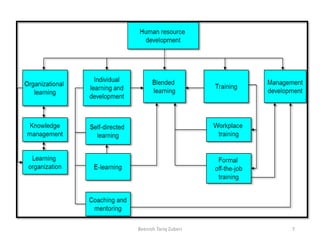
The document outlines the concept of Human Resource Development (HRD) as introduced by Leonard Nadler in 1969, emphasizing the importance of investing in human potential and development. It describes HRD's goals, processes, and the frameworks for training, organizational development, and career development essential for enhancing employee performance and organizational effectiveness. Additionally, it highlights the challenges faced by HRD, including workforce changes and the need for lifelong learning.