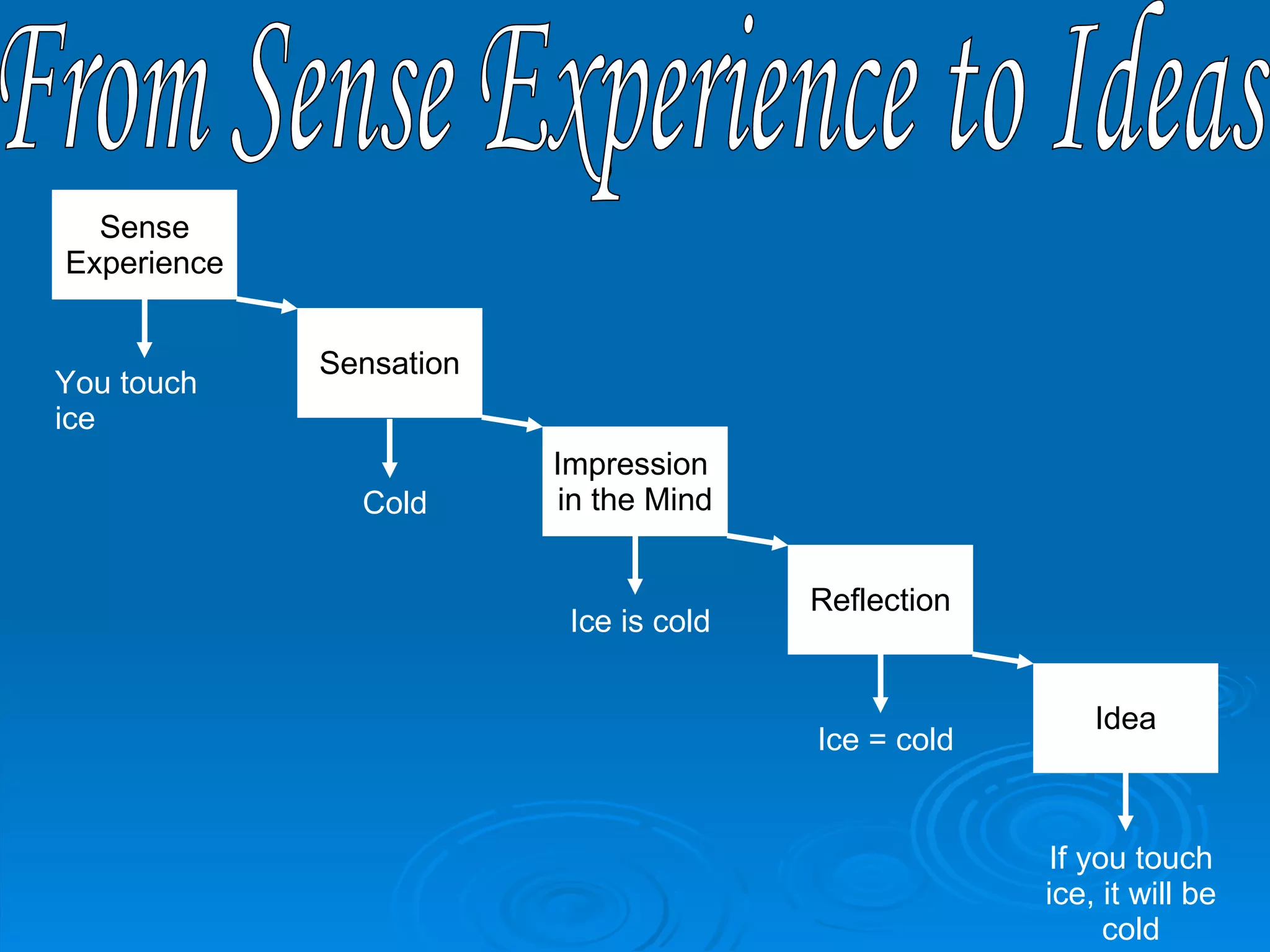
John Locke was an empiricist who believed that all knowledge comes from experience. He disagreed with Descartes' view that humans are born with innate ideas, and instead agreed with Aristotle that humans are born with a blank slate. According to Locke, we gain simple ideas from our senses, and complex ideas are combinations of simple ideas. He distinguished between primary qualities like shape and size that are objective, and secondary qualities like color and taste that are subjective. Our sense experiences lead to sensations and impressions in the mind, which we then reflect on to form ideas.