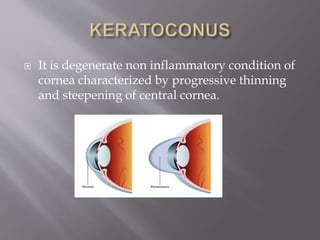
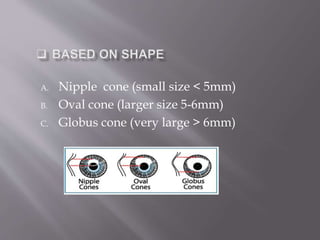
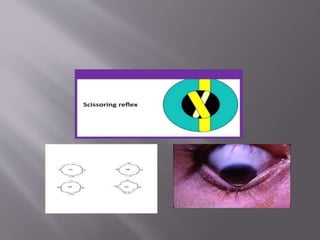
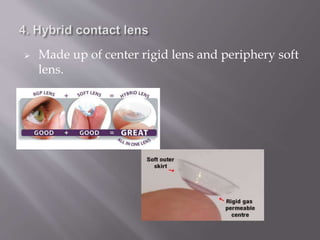
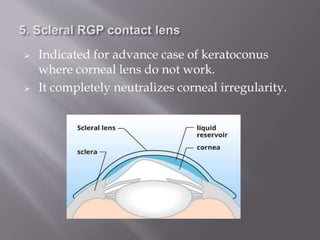
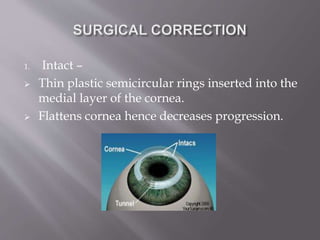
This document discusses keratoconus, a degenerative condition characterized by thinning and steepening of the central cornea. It classifies keratoconus by severity from mild to severe based on diopter measurement. Symptoms include defective vision, photophobia, ghost images, and halos around lights. Diagnosis involves examination findings like scissor reflex on retinoscopy, irregular circles on Placido disc, and thinning/bulging of the central cornea on corneal topography. Management includes spectacle correction for mild cases, rigid contact lenses fitted with light central touch, and intracorneal ring segments or collagen cross-linking to halt progression. Surgery like lamellar or penetrating keratoplasty is indicated for