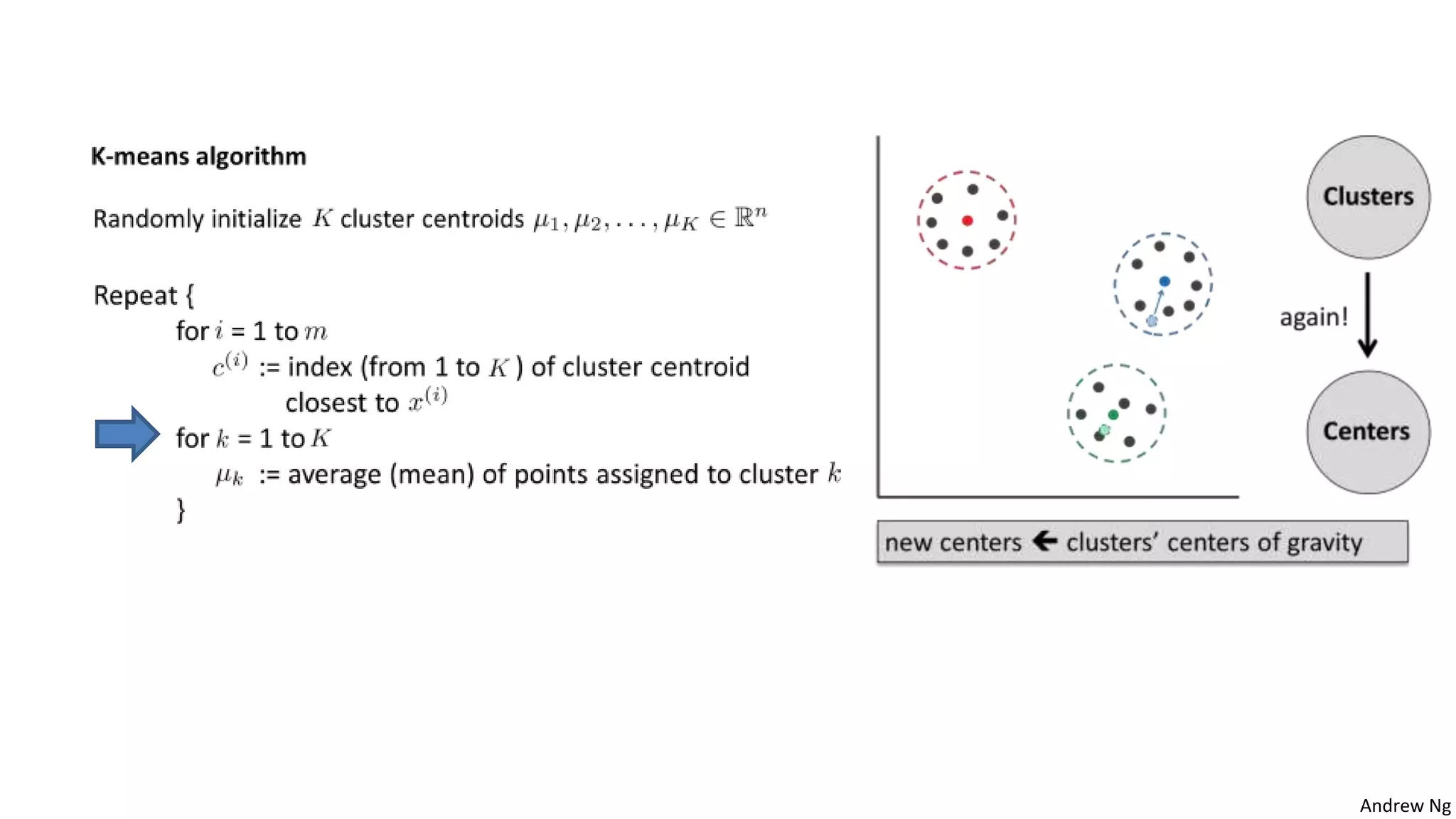
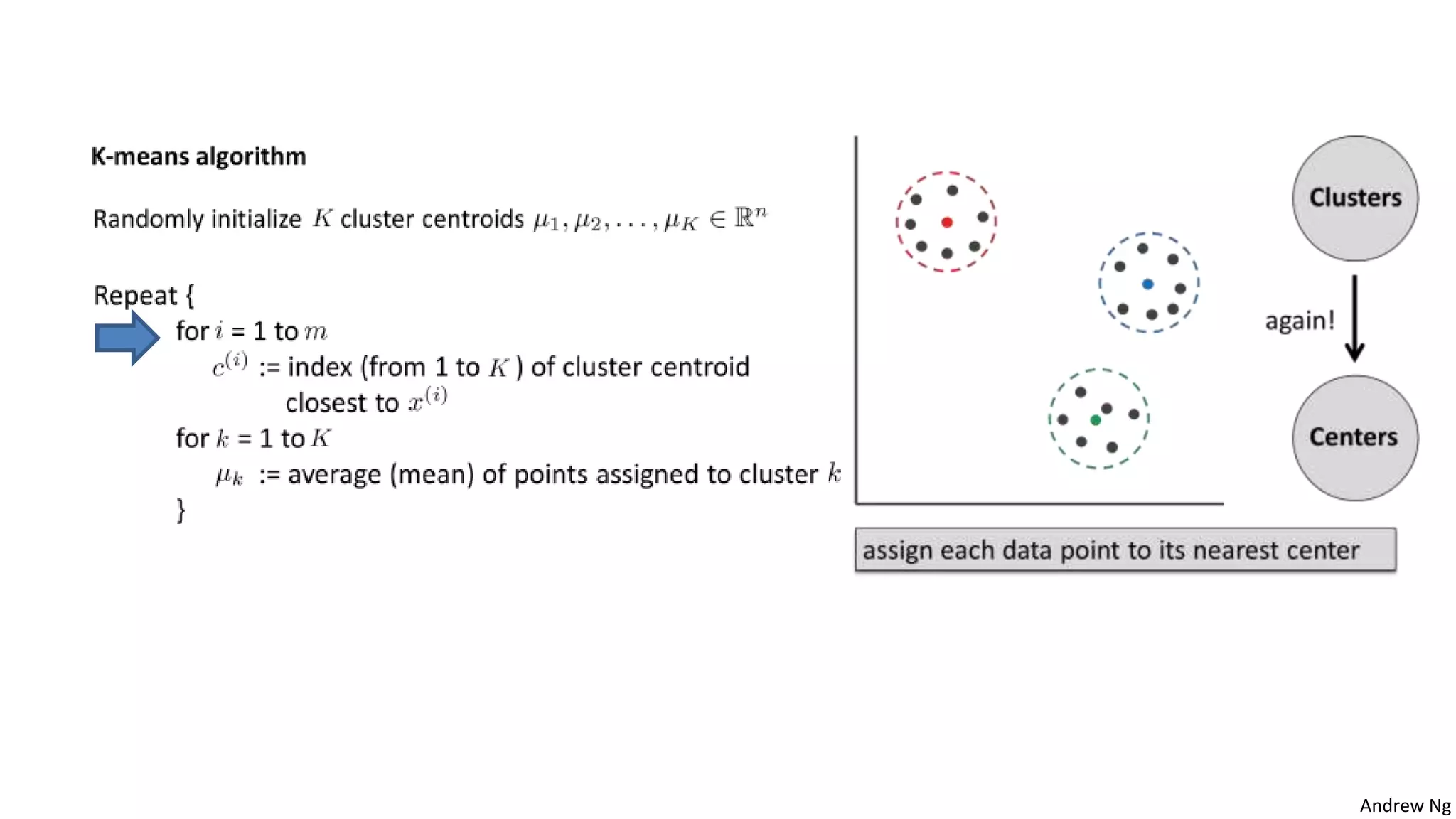
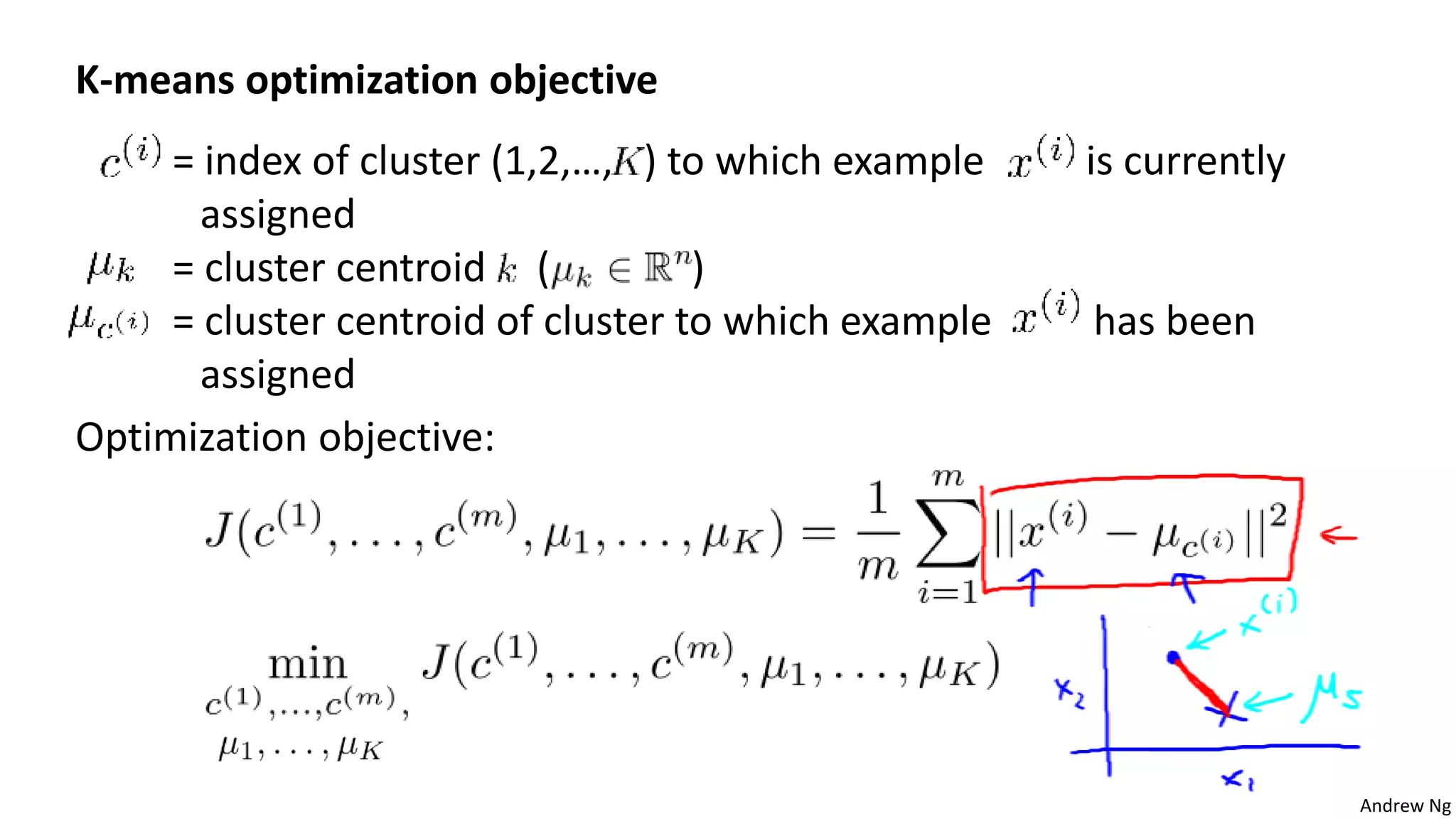
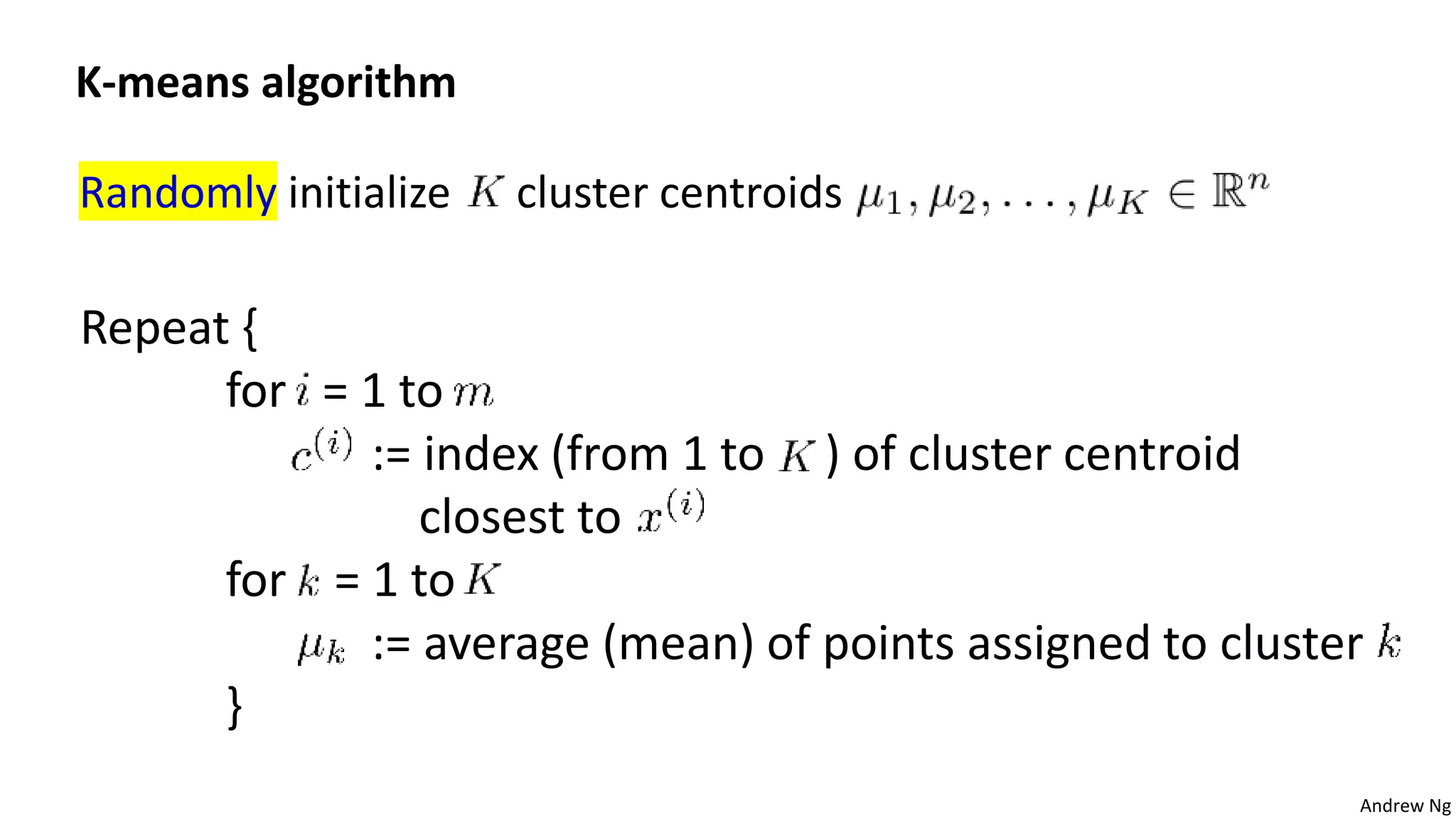
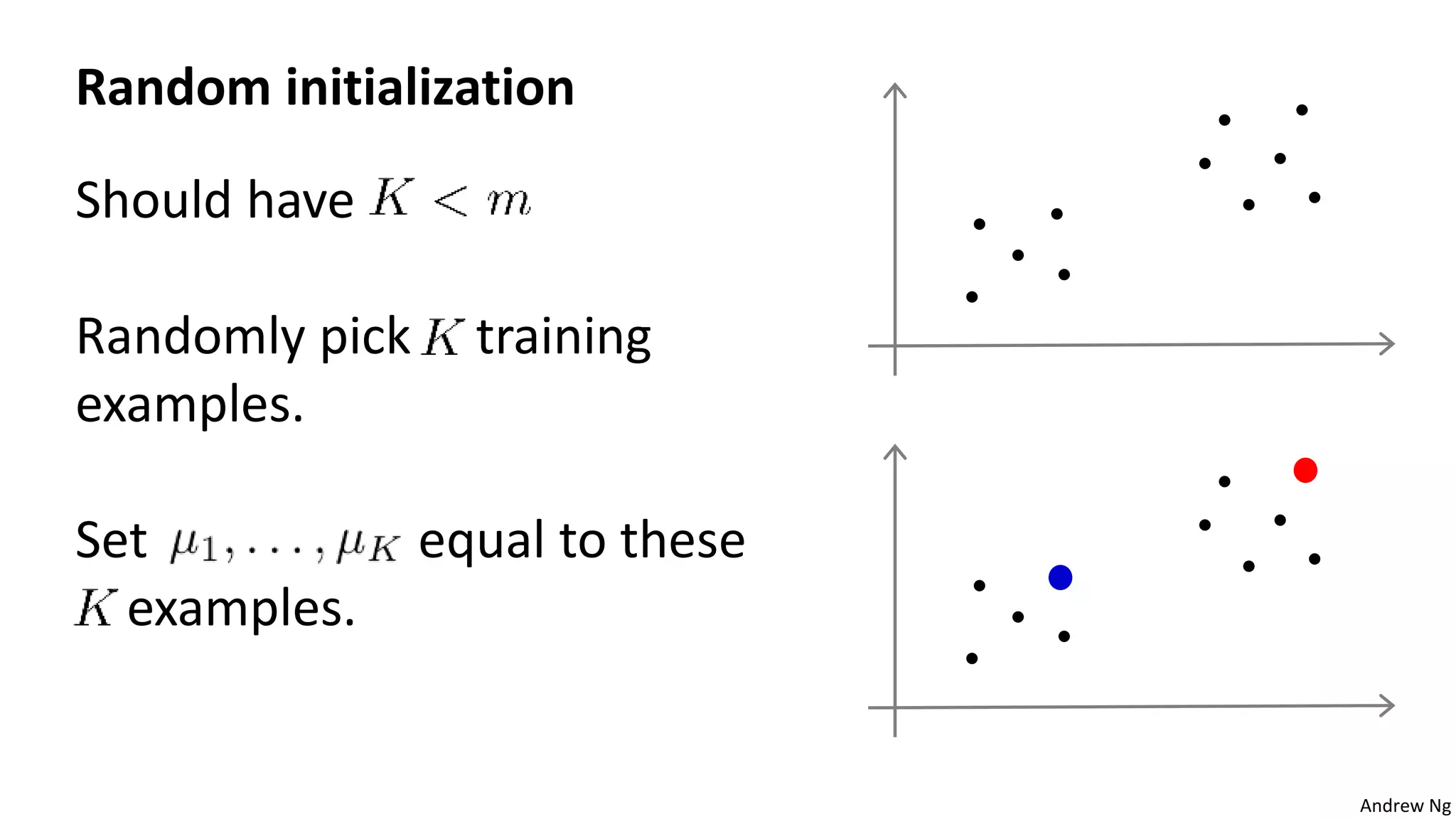
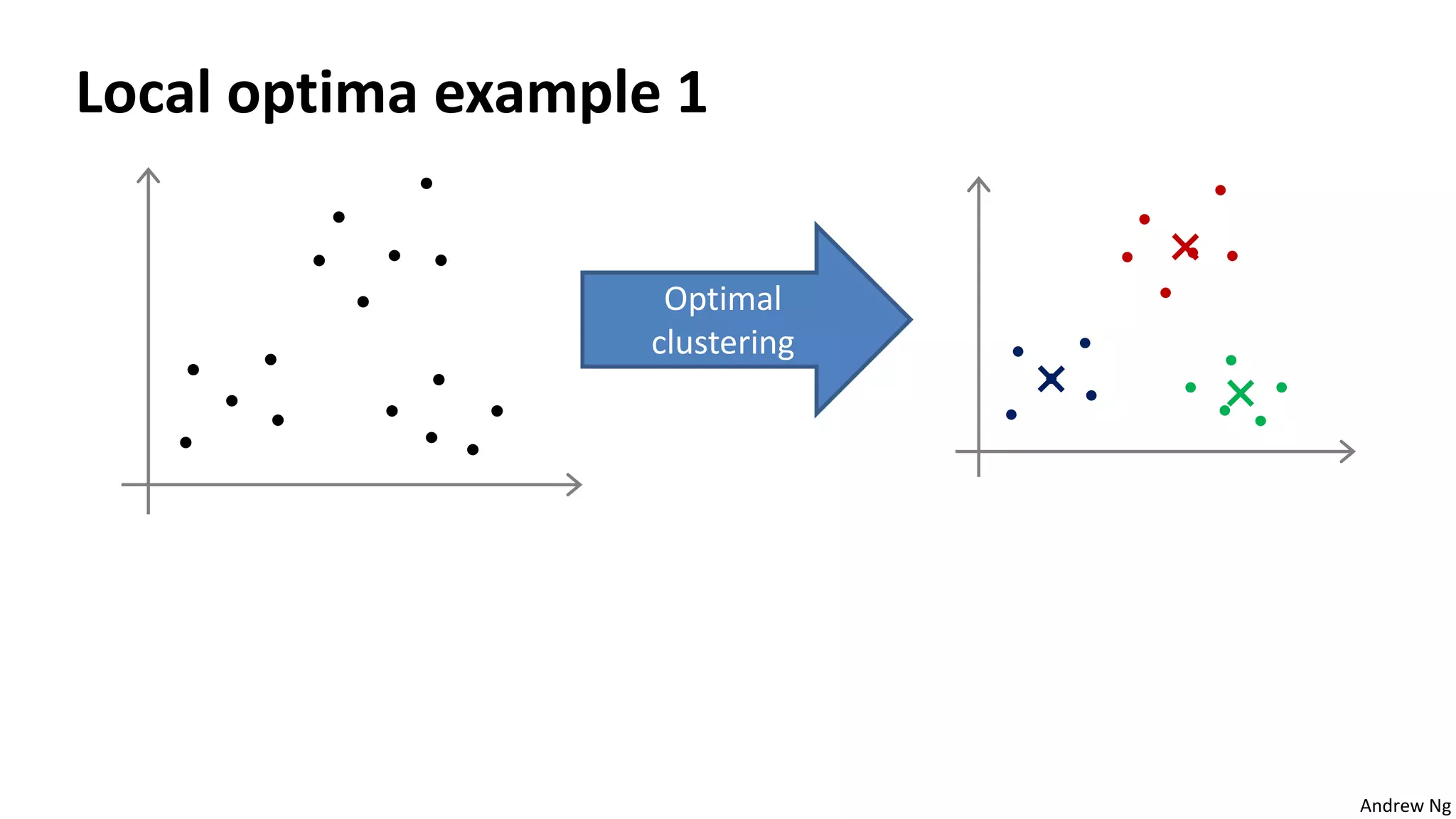
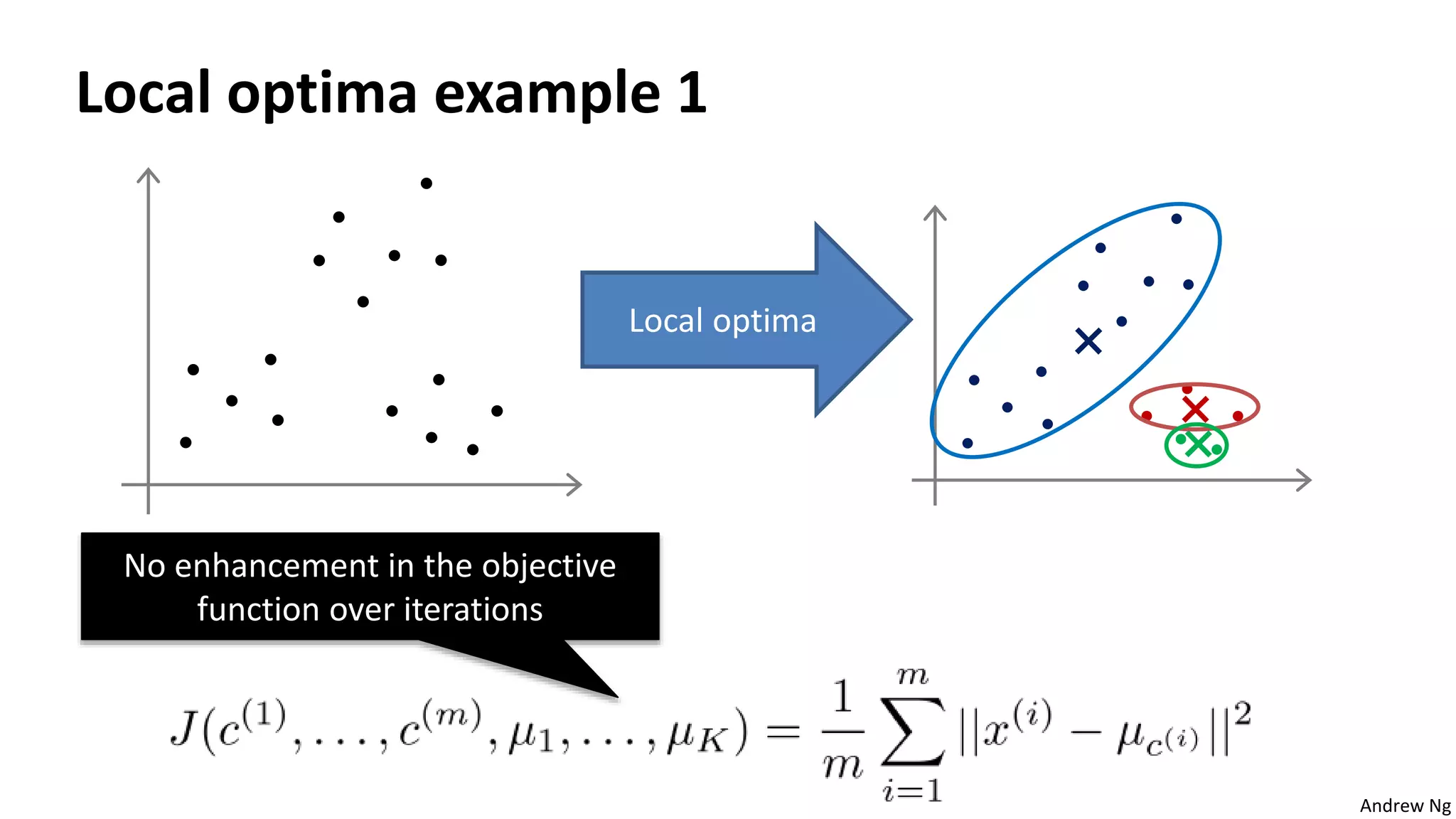
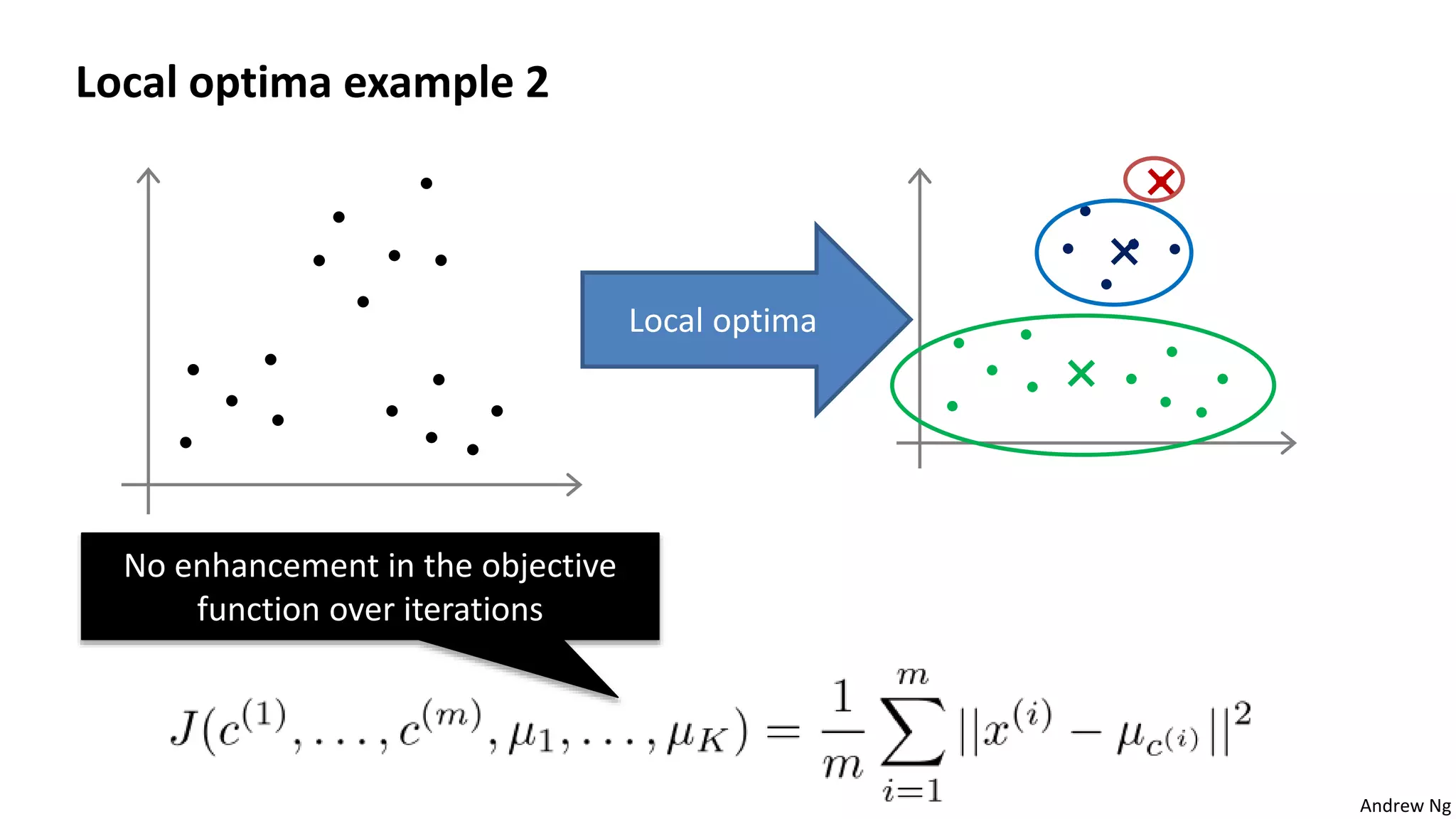
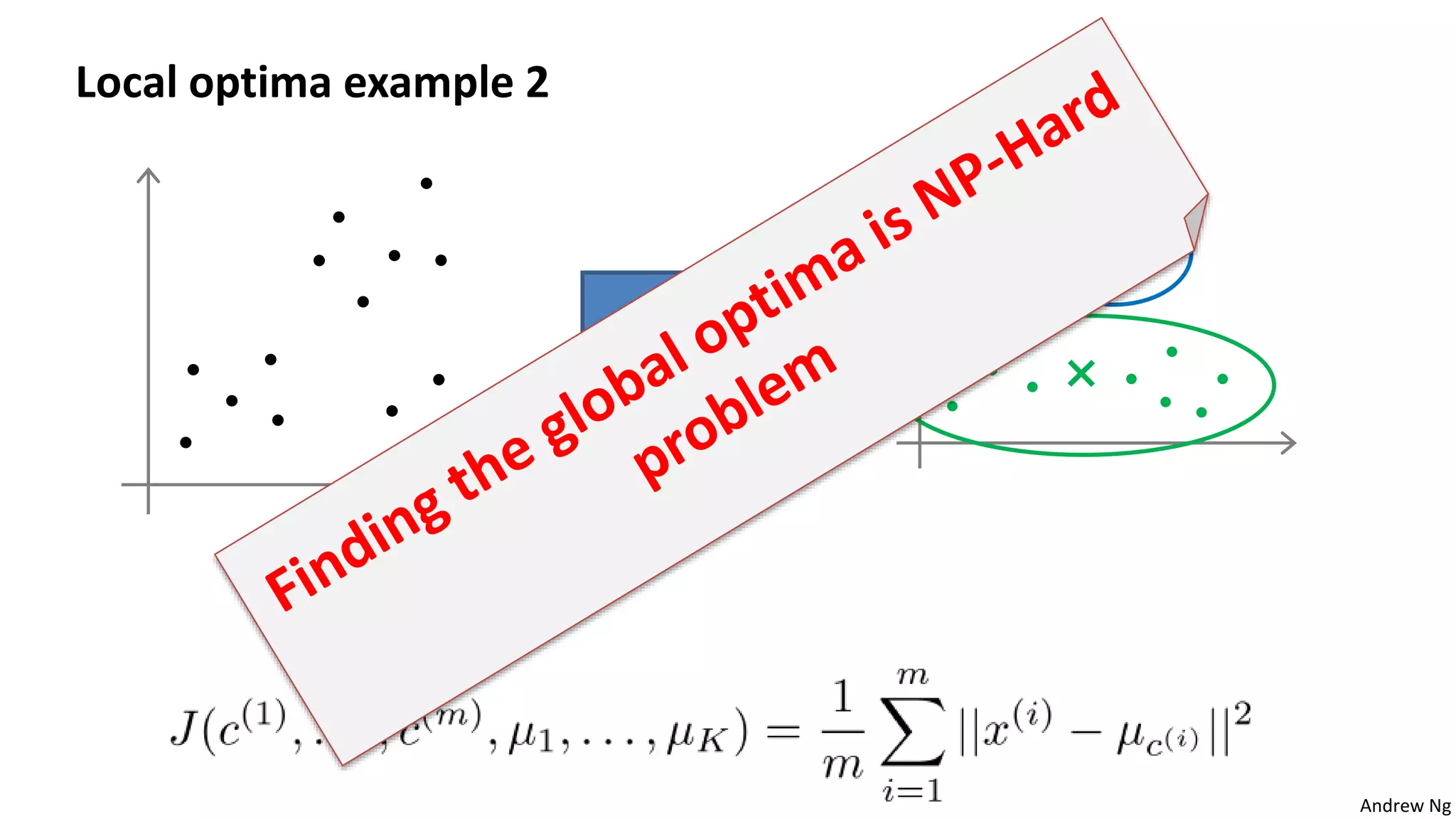
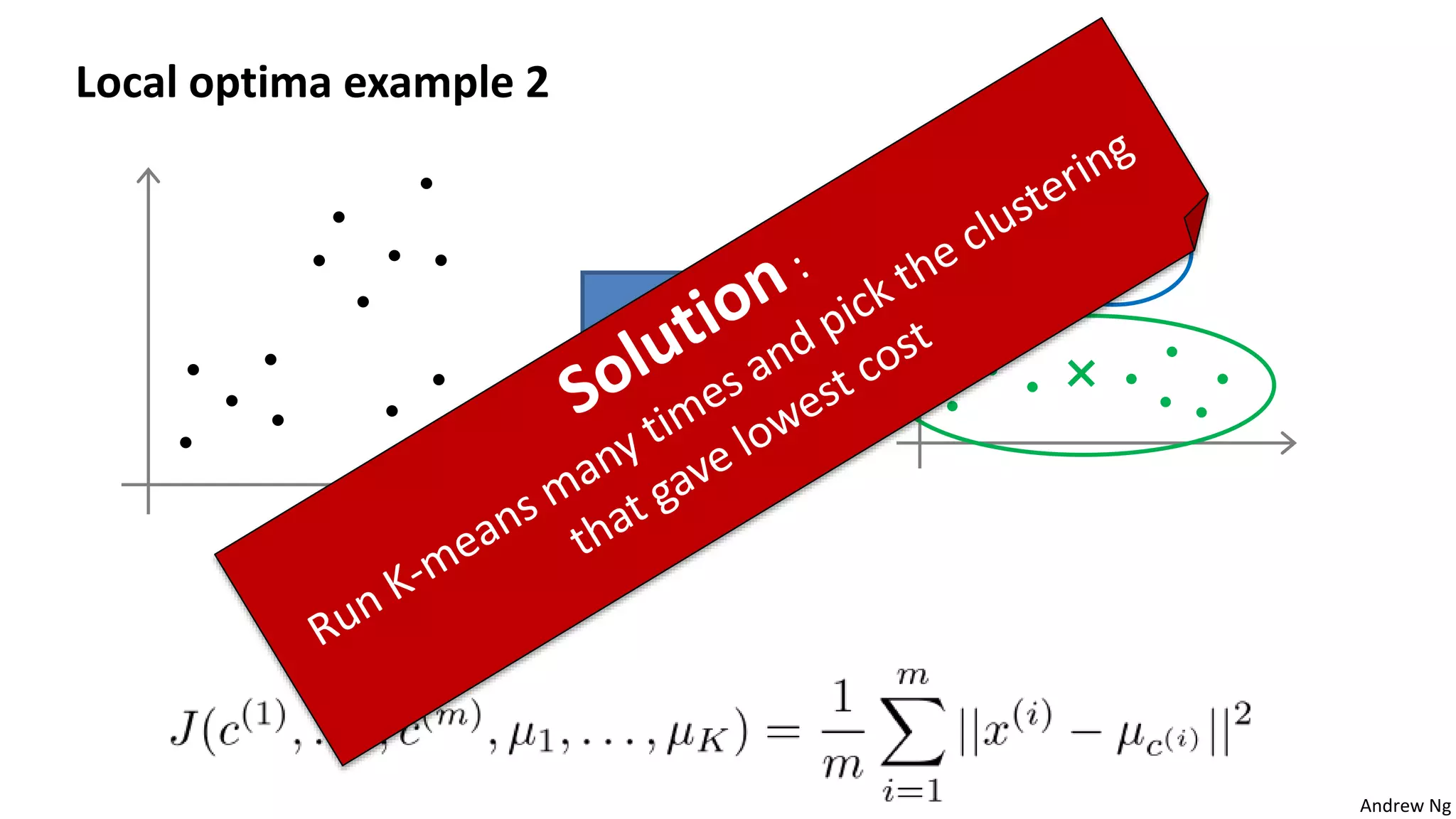
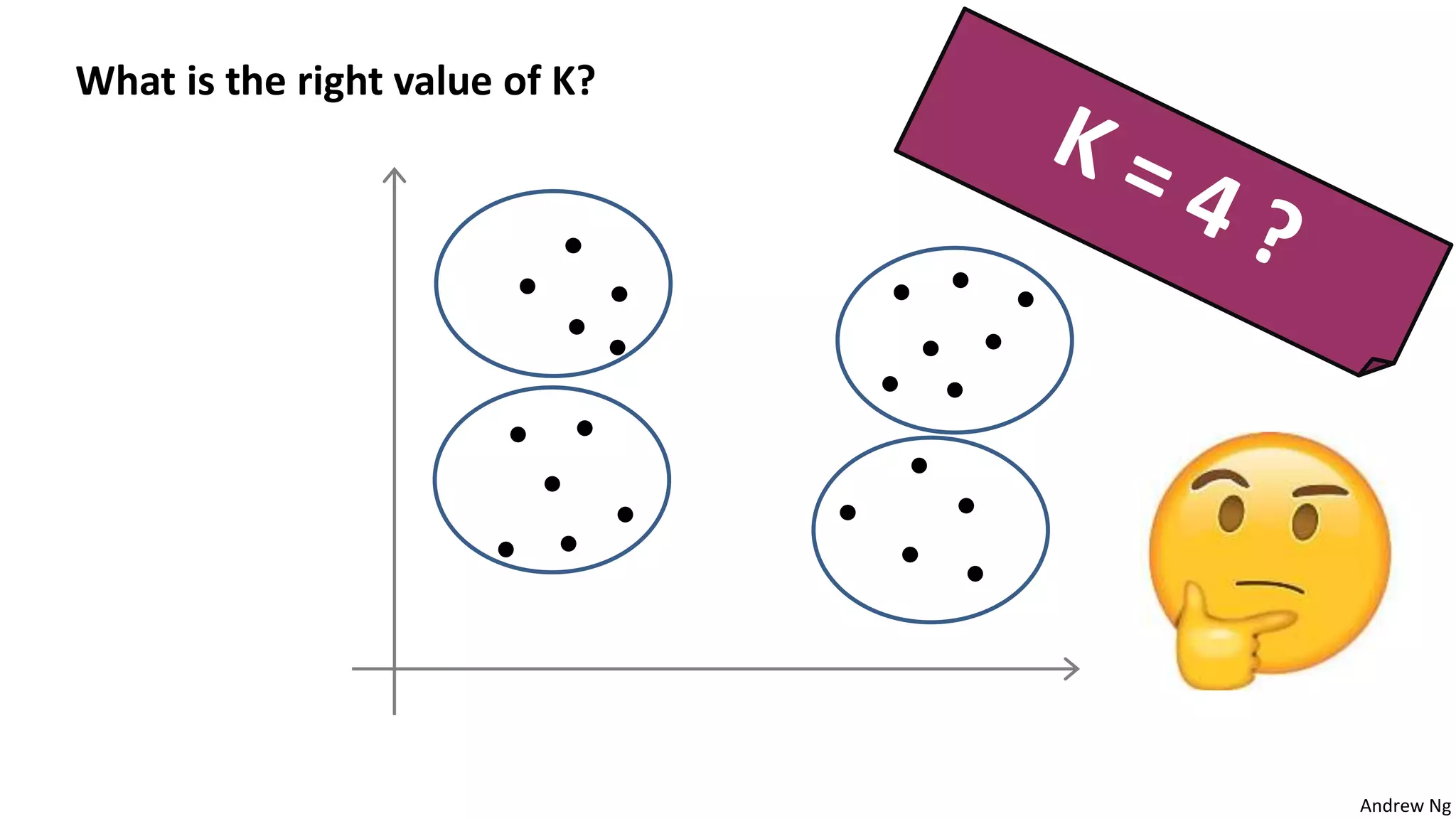
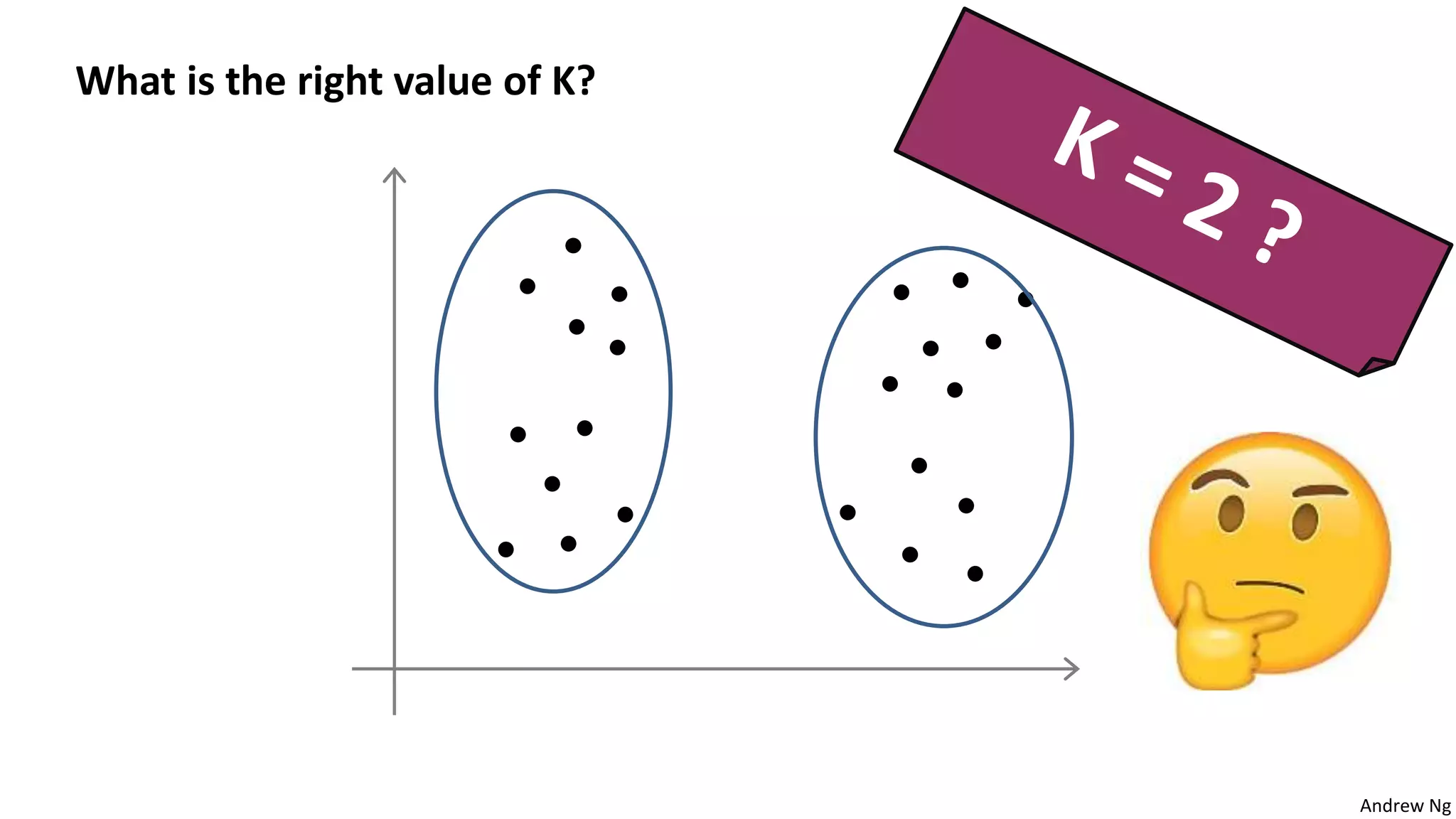
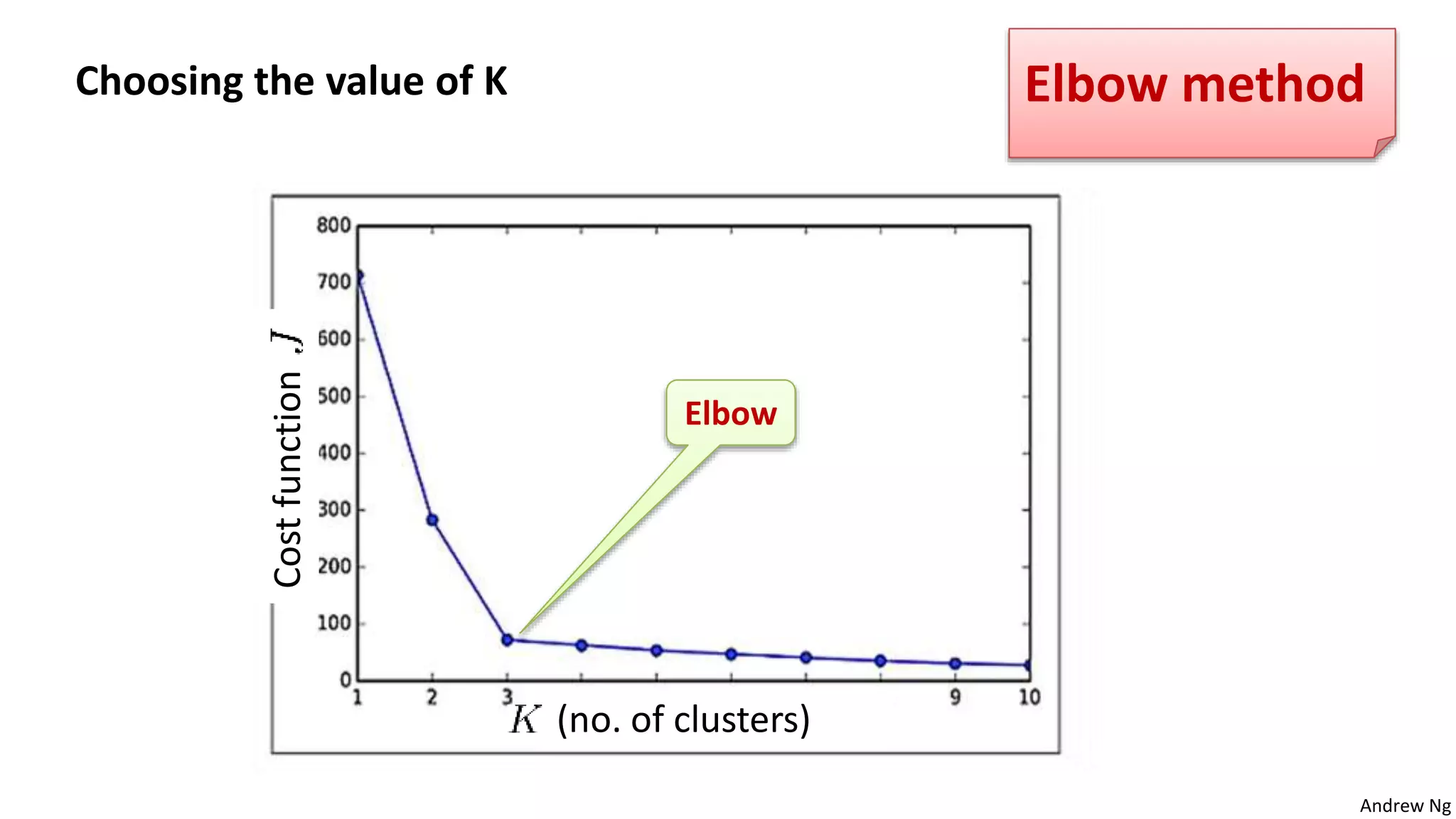
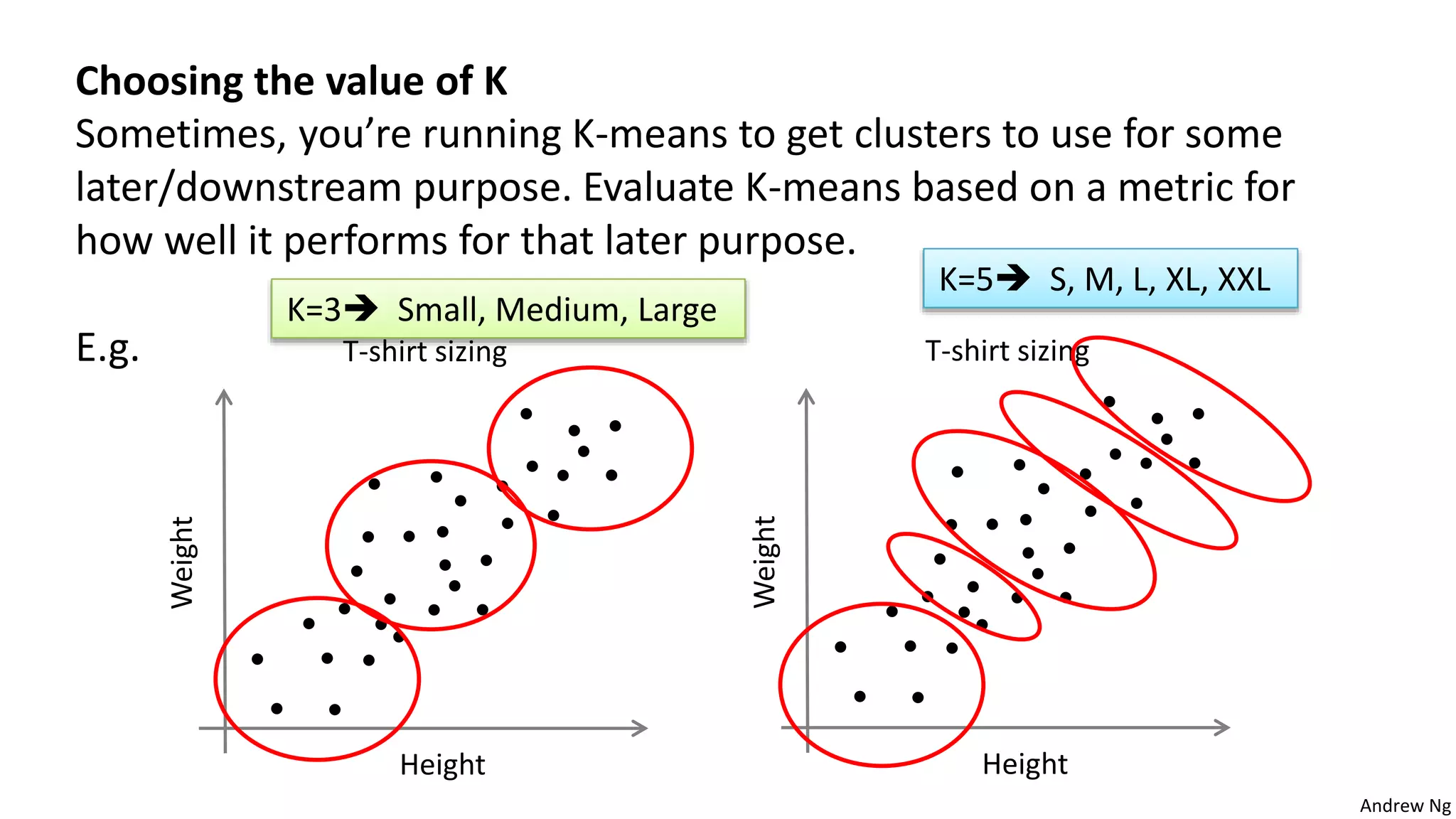
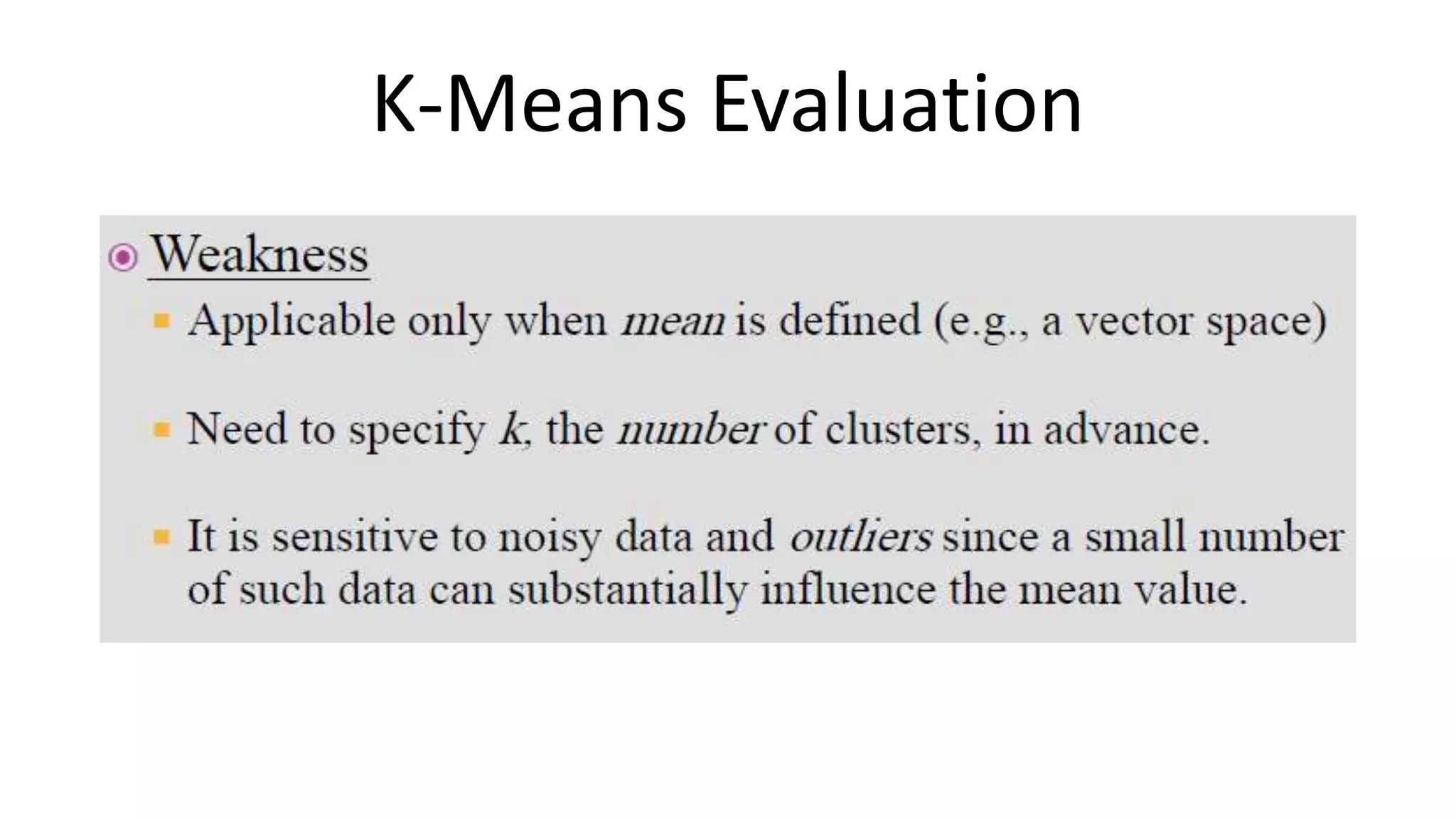
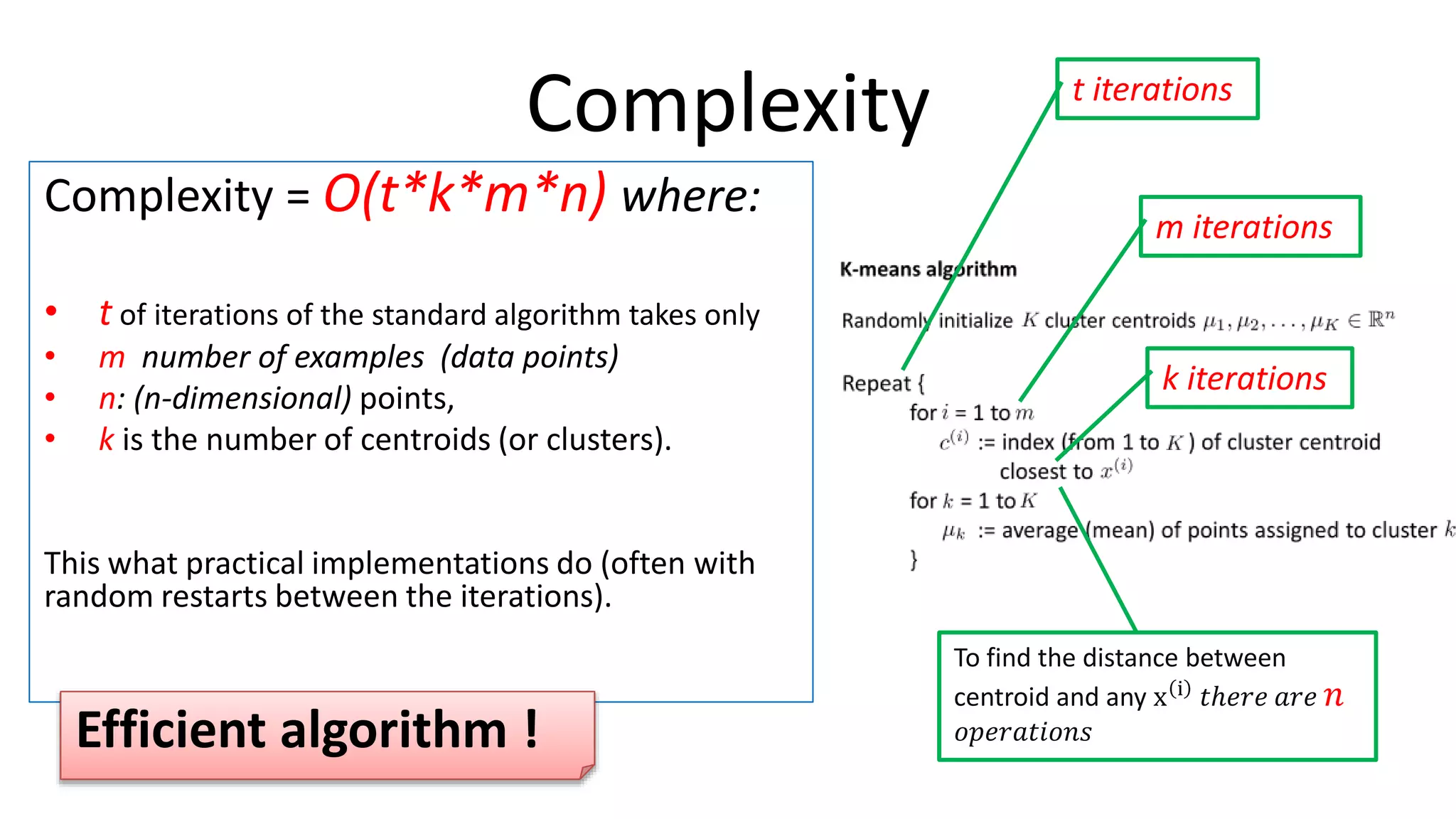
This document discusses machine learning and K-means clustering. It provides an overview of the K-means algorithm, including random initialization of clusters, cluster assignment and moving centroid steps. It also discusses choosing the number of clusters, evaluating and visualizing K-means clustering, and some applications of clustering like image analysis and market segmentation. The document is attributed to Andrew Ng and references his lecture slides on machine learning and K-means clustering.