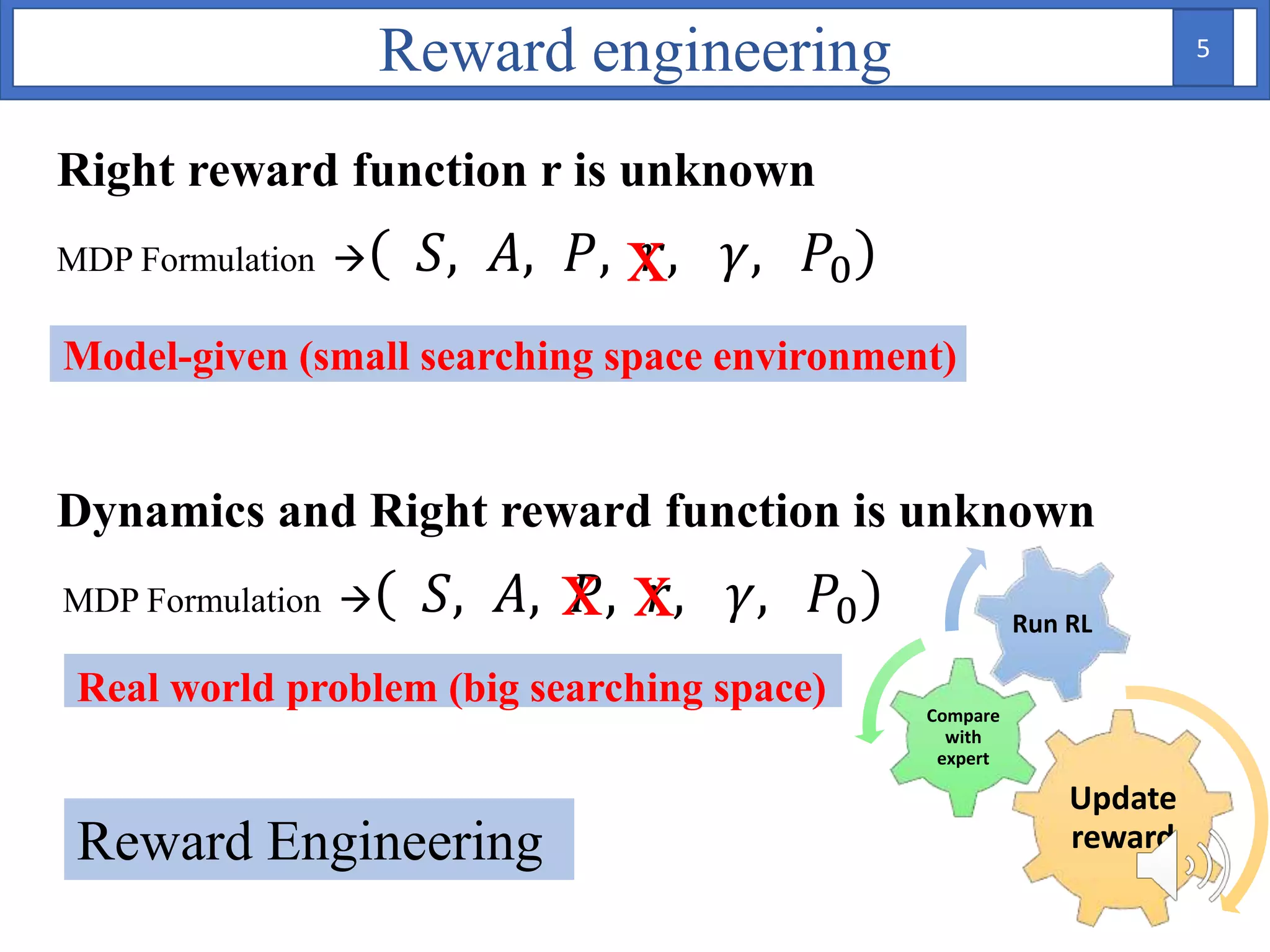
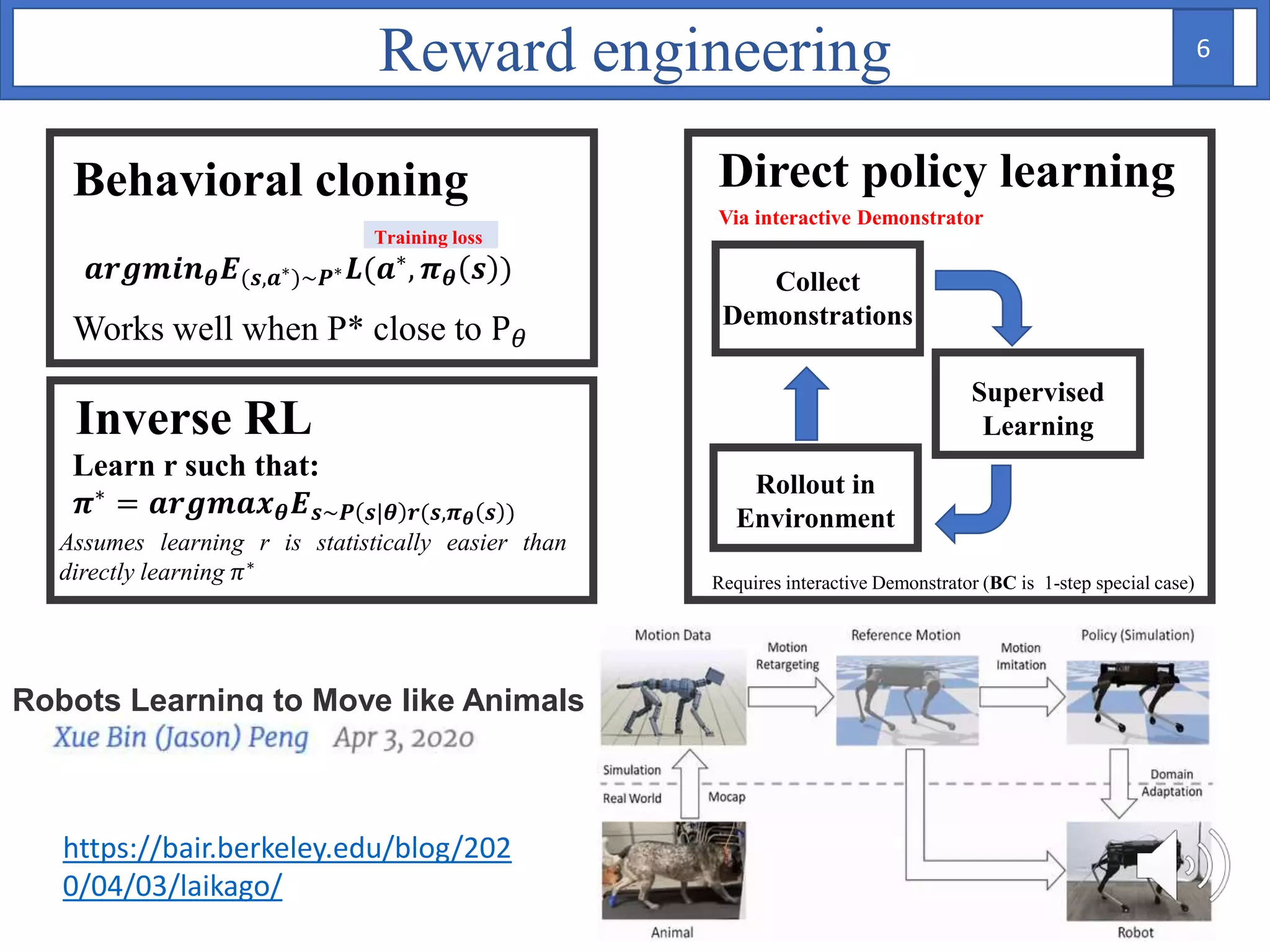
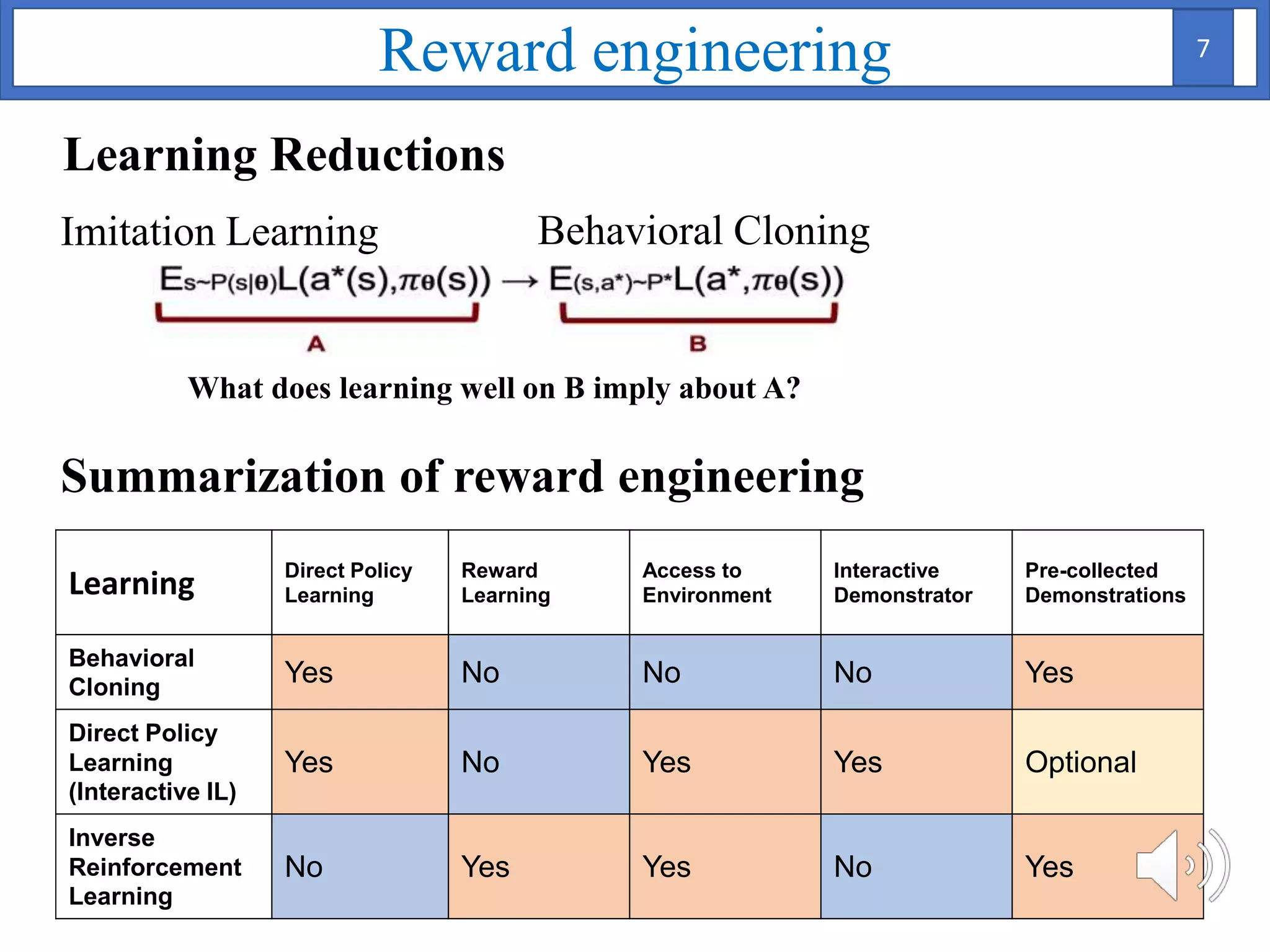
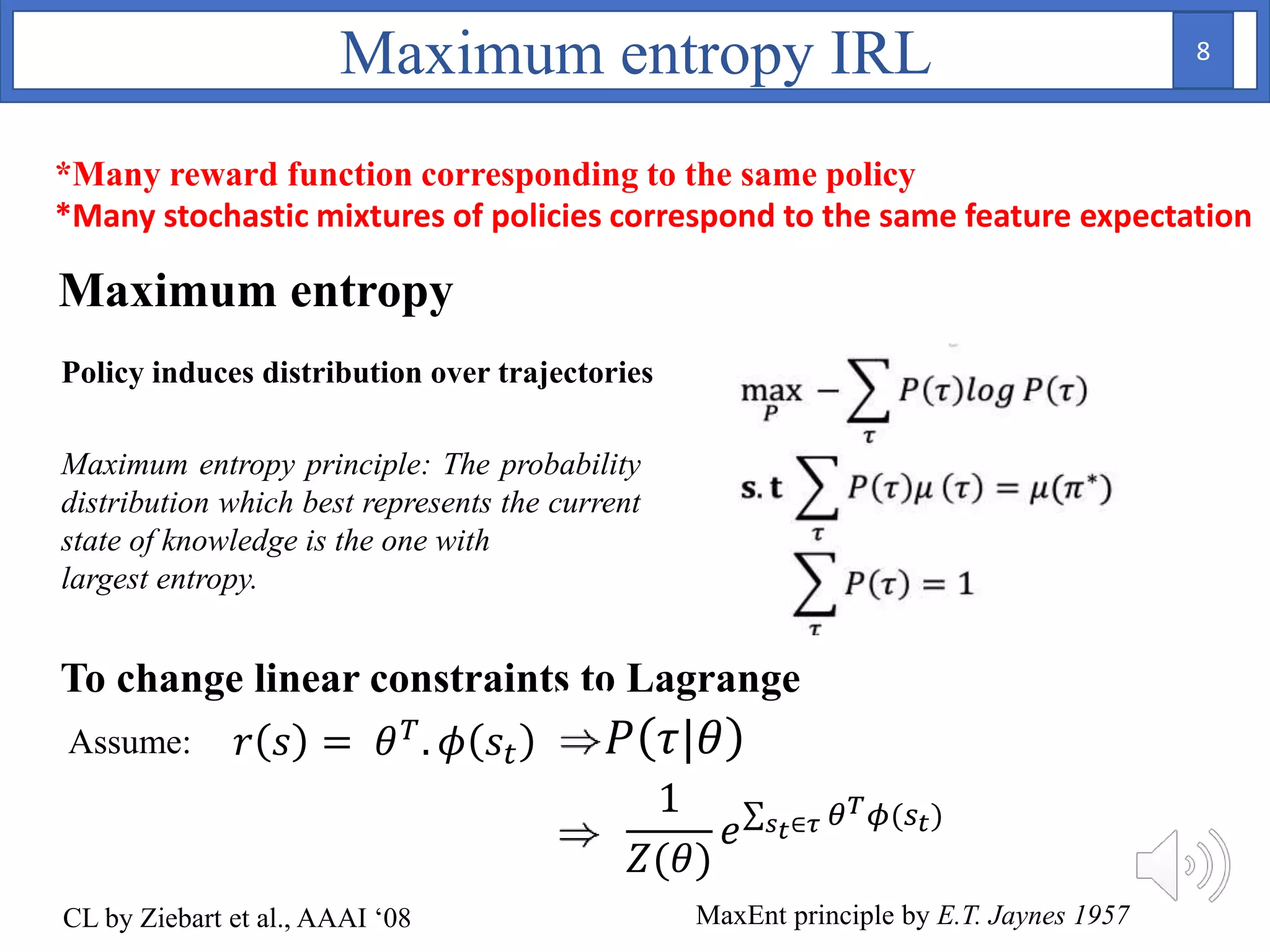
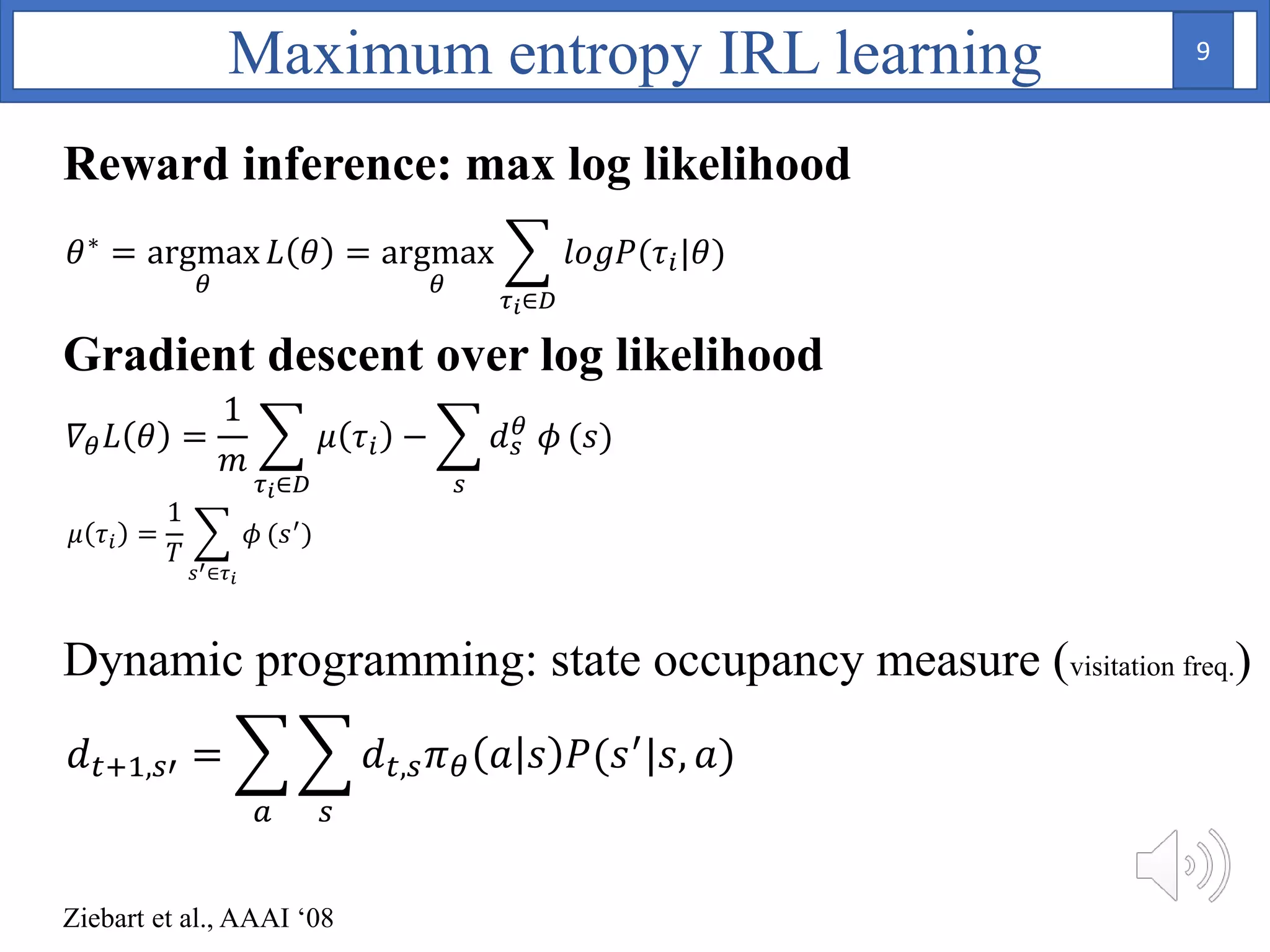
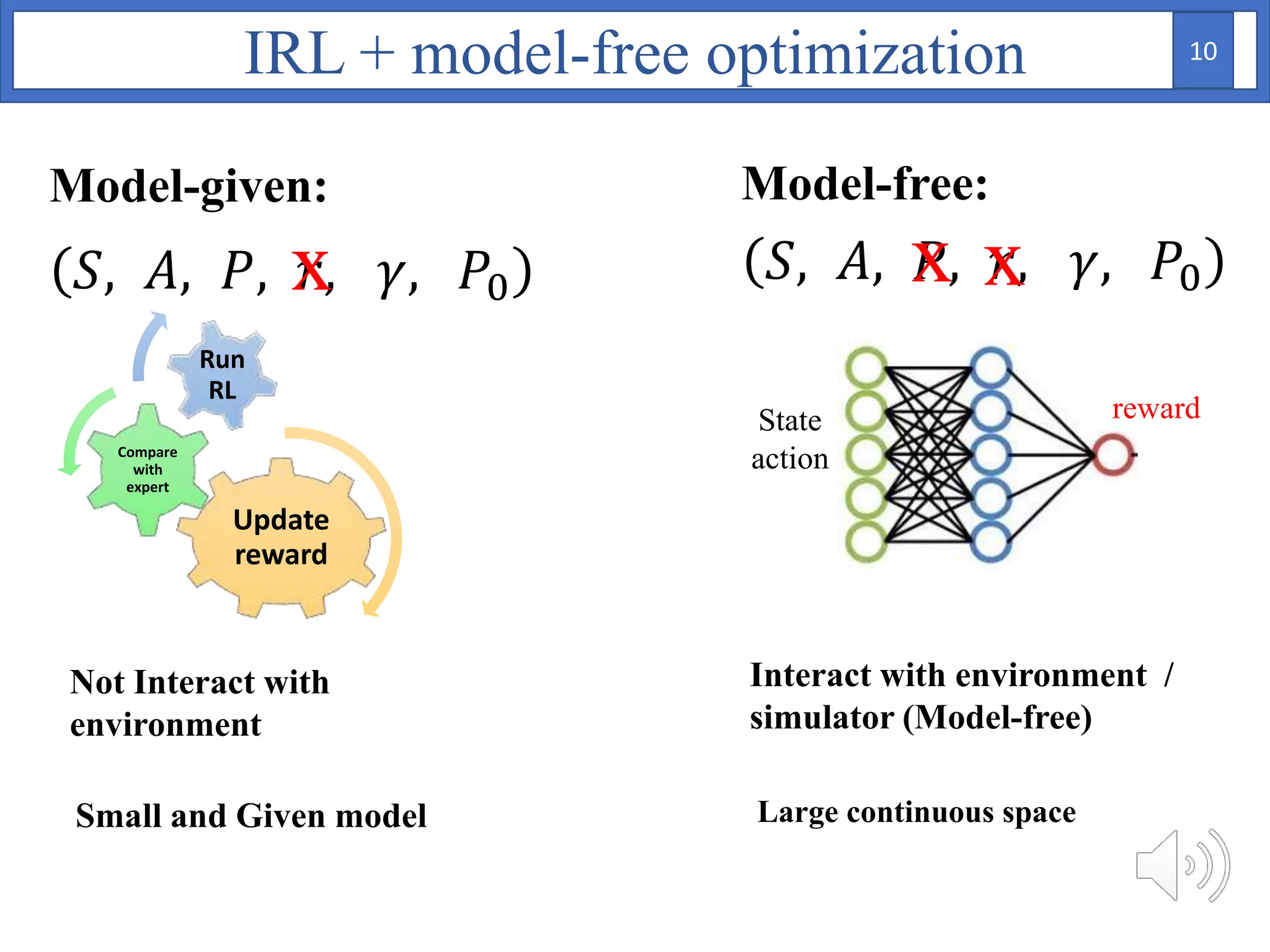
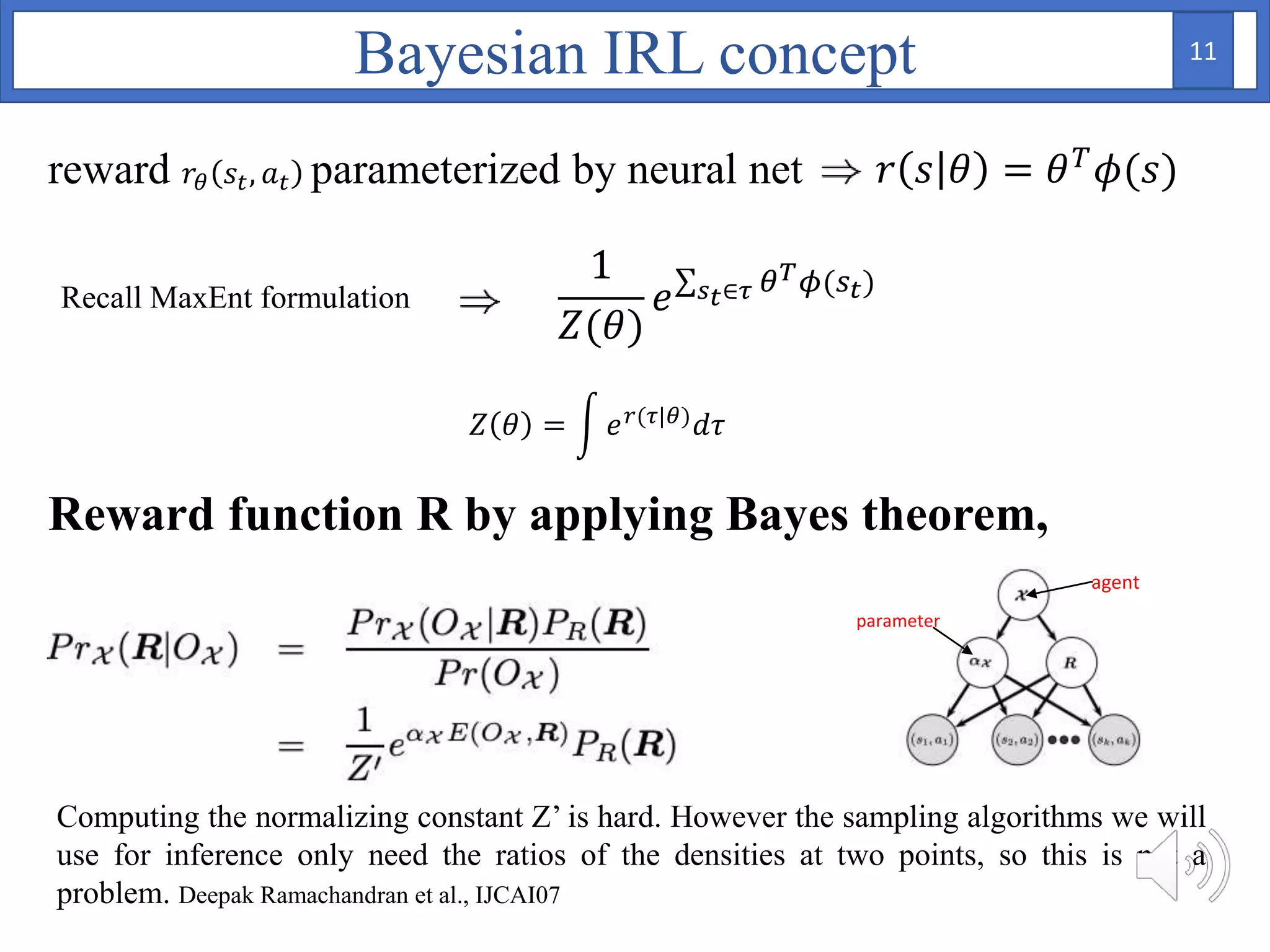
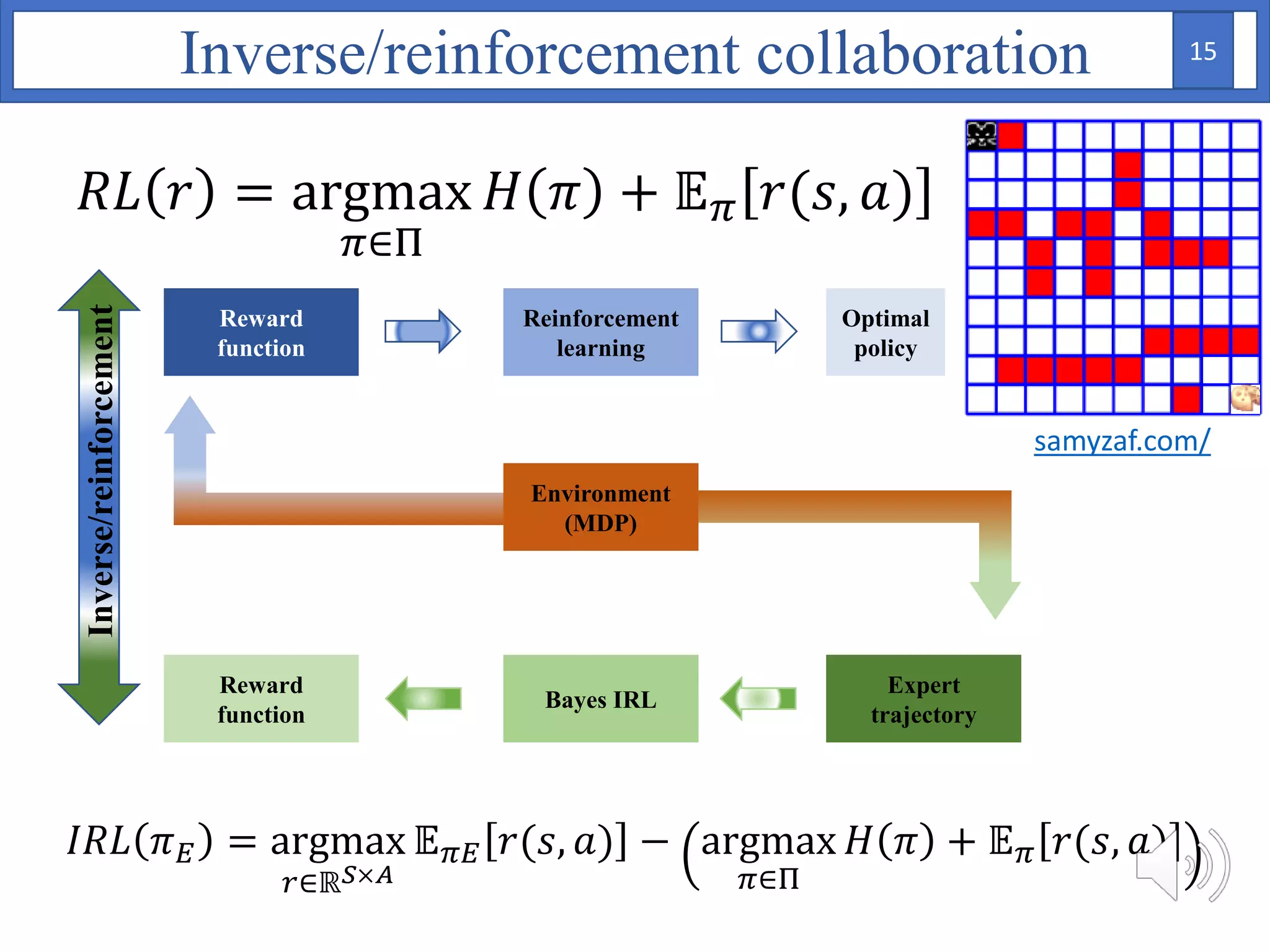
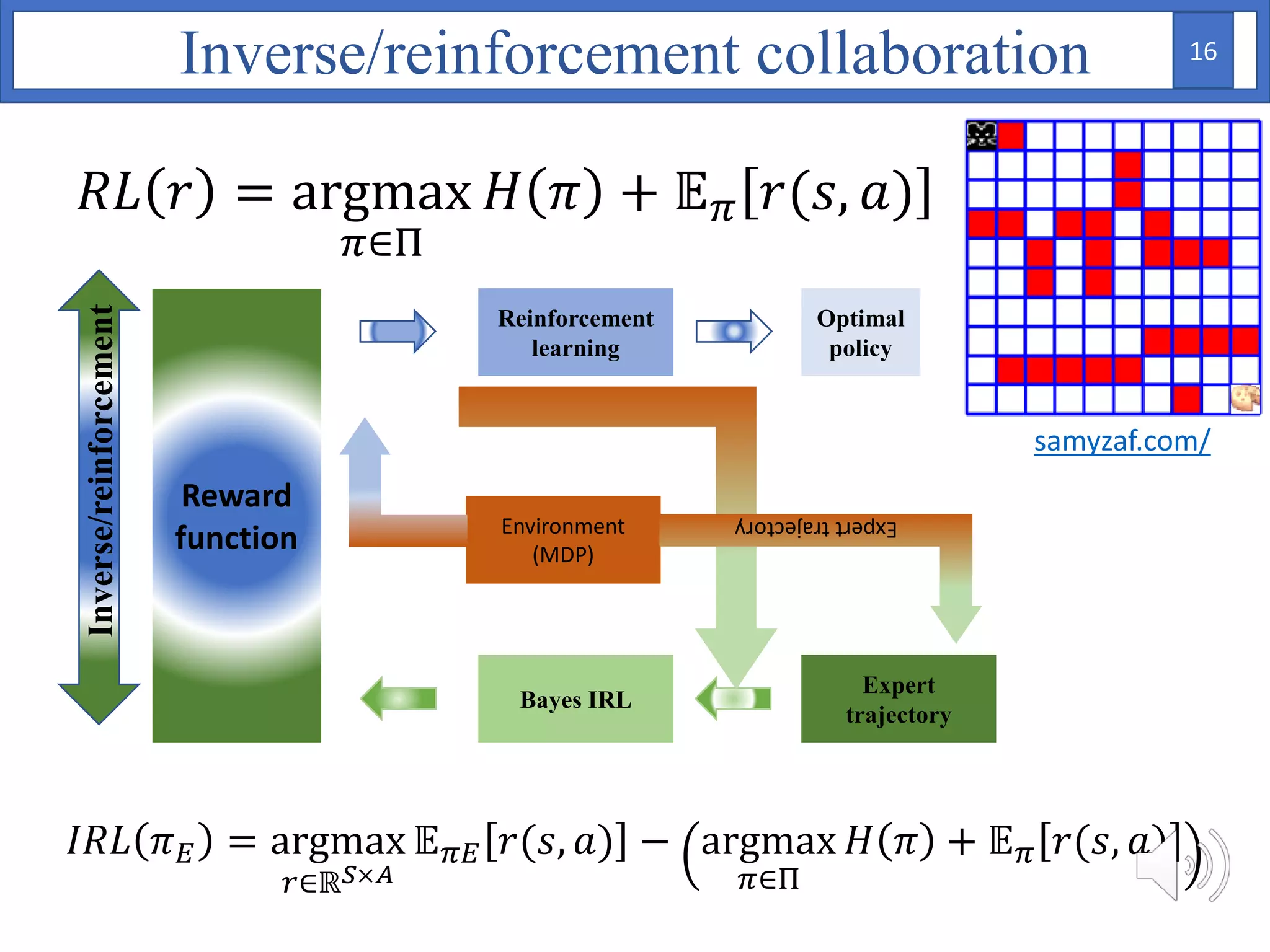
1. The document proposes using Bayesian inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) with neural networks for anomaly prediction detection. It formulates the problem as a Markov decision process to learn the reward function from expert trajectories.
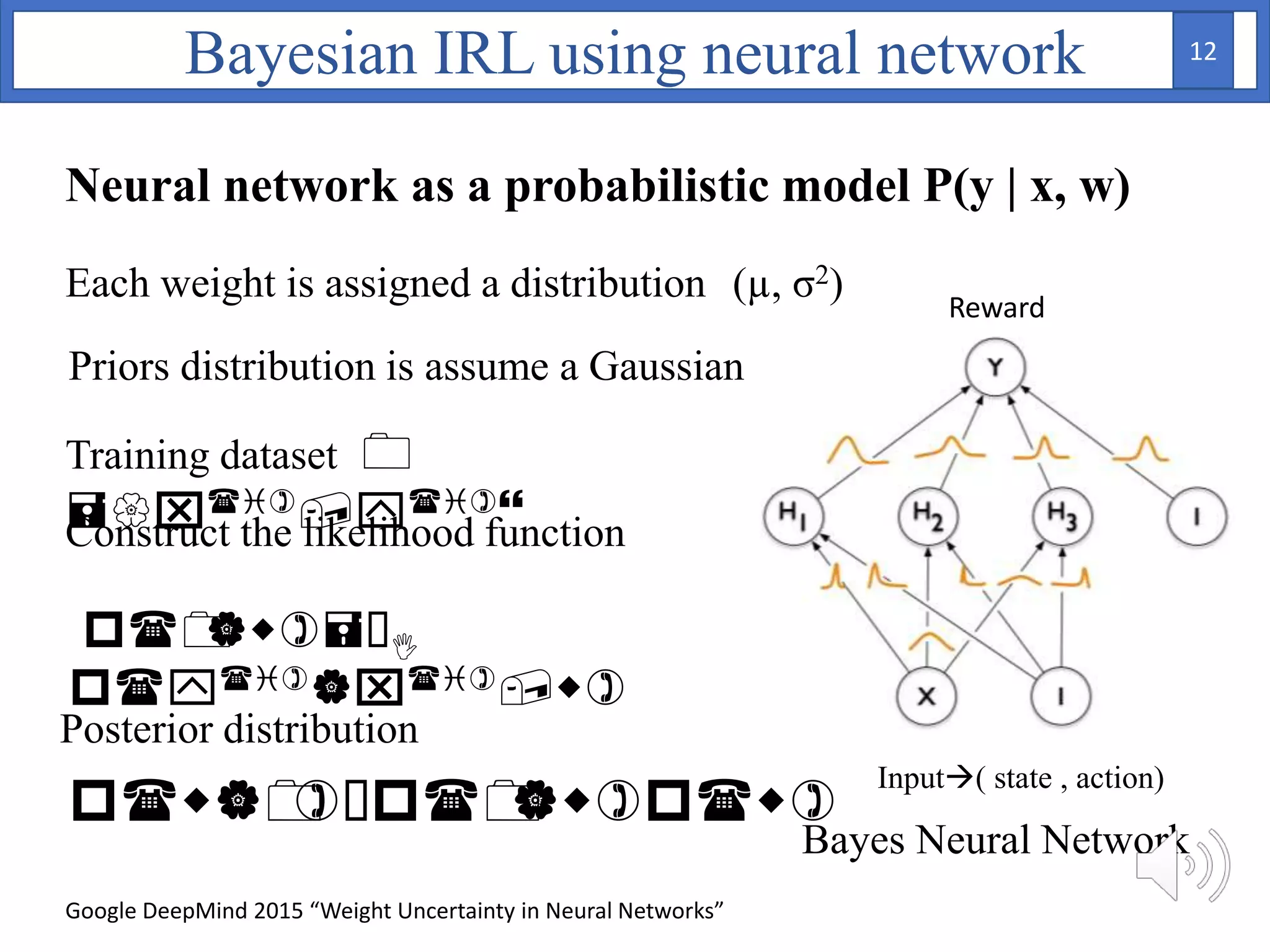
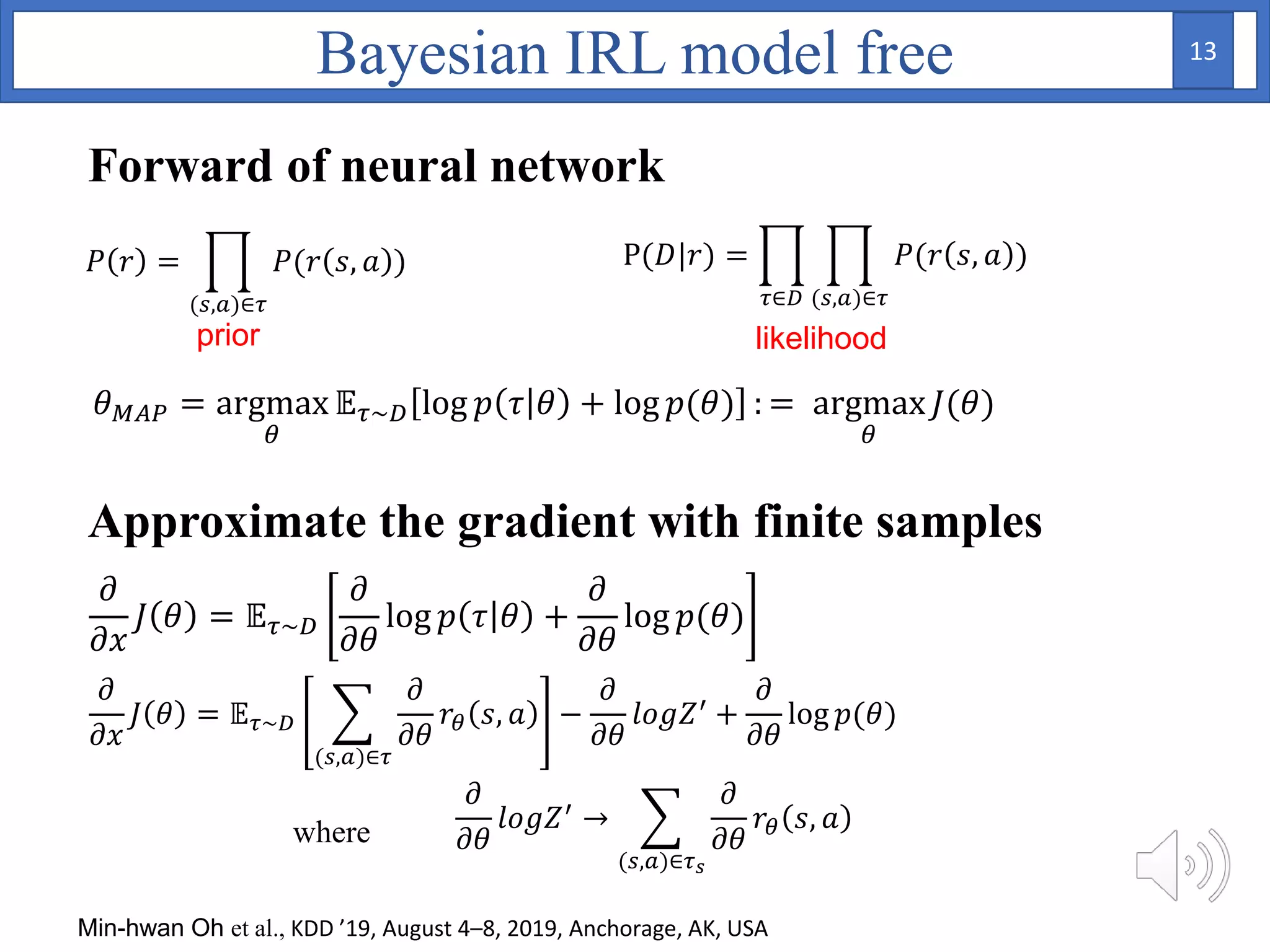
2. A Bayesian neural network is used to model the reward function, with weights assigned prior distributions. The model is trained by maximizing the log likelihood of the training data to find the posterior distribution over weights.
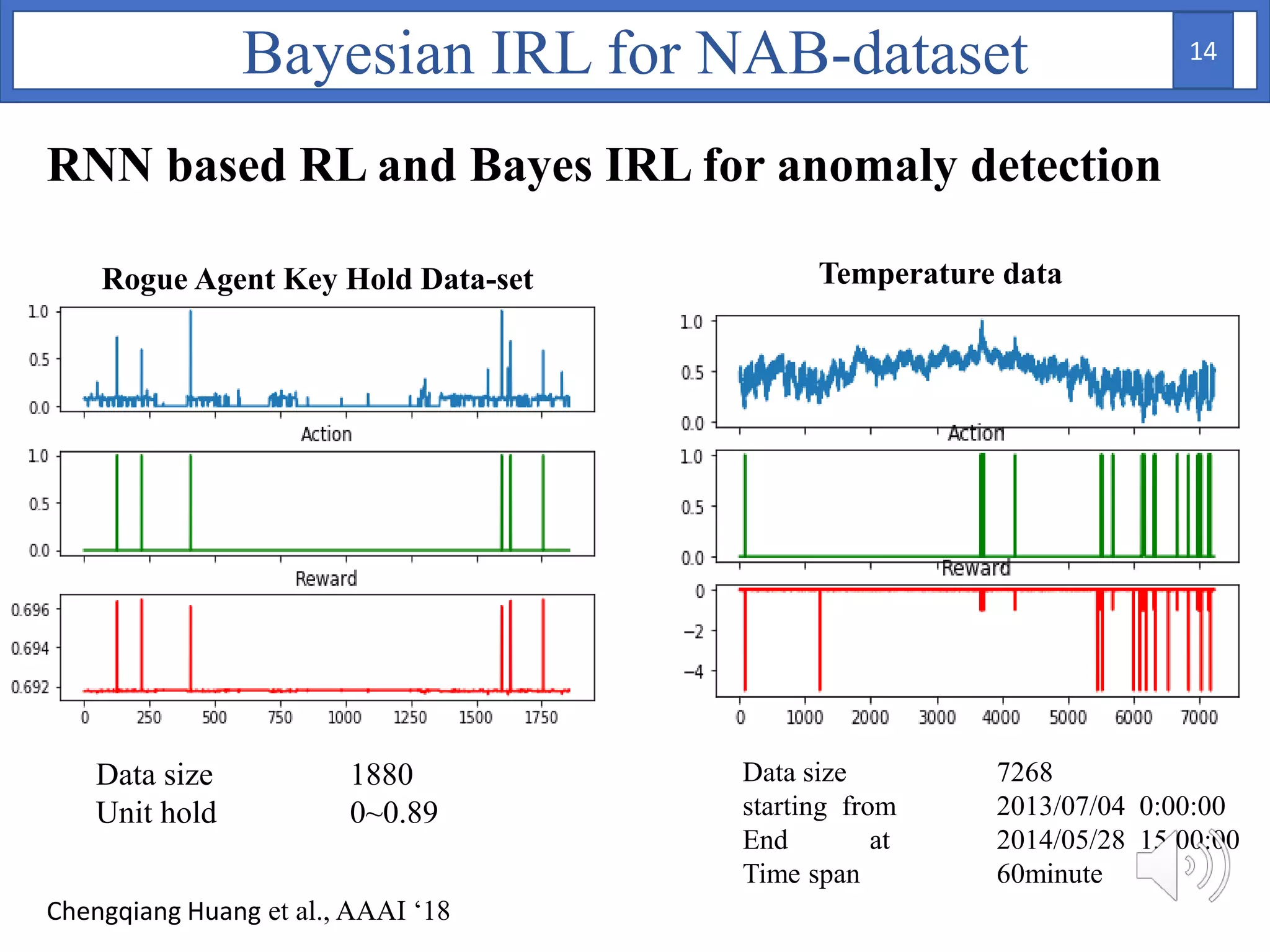
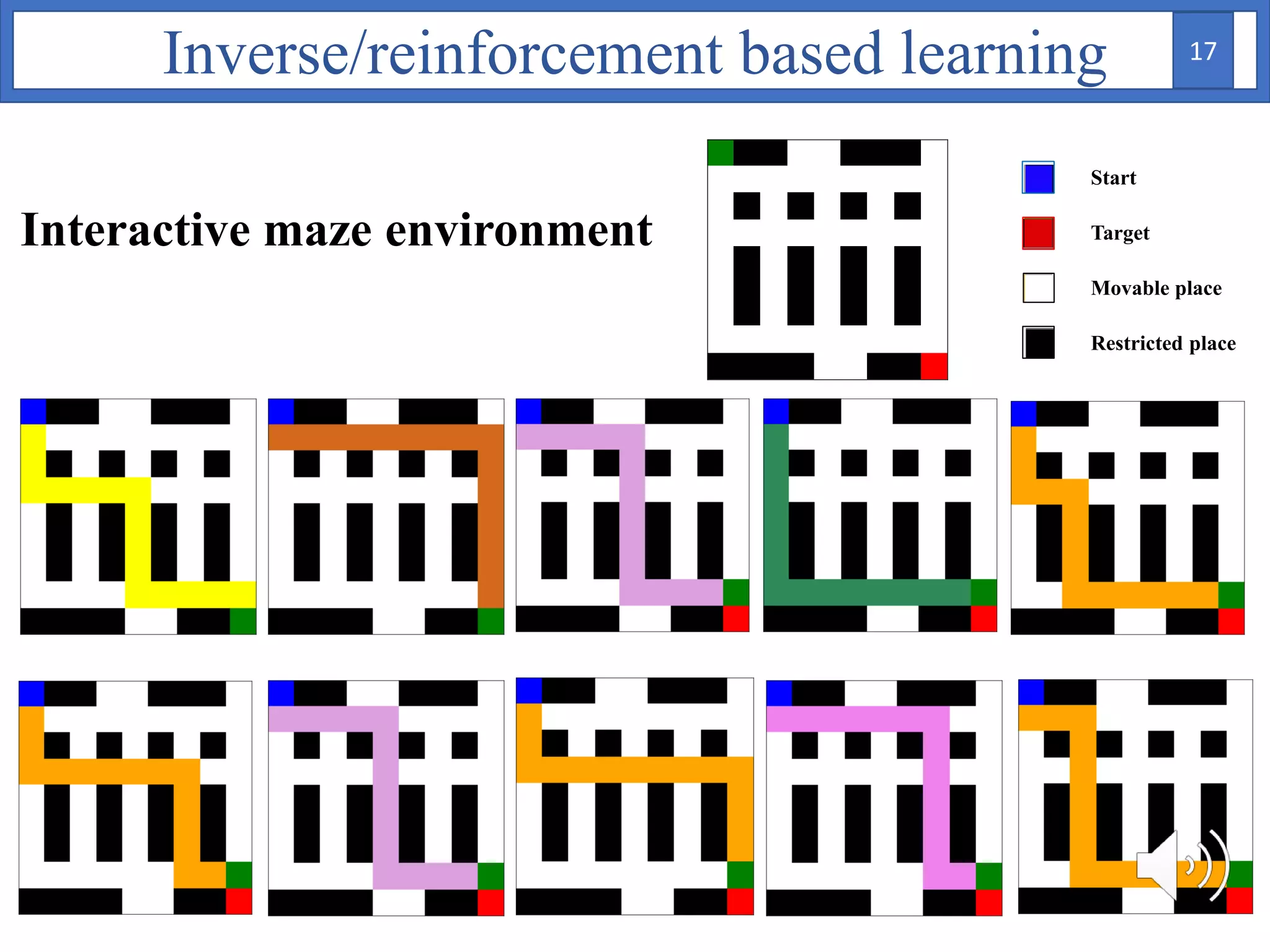
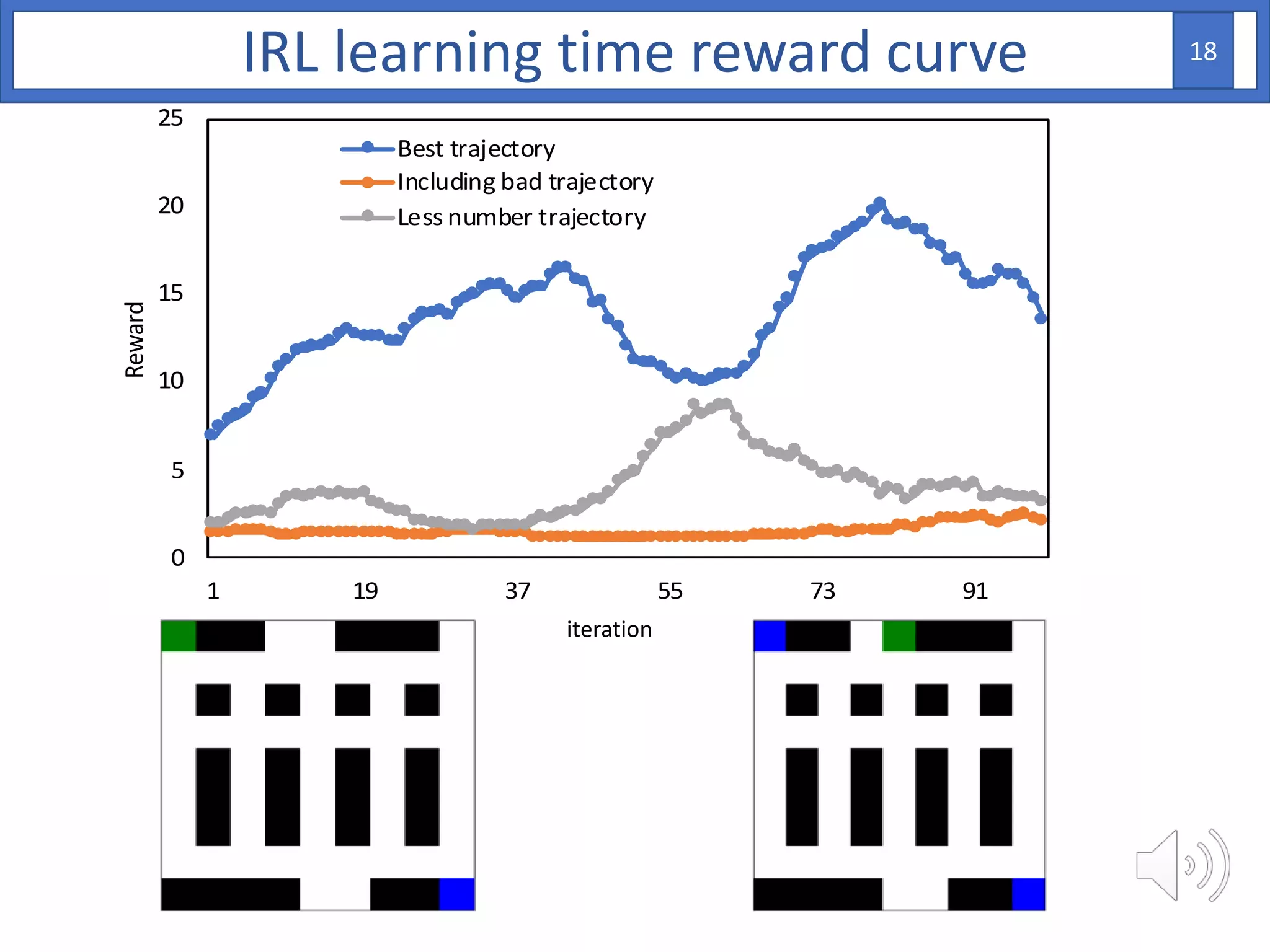
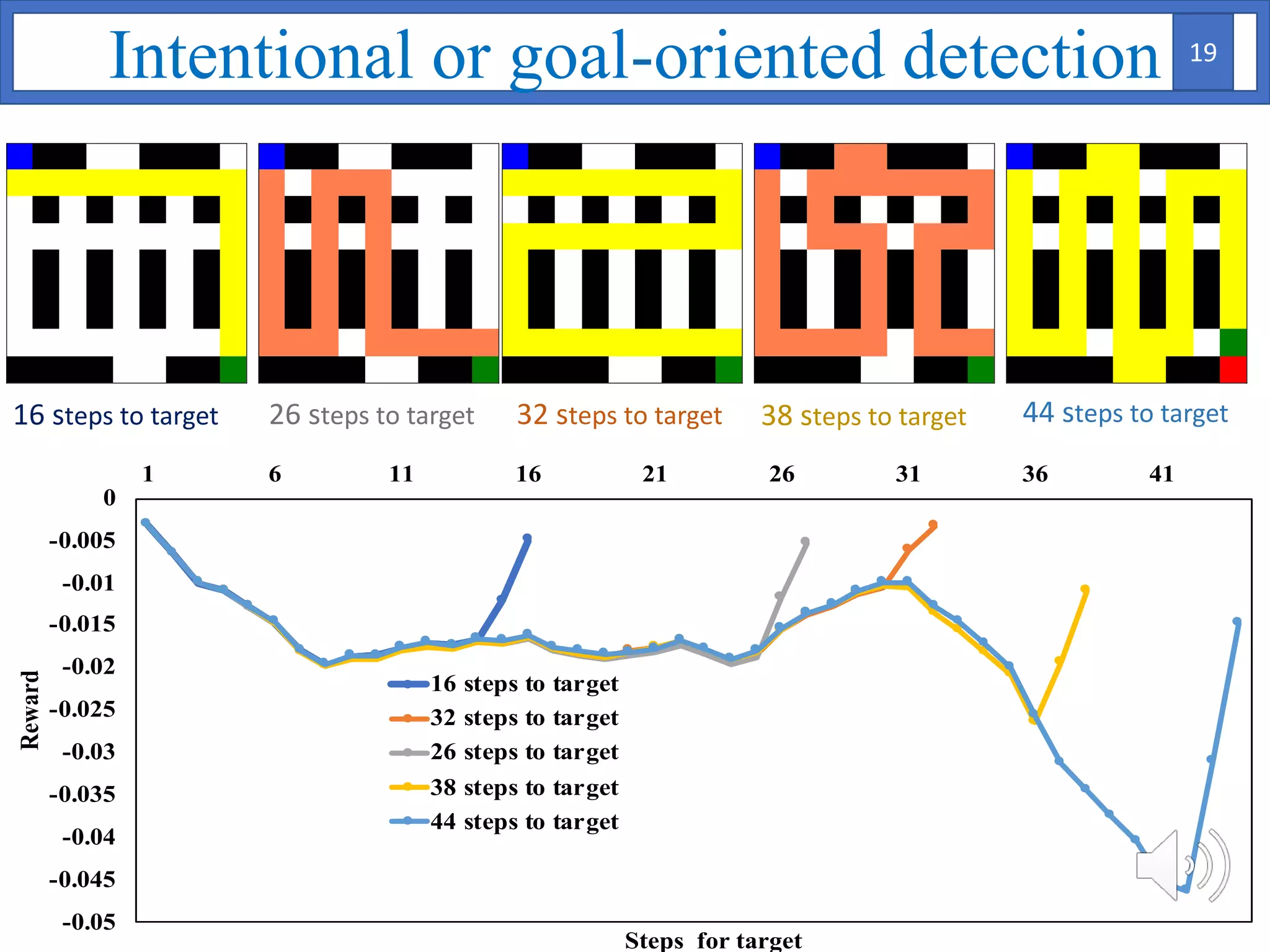
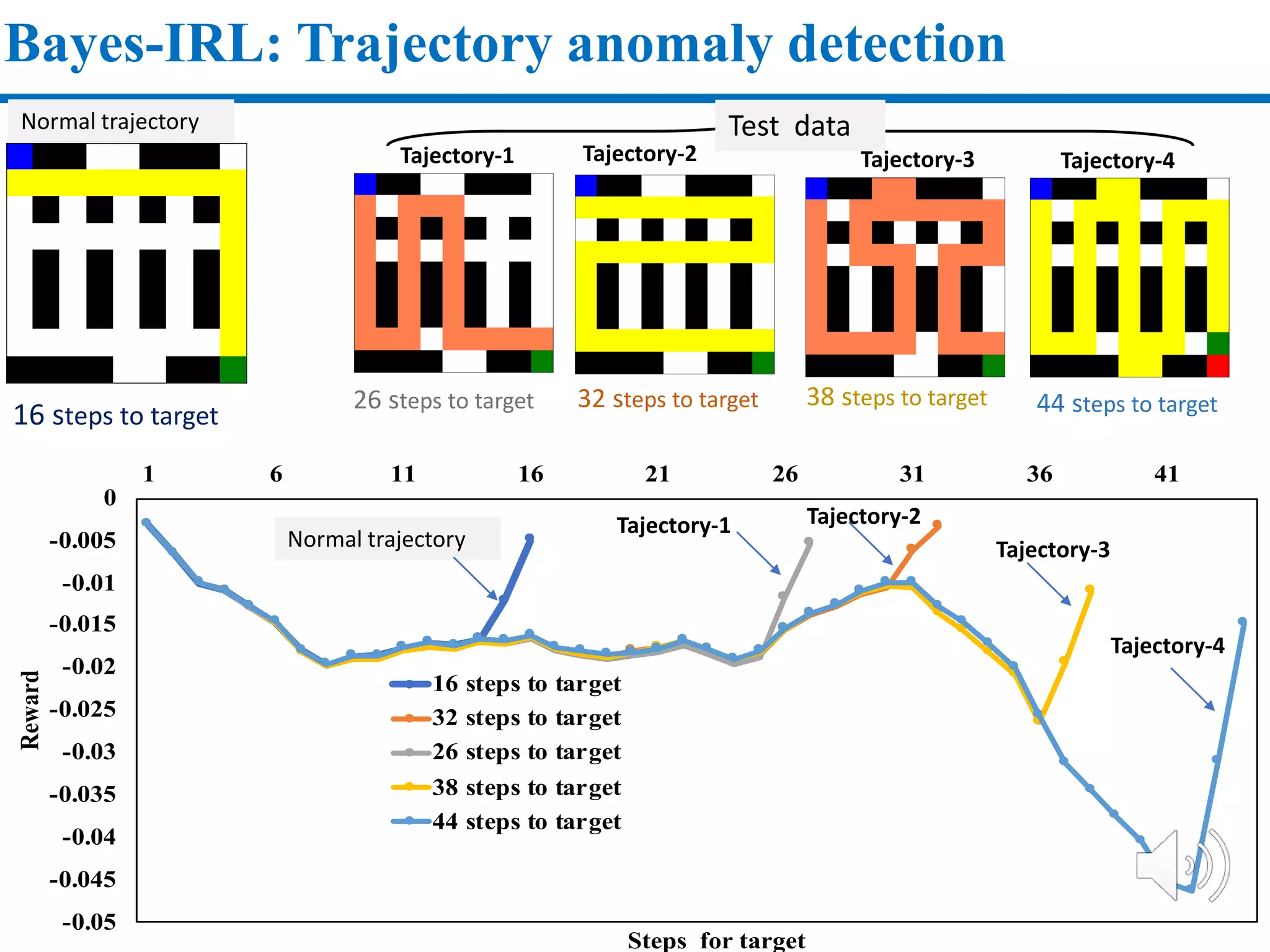
3. The approach is evaluated on temperature anomaly detection and maze navigation tasks. Bayesian IRL is able to distinguish normal trajectories from anomalous ones in test data for intentional anomaly detection.

![MDP Formulation 𝑆, 𝐴, 𝑃, 𝑟, 𝛾, 𝑃0
max
𝜋∈Π
𝑉(𝜋) ≜ max
𝜋∈Π
𝔼 𝜋[𝑟 𝑠, 𝑎 ] = max
𝜋∈Π
𝔼 𝑠0~𝑝0
𝑡=0
∞
𝛾 𝑡 𝑟 𝑠𝑡, 𝑎 𝑡 |𝜋
S : state r : reward function 𝑃0: starting state distribution
A : action P : model 𝛾 : discount factor
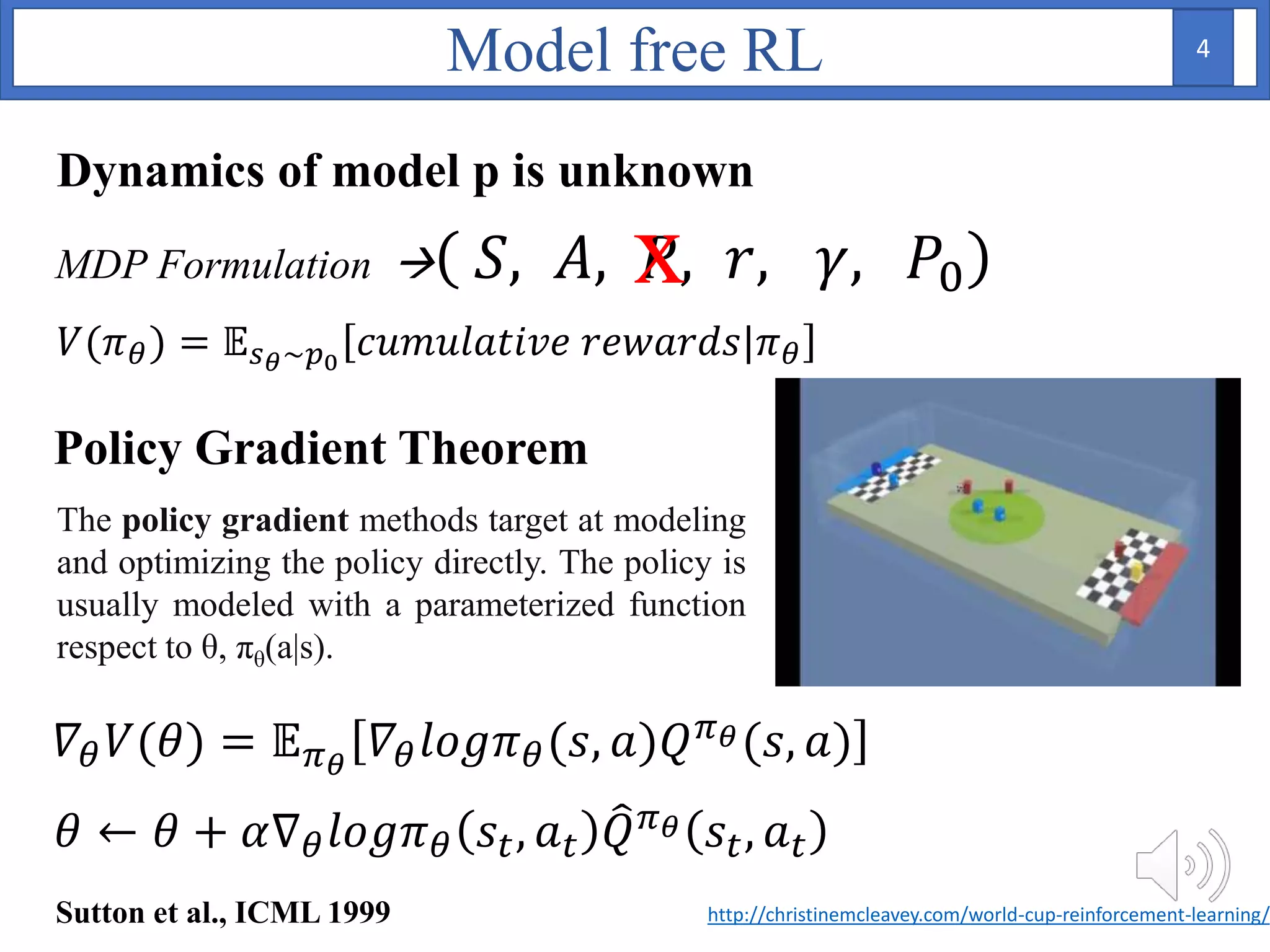
Goal: maximize cumulative rewards
Fully specified MDP: value iteration & policy iteration
RL for fully specified MDP 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jsaifinalfinalfinal-200611123701/75/Jsai-final-final-final-4-2048.jpg)