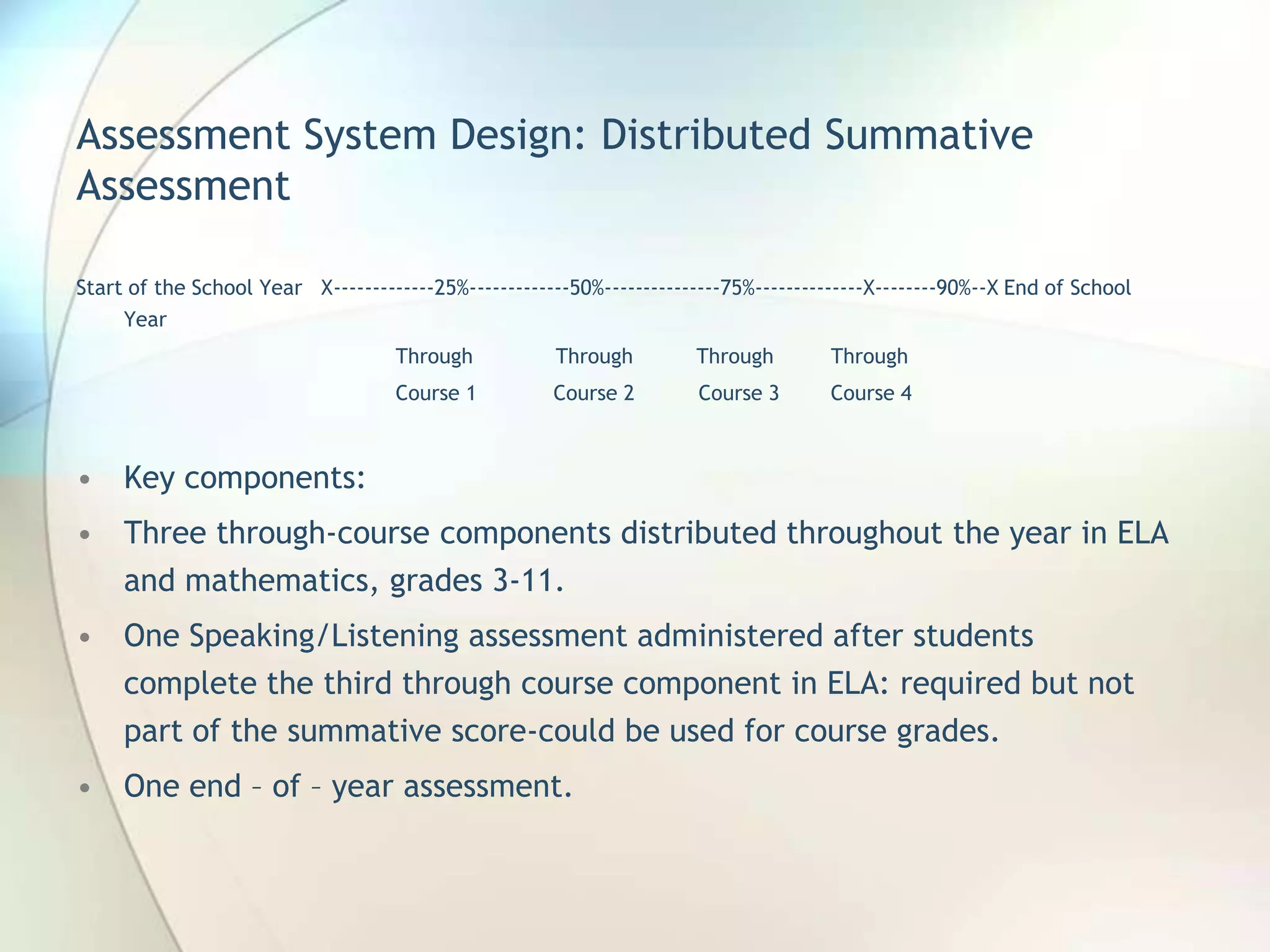
The Common Core State Standards were developed by the National Governors Association and the Council of Chief State School Officers to provide consistent, clear educational standards across states. They are designed to ensure students are prepared for college and careers. The standards focus on developing critical thinking, problem solving, research, and writing skills. Assessments will be administered throughout the school year via the Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers to provide feedback on student progress. States adopting the Common Core Standards will work together on common assessments and performance standards.