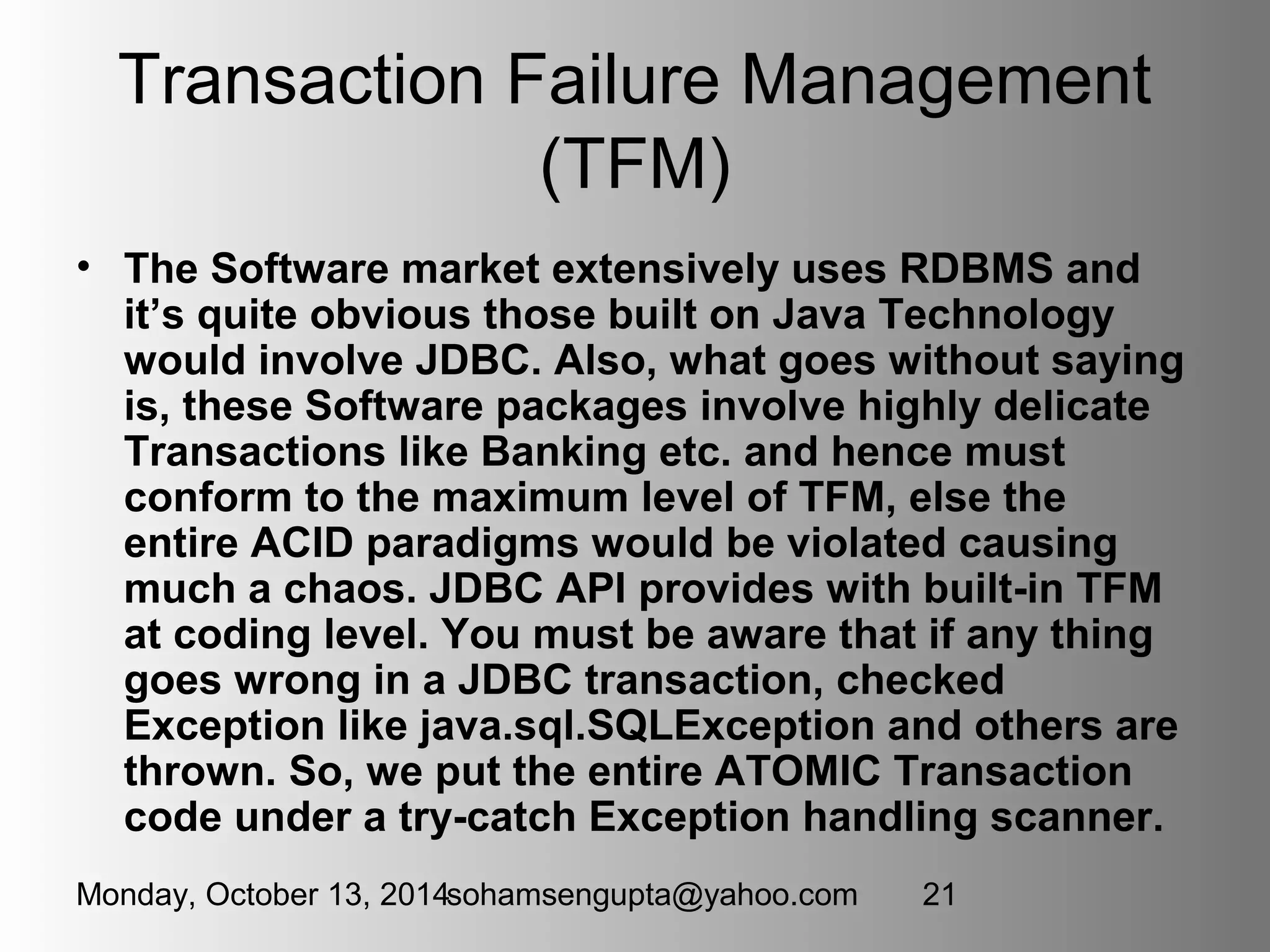
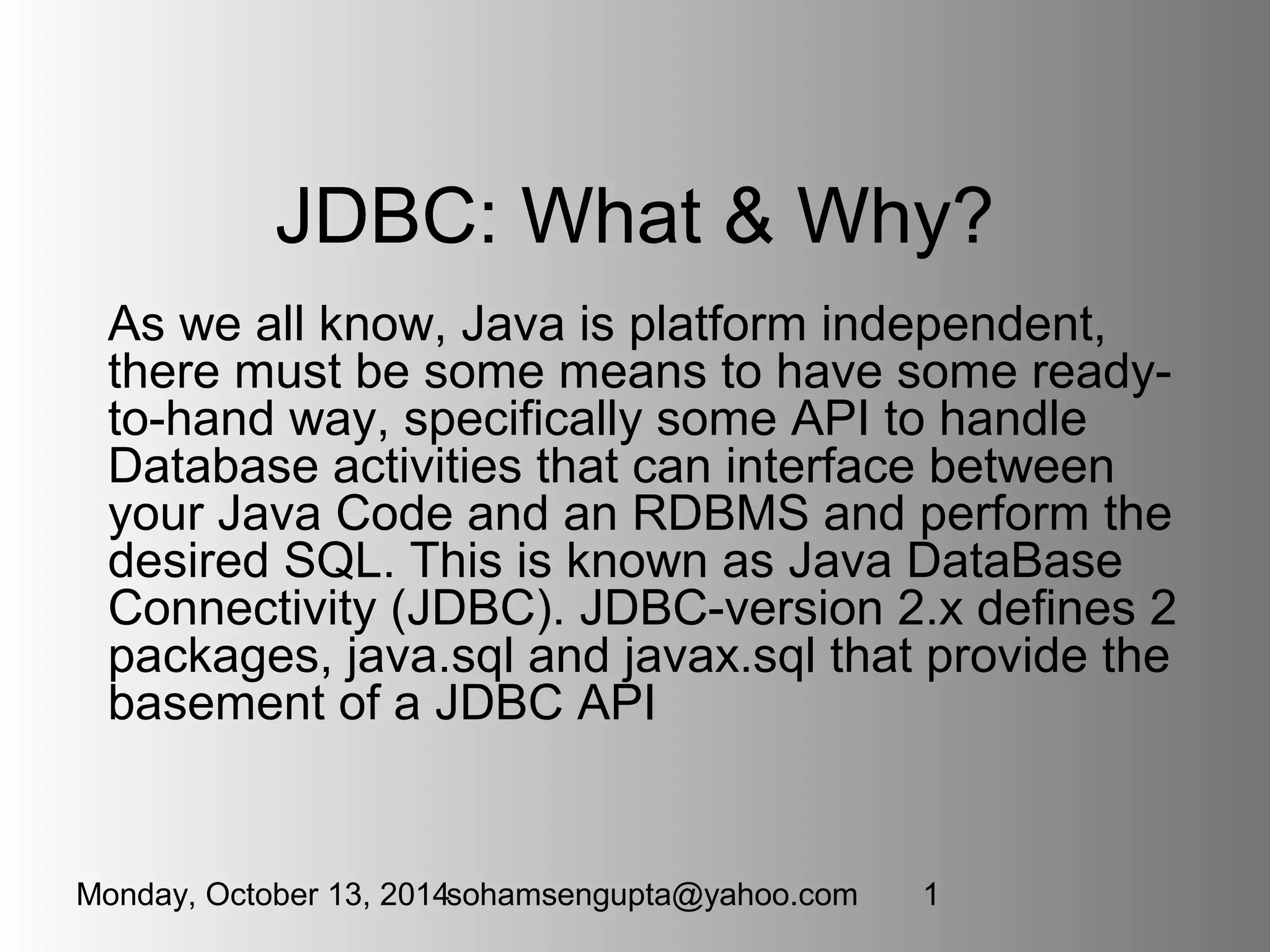
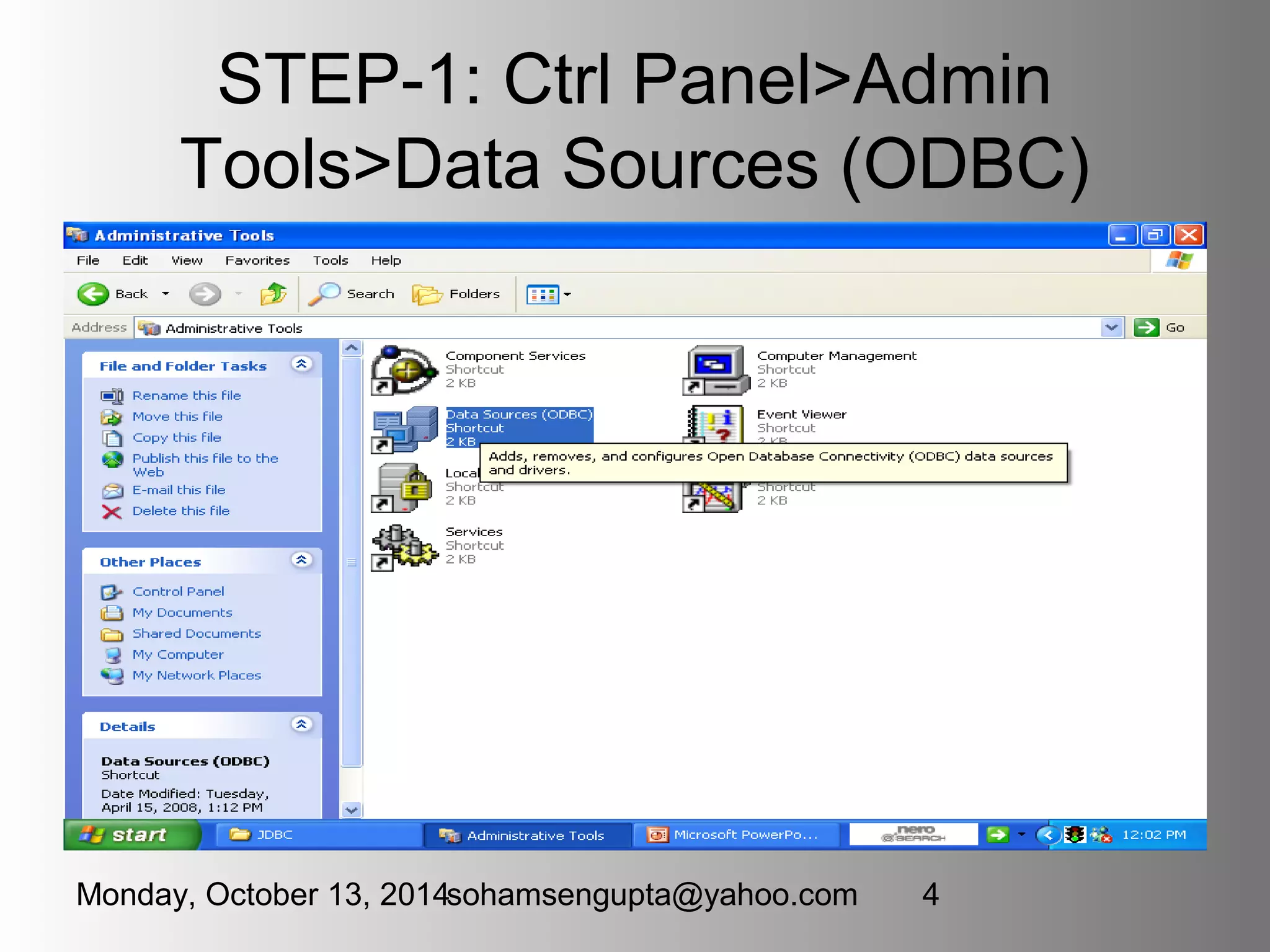
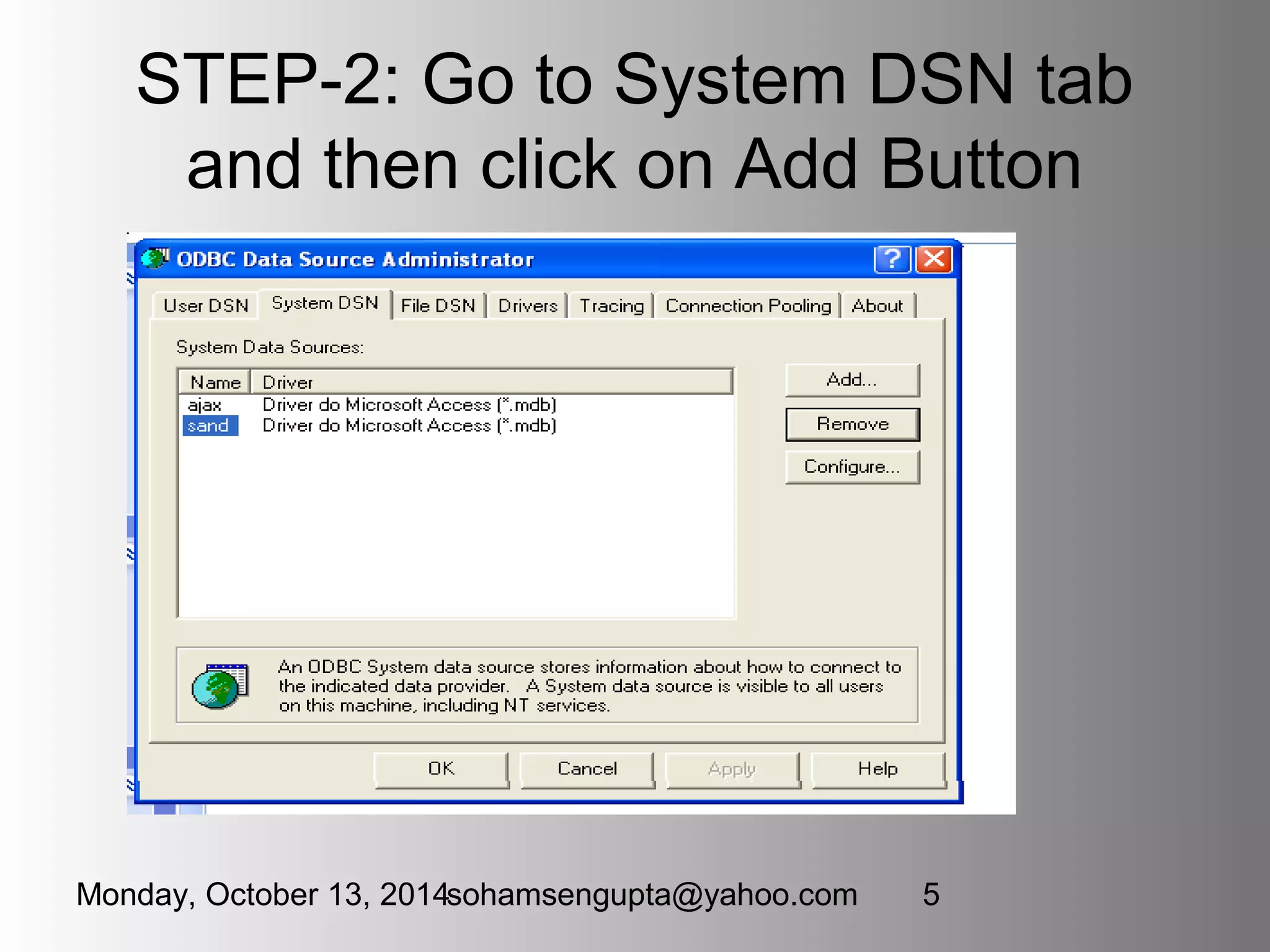
This document discusses JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) which provides an API for interfacing Java code with databases. It describes the four types of JDBC drivers, focusing on Type 1 (JDBC-ODBC bridge) and Type 4 (Pure Java) drivers. It provides code examples for connecting to a database using a Type 1 driver, performing CRUD operations like creating tables, inserting rows, updating and fetching rows. It also covers topics like transactions, prepared statements, and handling exceptions.









![Finally Calling these methods
• public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception{
• createTable("StudentTable");
insertRow("it/00/57","Soham Sengupta",940);
• insertRow("it/00/01","Manas Ghosh",620);
• insertRow("it/00/2","Tanay Das",657);
• insertRow("it/00/63","Abhisek Biswas",721);
• selectAllRowsOtherMethod();
• selectAStudent("it/00/02");
• updateAStudent("it/00/1",755);
• updateARowOtherMethod(102,"Tanoy Dash");
• }
Monday, October 13, 2014sohamsengupta@yahoo.com 16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdbc-day-1-141013052035-conversion-gate01/75/Jdbc-day-1-16-2048.jpg)