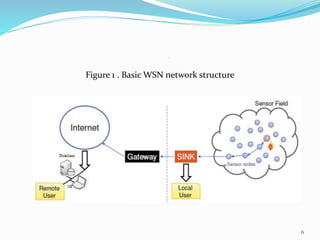
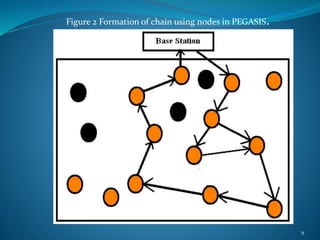
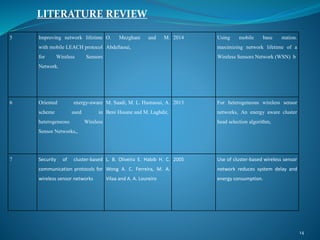
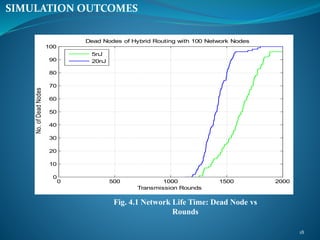
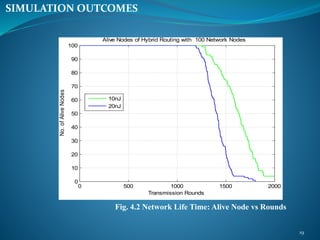
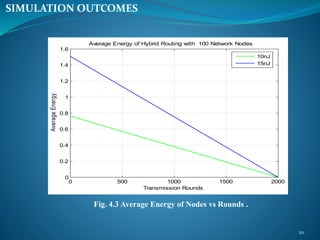
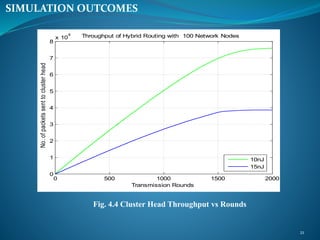
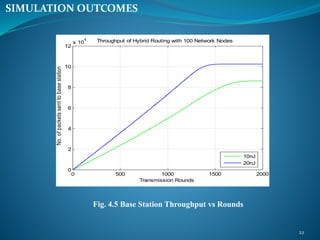
The document summarizes a student's M. Tech thesis project on improving routing protocols in wireless sensor networks. It begins with an objective to develop a hybrid routing protocol combining features of PEGASIS and LEACH to increase network lifetime. It then reviews related work on routing protocols and energy efficiency. The proposed methodology describes a hybrid protocol that selects cluster heads probabilistically like LEACH while forming chains to route data like PEGASIS. Simulation results show the hybrid protocol increases network lifetime to over 2000 rounds compared to 2000 rounds for previous work. The conclusion is that lower cluster head election probabilities in the hybrid protocol extend network lifetime. Future work could analyze different network parameters.