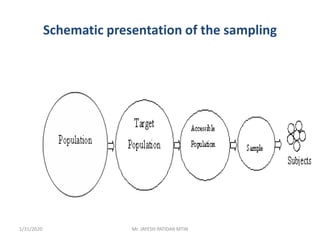
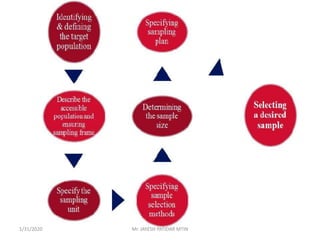
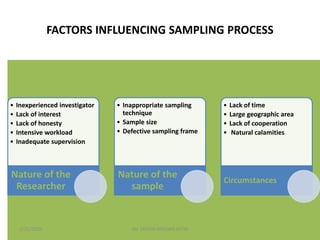
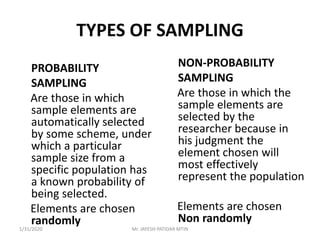
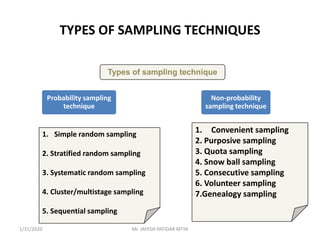
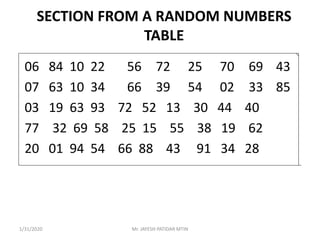
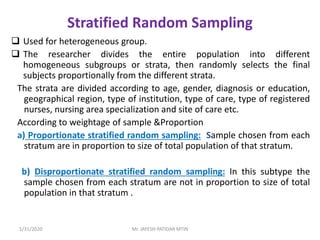
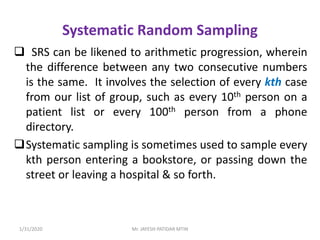
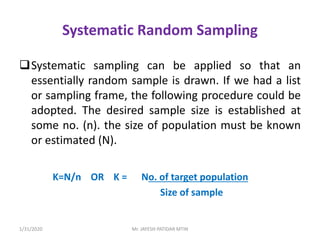
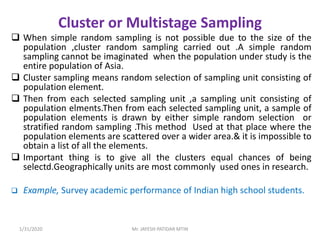
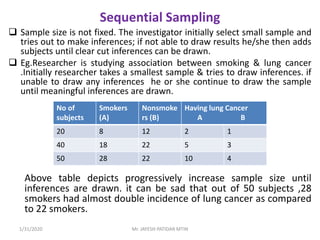
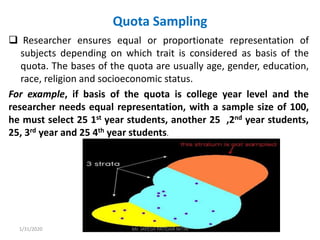
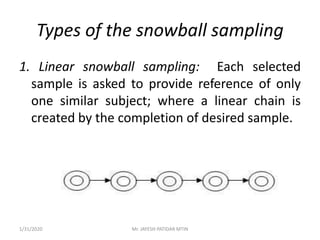
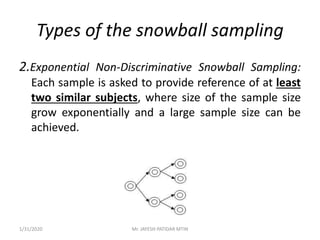
This document discusses sampling techniques used in research. It defines key terms like population, sample, sampling frame, and stratified random sampling. Stratified random sampling involves dividing the population into homogeneous subgroups or strata first, then randomly selecting subjects proportionally from each strata. This ensures representation from different subgroups. Some advantages are it reduces bias, allows for comparisons between strata, and gives higher statistical precision than simple random sampling. Probability sampling methods like simple random and stratified random sampling are more reliable if a complete sampling frame is available.