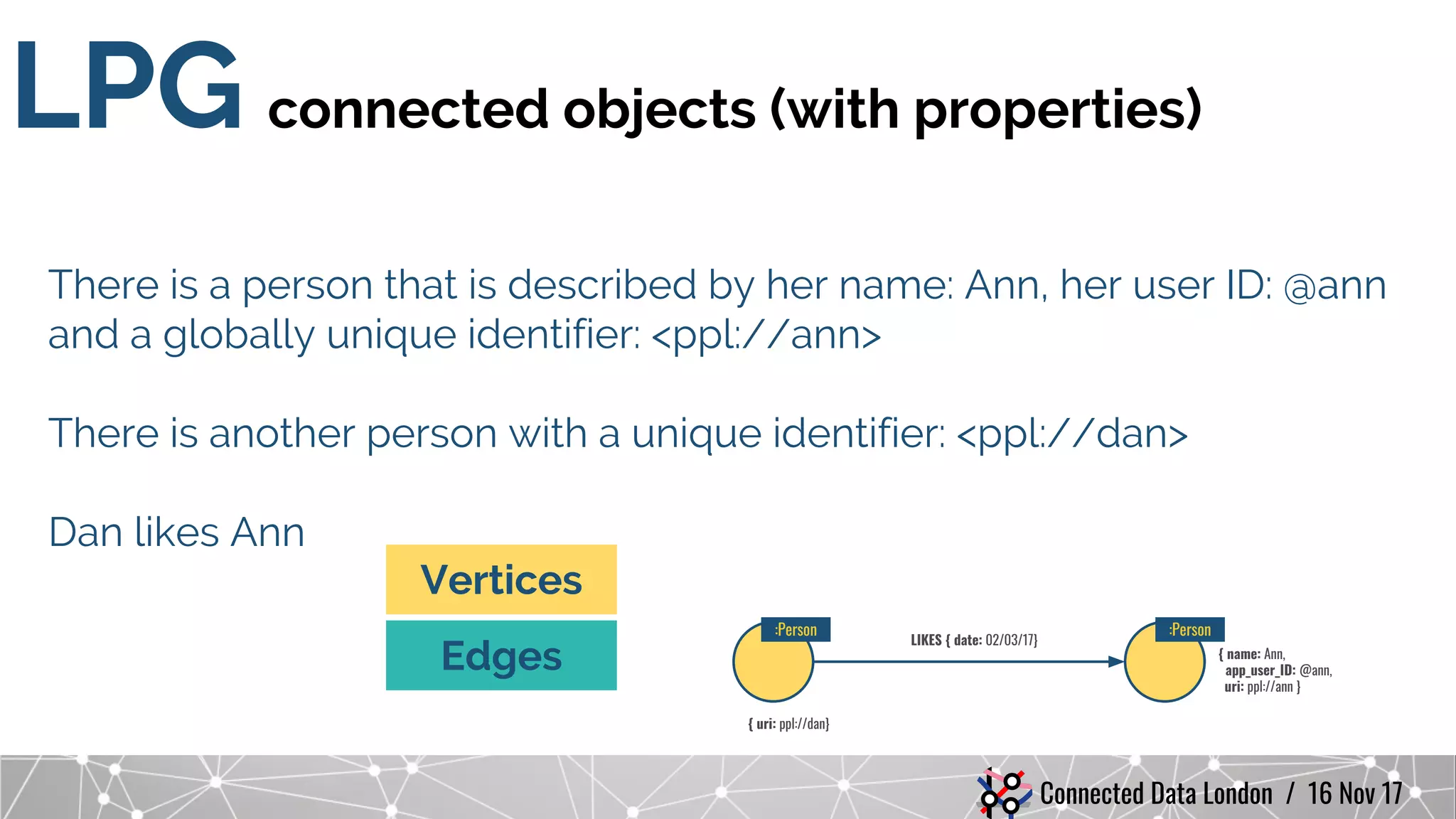
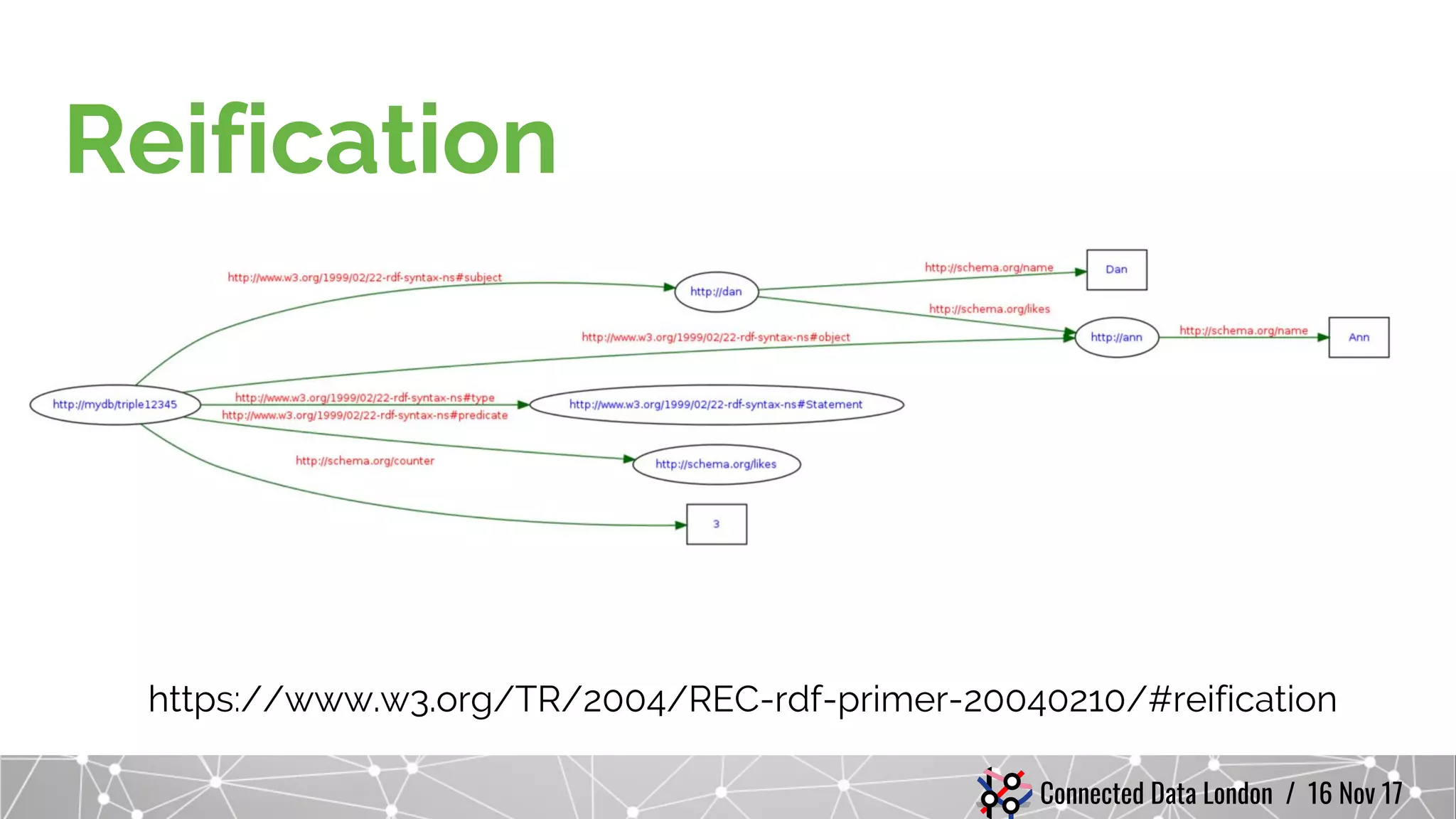
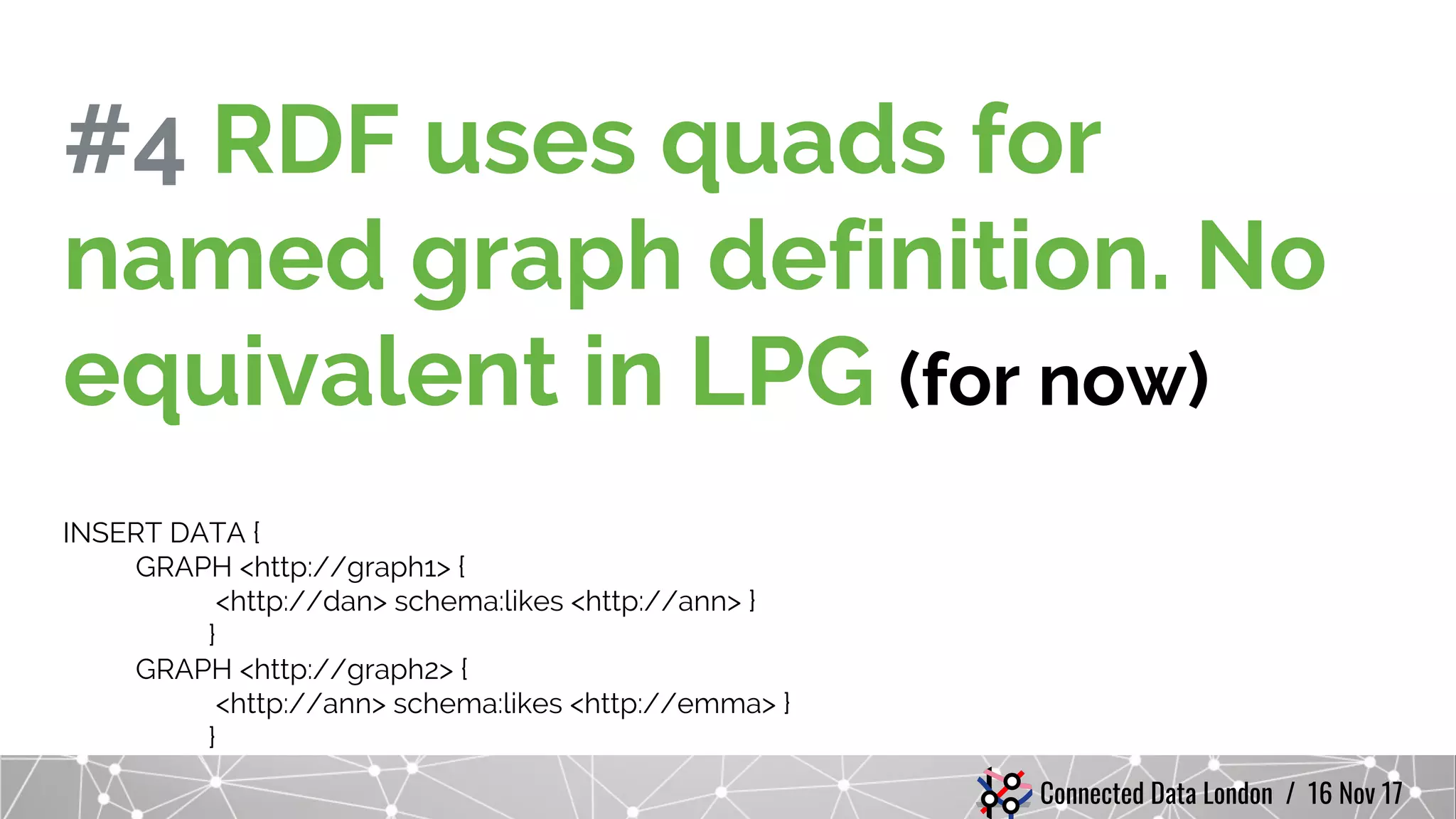
The document compares RDF and property graph data models. It discusses how RDF does not uniquely identify relationships between resources and cannot qualify relationships with attributes. Property graphs in LPGs can model these with unique relationship IDs and edge properties. It also notes RDF uses quads for named graphs while property graphs currently have no equivalent, and that RDF supports multivalued properties using lists while property graphs use arrays. The document cautions comparing RDF and graph databases by focusing on their underlying models rather than specific storage implementations. It demonstrates RDF can be modeled in a native graph database and that semantics are defined through optional rules and vocabularies rather than being inherent to RDF.


















![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
Query: Who likes this person named Ann?
Cypher
MATCH (who)-[:LIKES]->(a:Person)
WHERE a.name CONTAINS ‘Ann’
RETURN who
SPARQL
prefix ms: <http://myschma.me/>
prefix rdf: <http://www[...]#>
SELECT ?who
{
?a rdf:type ms:Person .
?a ms:name ?asName .
FILTER regex(?asName,’Ann’)
?who ms:likes ?a .
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-24-2048.jpg)



![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
LPG in Neo4j
Dan has liked Ann three times
CREATE (d {name: "Dan"})-[:LIKES]->(a {name: "Ann"})
CREATE (d)-[:LIKES]->(a)
CREATE (d)-[:LIKES]->(a)
MATCH (d {name: "Dan"})-[l:LIKES]->(a {name:
"Ann"})
RETURN COUNT(l)
╒════════╕
│COUNT(l)│
╞════════╡
│3 │
└────────┘
{ name: Dan }
{ name: Ann }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-29-2048.jpg)

![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
LPG in Neo4j
Connection NYC-SFO is $300 and 4100Km
CREATE ( {name: "NYC"})-[:CONNECTION { distanceKm : 4100, costUSD: 300}]->( {name: "SFO"})
MATCH ( {name: "NYC"})-[c:CONNECTION]->( {name: "SFO"})
RETURN c.costUSD, c.distanceKm
╒═════════╤════════════╕
│c.costUSD│c.distanceKm│
╞═════════╪════════════╡
│300 │4100 │
└─────────┴────────────┘
{ name: NYC }
{ name: SFO }
{ distanceKm: 4100,
costUSD: 300 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-31-2048.jpg)





![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
Example
The genre of this album is Jazz, or
more precisely Orchestral Jazz.
prefix schema: <http://schema.org/>
INSERT DATA {
<http://g.co/kg/m/0567wt>
schema:name "Sketches of Spain" ;
schema:genre "Jazz", "Orchestral Jazz" . }
}
CREATE (s:Album { name: "Sketches of Spain",
genre: [ "Jazz","Orchestral Jazz" ] } )
{ name: Sketches of Spain
genre: [ Jazz, Orchestral Jazz ] }
CypherSPARQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-38-2048.jpg)




![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
#2 The semantics of semantics
“suppose you entered the details ‘Philip owns a Mercedes’
where ‘Philip’ and ‘Mercedes’ are both entities and ‘owns’
is a relationship. An inference engine can deduce that
Mercedes in this instance is a car whereas in ‘Juan is
married to Mercedes’ it would deduce that Mercedes is a
person
[...]
contrast this with the inability of a database to understand
anything it isn’t explicitly told then you should be able to
see the potential advantages”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-45-2048.jpg)
![Connected Data London / 16 Nov 17
#2 The semantics of semantics
“suppose you entered the details ‘Philip owns a Mercedes’
where ‘Philip’ and ‘Mercedes’ are both entities and ‘owns’
is a relationship. An inference engine can deduce that
Mercedes in this instance is a car whereas in ‘Juan is
married to Mercedes’ it would deduce that Mercedes is a
person
[...]
contrast this with the inability of a database to understand
anything it isn’t explicitly told then you should be able to
see the potential advantages”
WRONG!!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jesus-171117144638/75/Jesus-Barrasa-46-2048.jpg)


