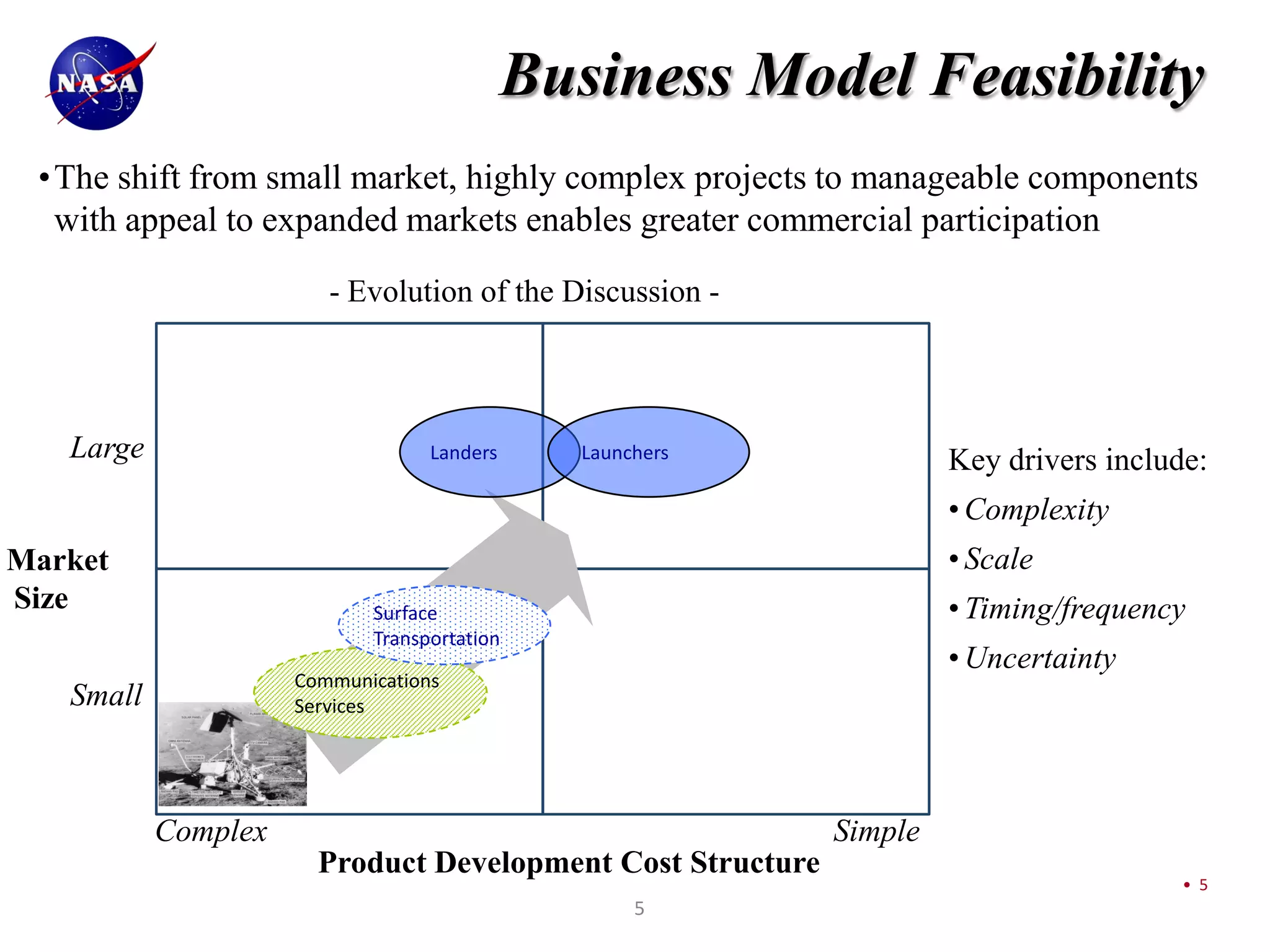
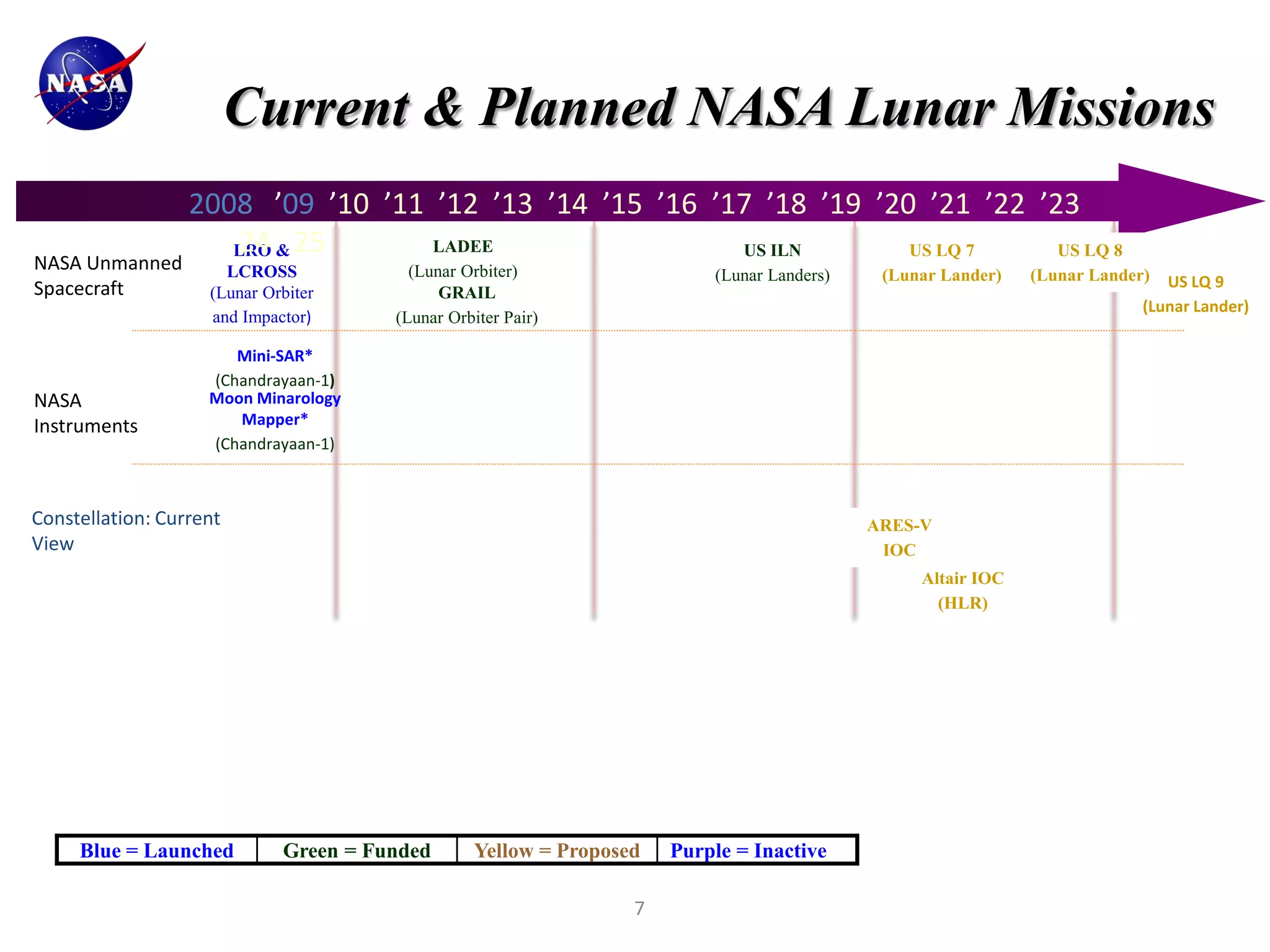
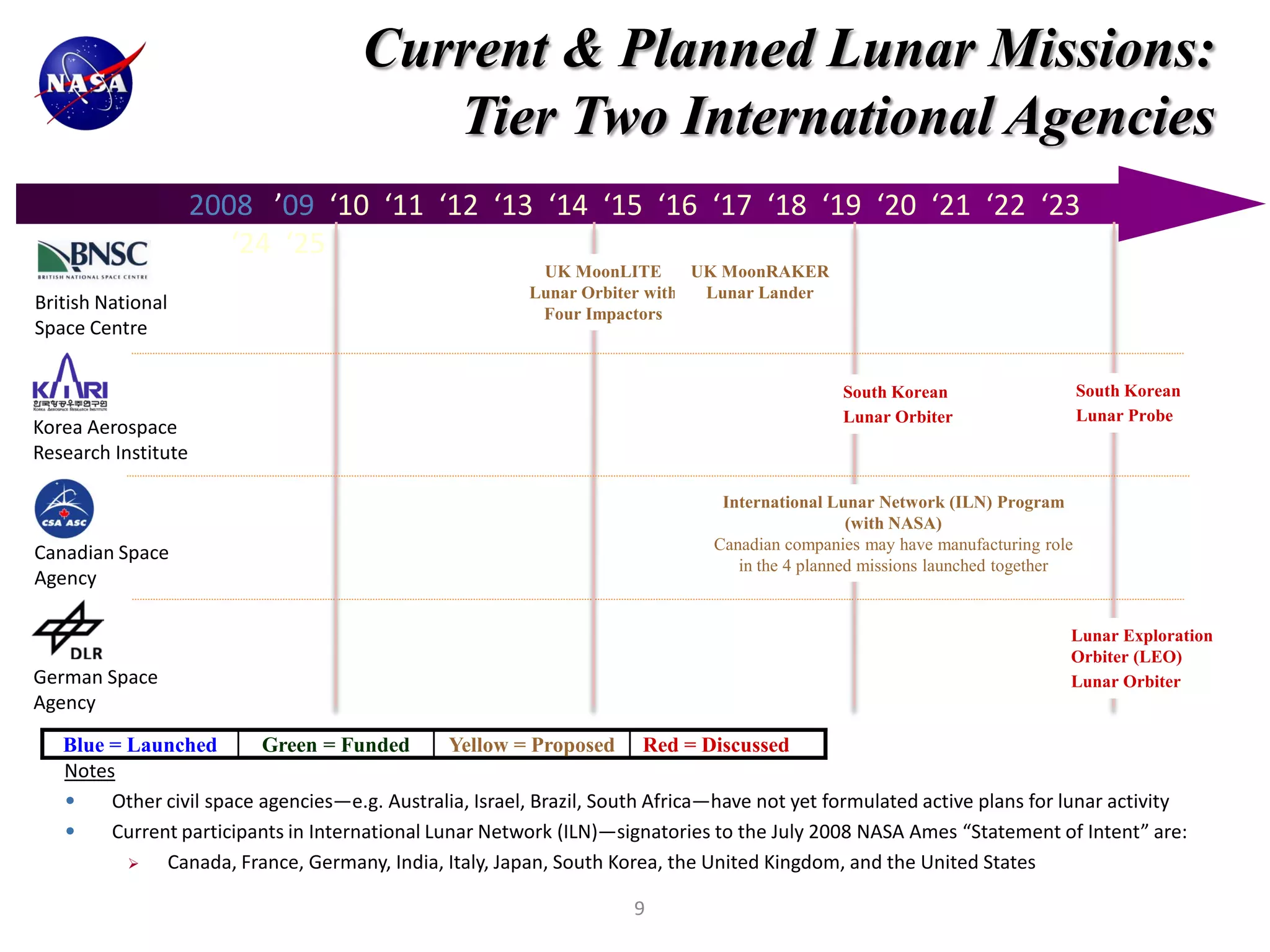
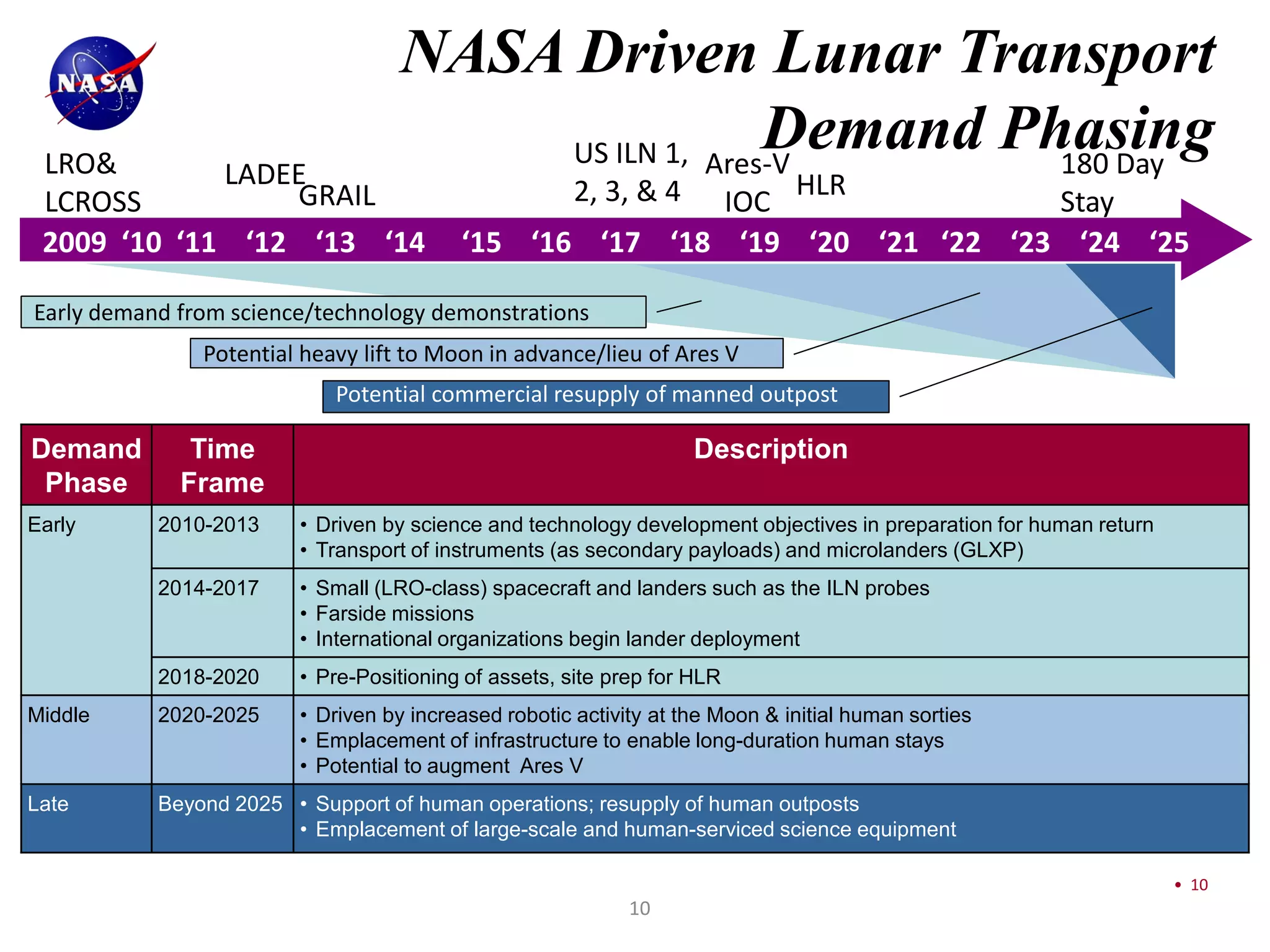
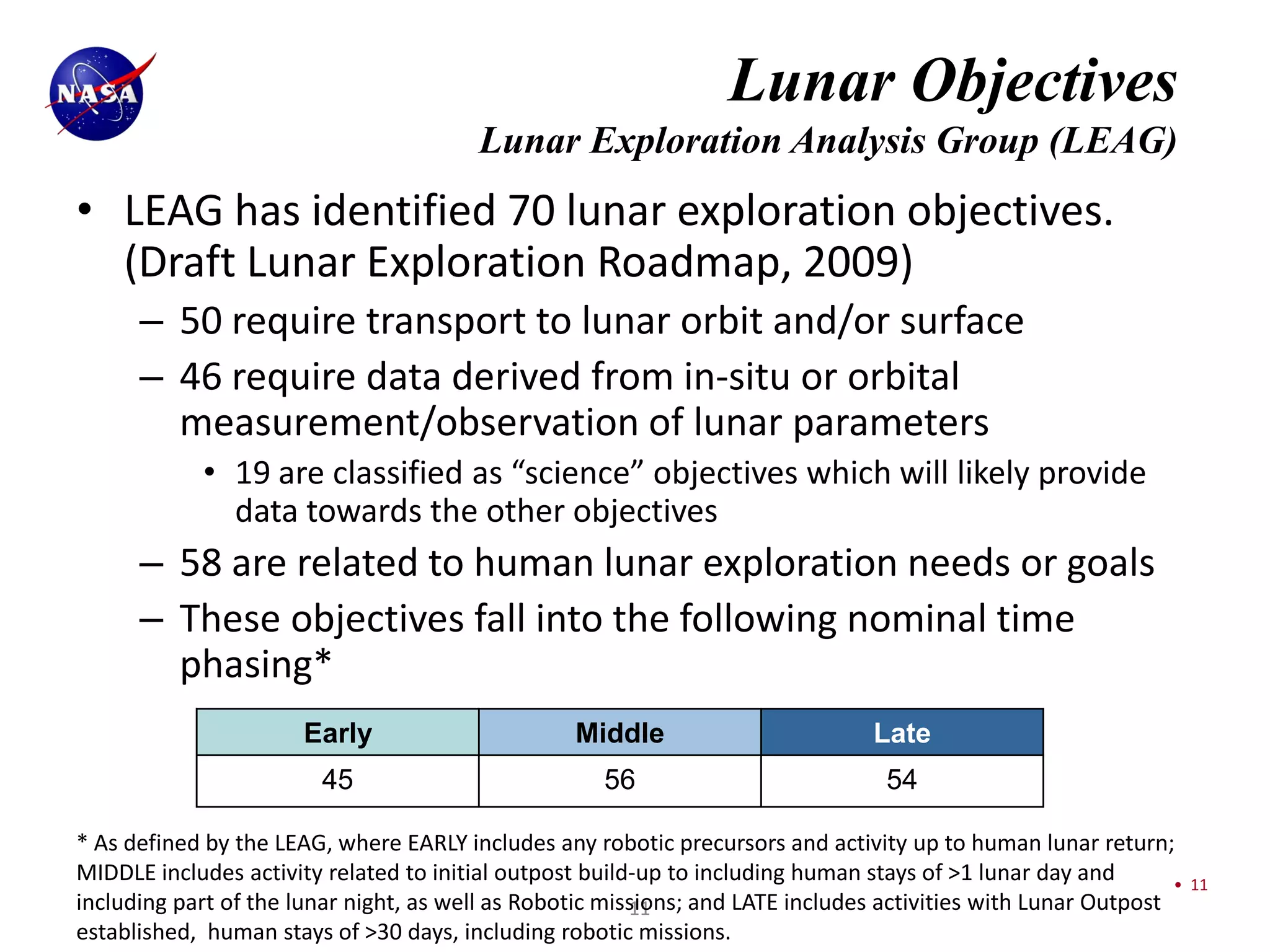
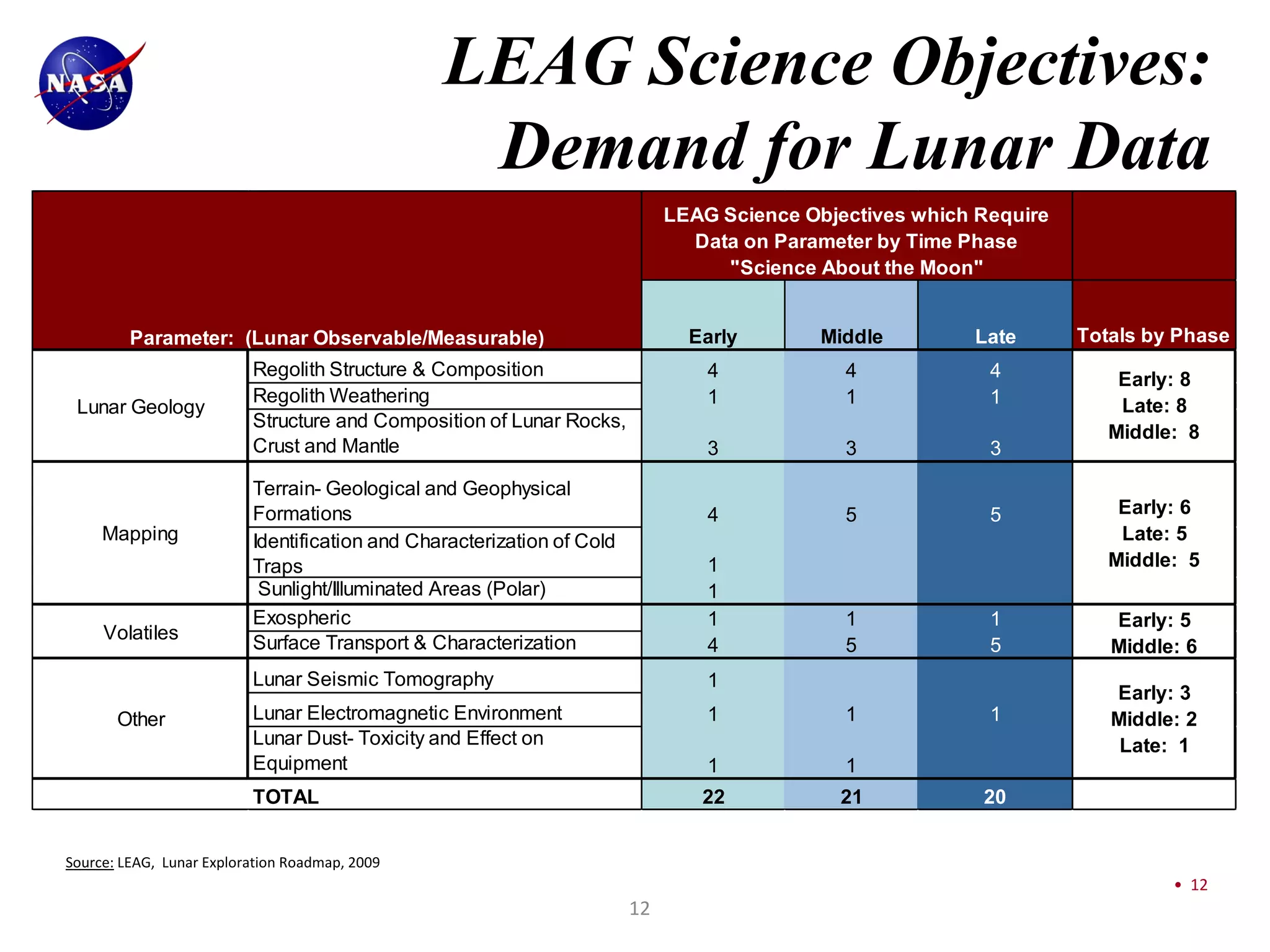
This document discusses NASA's vision for lunar exploration and utilization through commercial partnerships. It outlines three main goals: 1) Using the moon for exploration and technology development to support missions to Mars; 2) Conducting scientific observations of Earth and space from the moon; 3) Advancing scientific understanding of the moon's composition and evolution. The document proposes obtaining lunar data for NASA through commercial landers and payloads beginning in late 2011 to reduce costs compared to dedicated NASA missions. It discusses how commercial models with fixed-price contracts can increase private sector involvement compared to traditional cost-plus contracts. Finally, it provides charts summarizing current and planned lunar missions by NASA and other international space agencies.