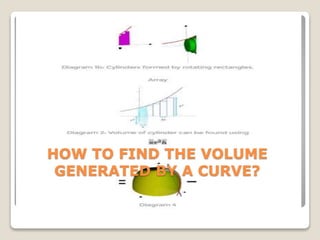
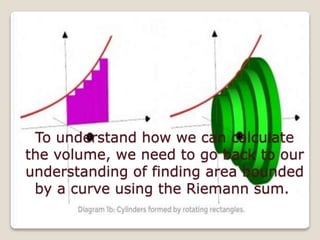
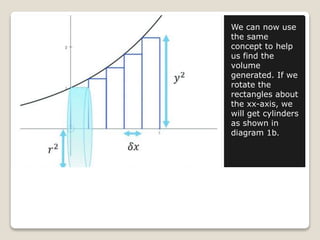
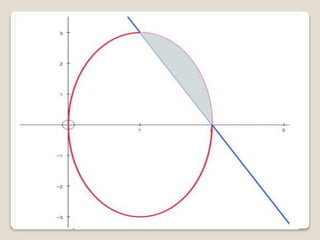
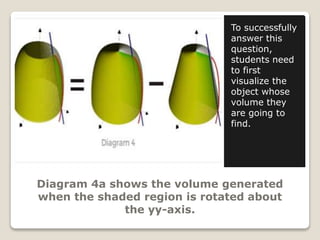
The document discusses how to find the volume generated by rotating an area bounded by a curve, a common challenge in JC math for A-levels. It emphasizes the importance of understanding integration and the visualization of volume, using the concept of Riemann sums to approximate area. Students are advised to approach the problem by visualizing the object and carefully calculating the volume by subtracting the volume generated by a line from that generated by the curve.