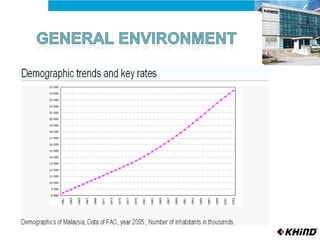
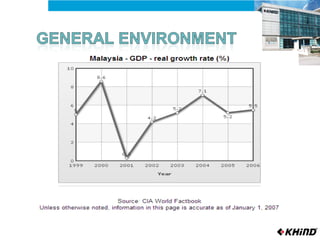
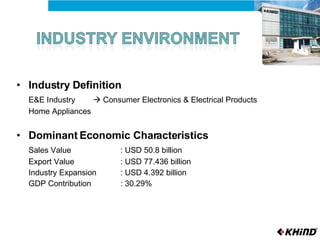
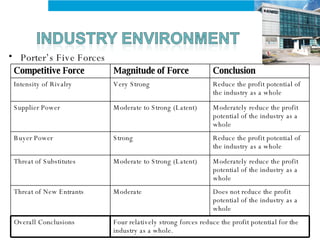
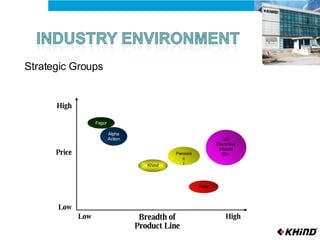
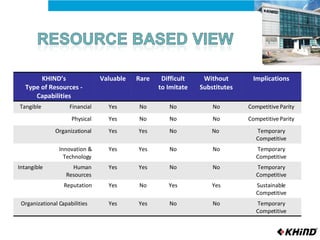
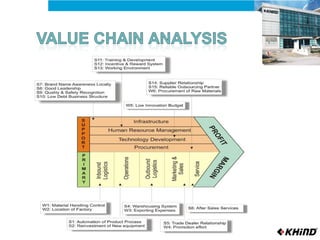
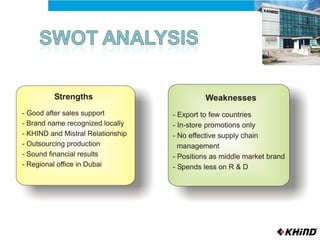
The document provides an analysis of KHIND, a Malaysian electronics company, including its background, the general business environment, an internal SWOT analysis, and recommendations. It analyzes demographic, economic, socio-cultural, political/legal, and technological factors impacting the industry. It also examines KHIND's resources and capabilities, and provides strategic recommendations focused on market penetration, product development, and functional strategies.