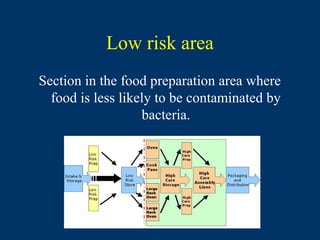
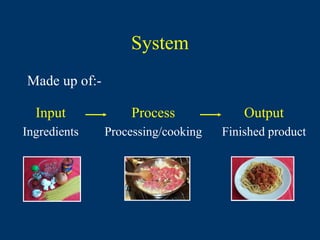
This document provides definitions for key terms used in food technology. It defines terms related to food production processes, food safety, product design, and food science. Some terms defined include additives, ambient temperature, batch production, blast chill, brand, consumer, cook-chill, diet, environmental health officer, flow diagram, HACCP, hazard, portion, product specification, quality assurance, sensory descriptors, shelf life, target group, and traceability. The document serves as a glossary for technical language in the field of food technology.