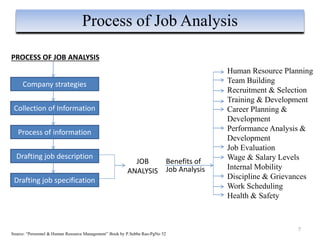
The document outlines the concepts of human resource planning (HRP), job analysis, and job descriptions/specifications, emphasizing their importance in aligning human resources with organizational goals. It details processes for collecting job analysis data, defining job descriptions and specifications, and the strategic planning of HR needs to address future requirements and employee management. Additionally, it discusses the benefits, objectives, and methodologies of HRP, including the necessity for effective implementation to adapt to organizational changes and enhance productivity.