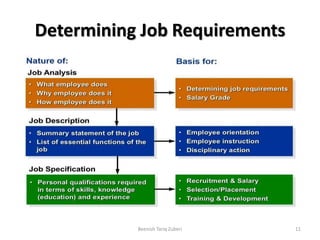
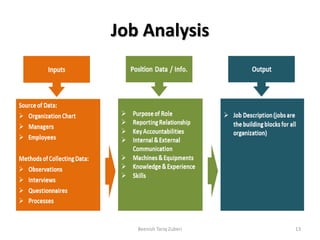
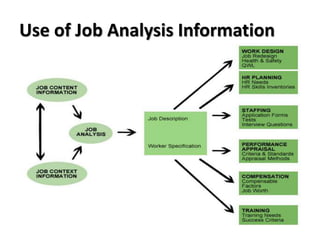
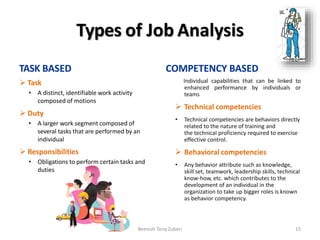
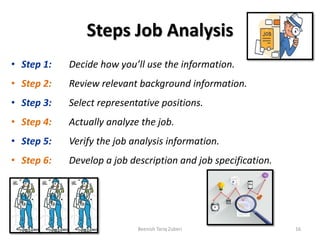
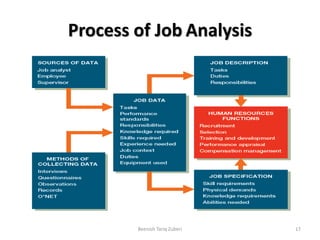
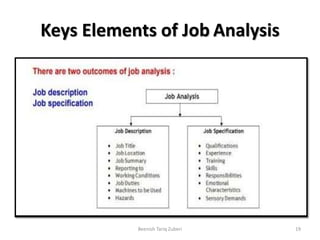
The document outlines key concepts in job analysis, including definitions of jobs, positions, job families, and job vacancies, as well as methods for analyzing jobs and designing job specifications and descriptions. It discusses recruitment strategies, differentiating between internal and external recruitment, along with their respective advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it details the steps involved in conducting job analysis, highlighting the importance of understanding job duties, skill requirements, and how this analysis contributes to enhancing organizational performance.