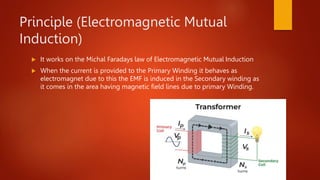
This document discusses transformers, which allow for adjusting voltage levels by exploiting electromagnetic induction. Transformers work by inducing an electric current in one coil (the secondary winding) through a changing magnetic field created in another coil (the primary winding). The ratio of winds between the primary and secondary determines whether a transformer steps up or steps down voltage. Transformers are crucial for power transmission as they enable increasing voltage for transport over long distances to reduce losses, before lowering it for end use. Their applications include electricity distribution, electronics, and regulating voltage.