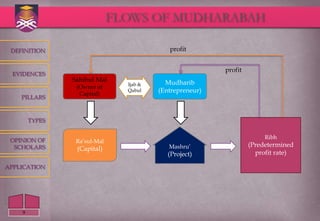
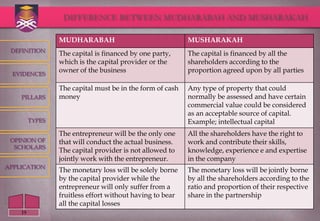
The document defines and discusses the concept of Mudharabah, which is a contract of partnership where one party provides capital and the other provides labor and management. It provides key details on the definition, pillars, categories, conditions and evidence for Mudharabah based on classical Islamic literature. The summary highlights that Mudharabah is a profit-sharing partnership where profits are shared according to a predetermined rate but losses are borne solely by the capital provider.