The document summarizes key aspects of the Juvenile Justice Act of 2015 in India. Some of the main points covered include:
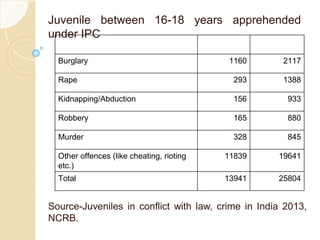
1. It classifies crimes committed by juveniles (those below 18 years of age) as petty, serious or heinous crimes. For heinous crimes allegedly committed by 16-18 year olds, a board will assess if it was committed as a child or adult.
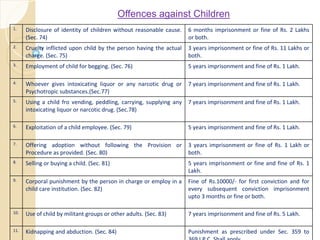
2. It establishes Child Welfare Committees and Special Juvenile Police Units to deal with matters related to children in conflict with law or in need of care and protection.
3. The legislation outlines various orders that can be passed for children in conflict with law, such as community service,