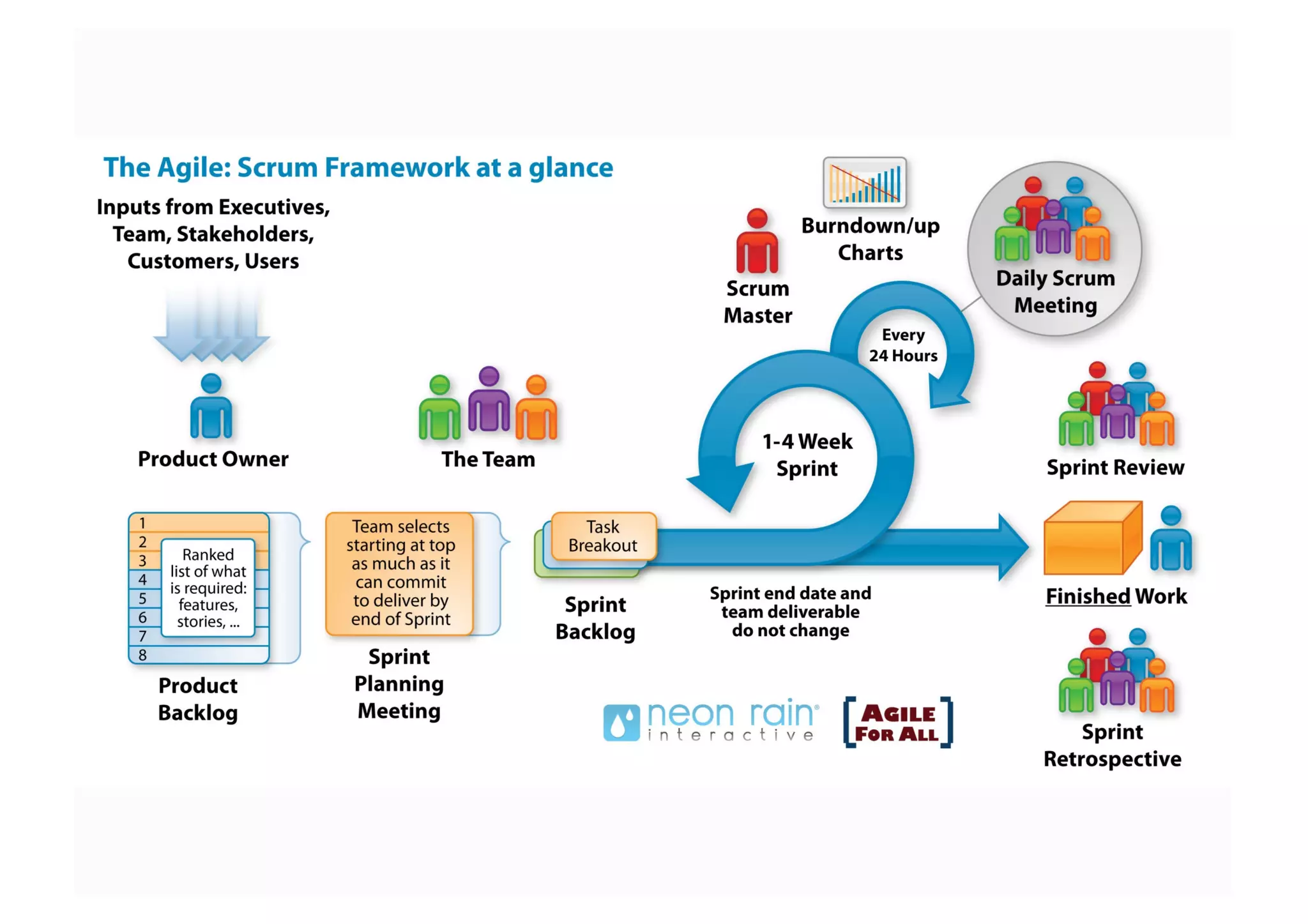
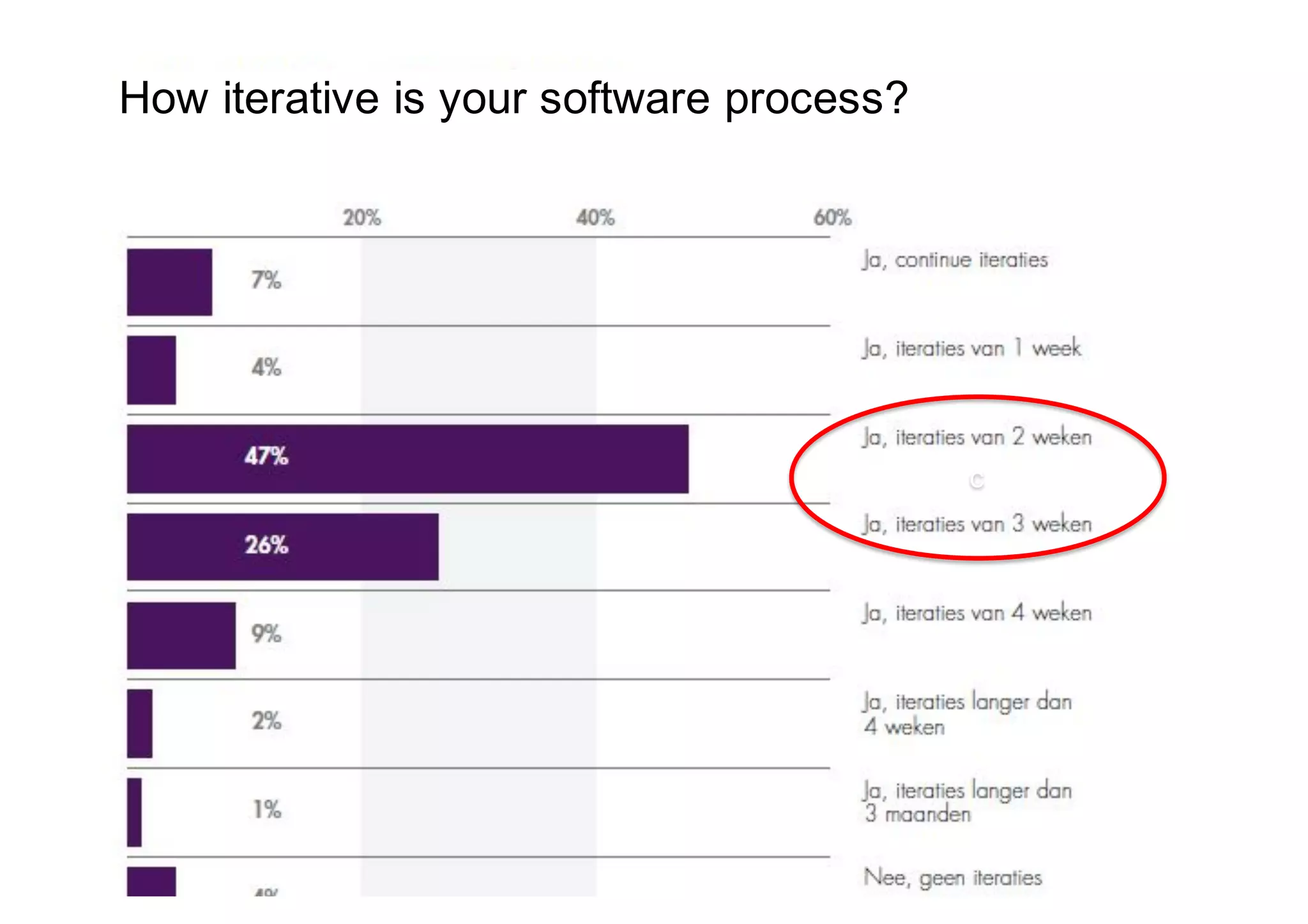
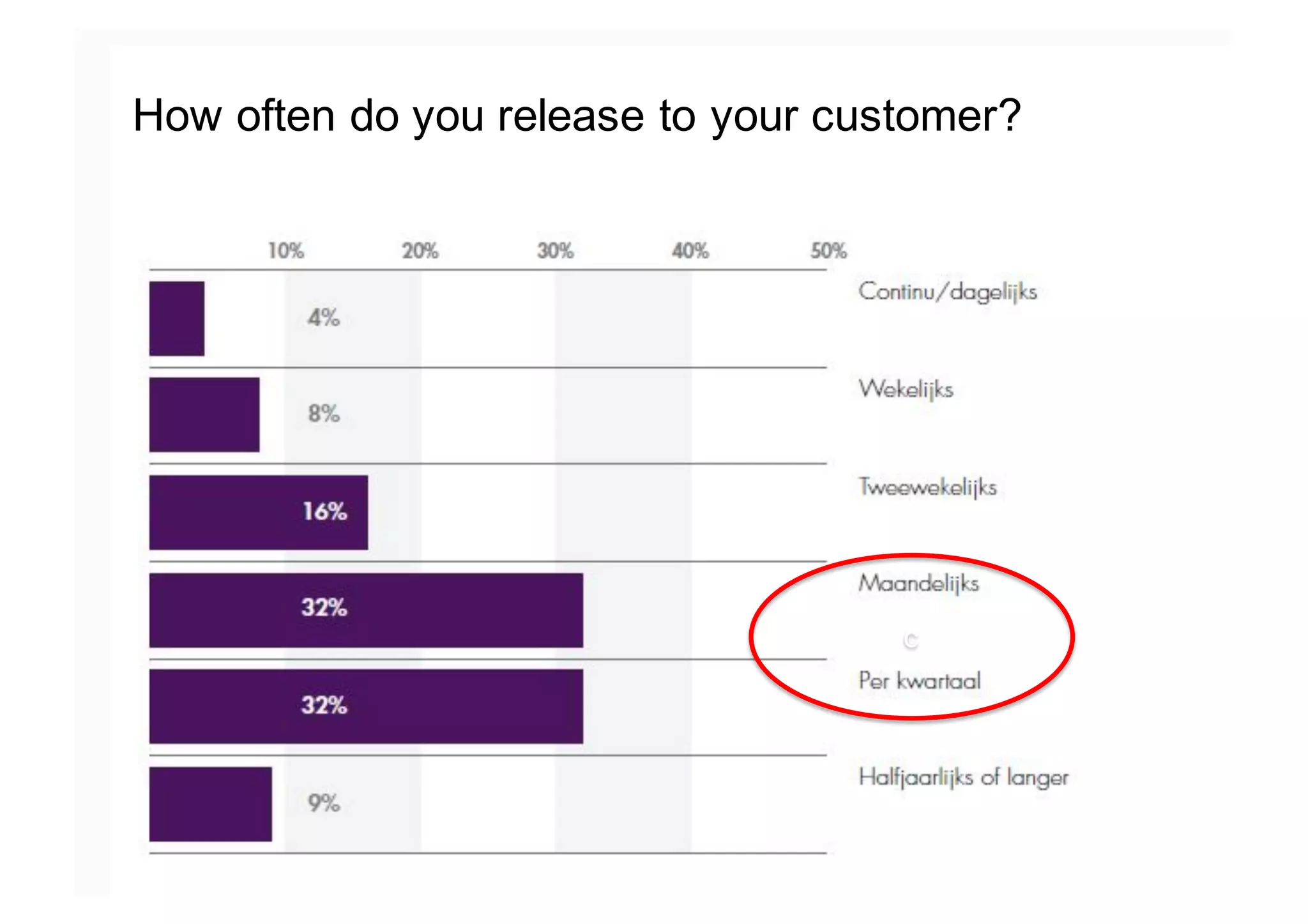
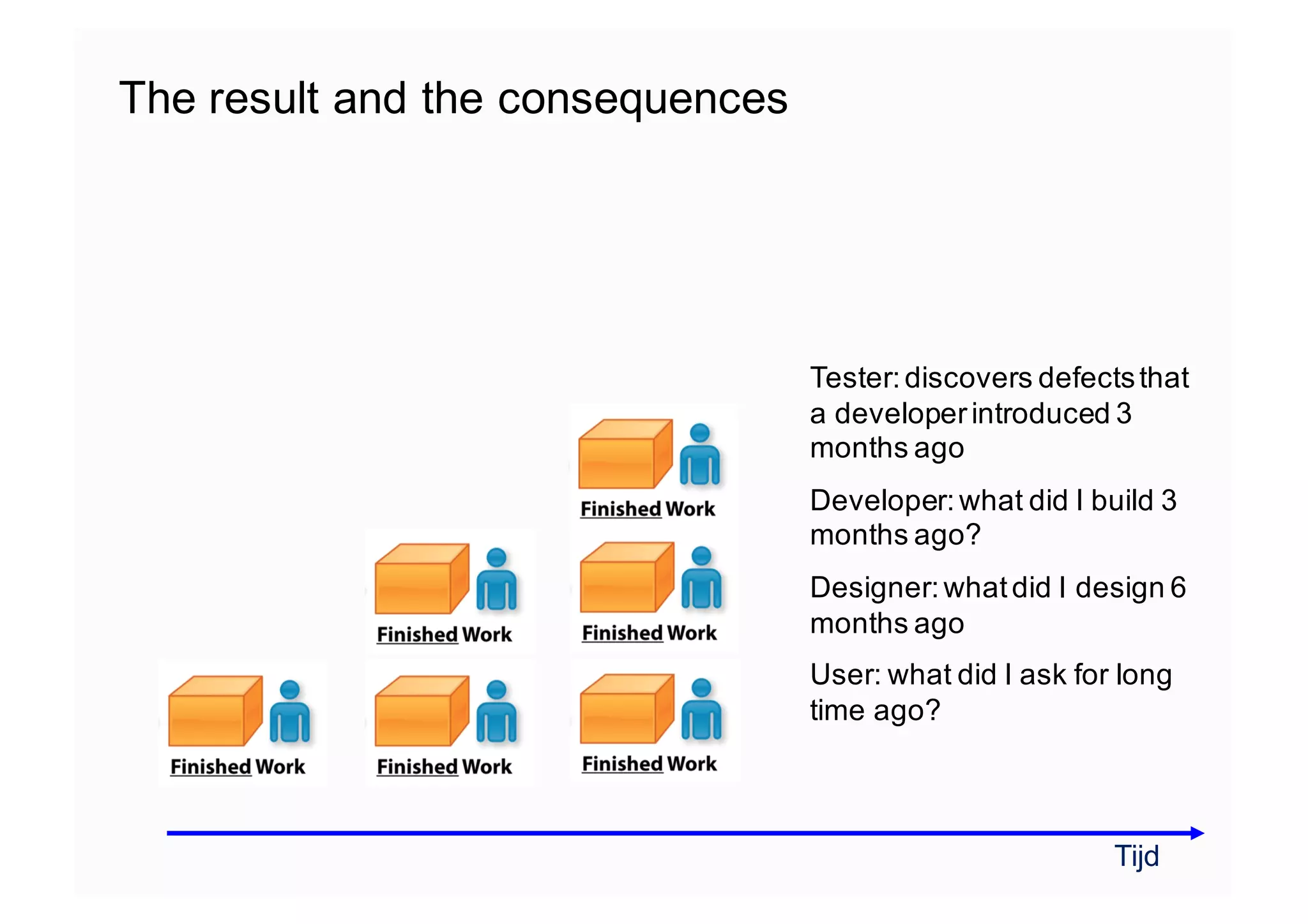
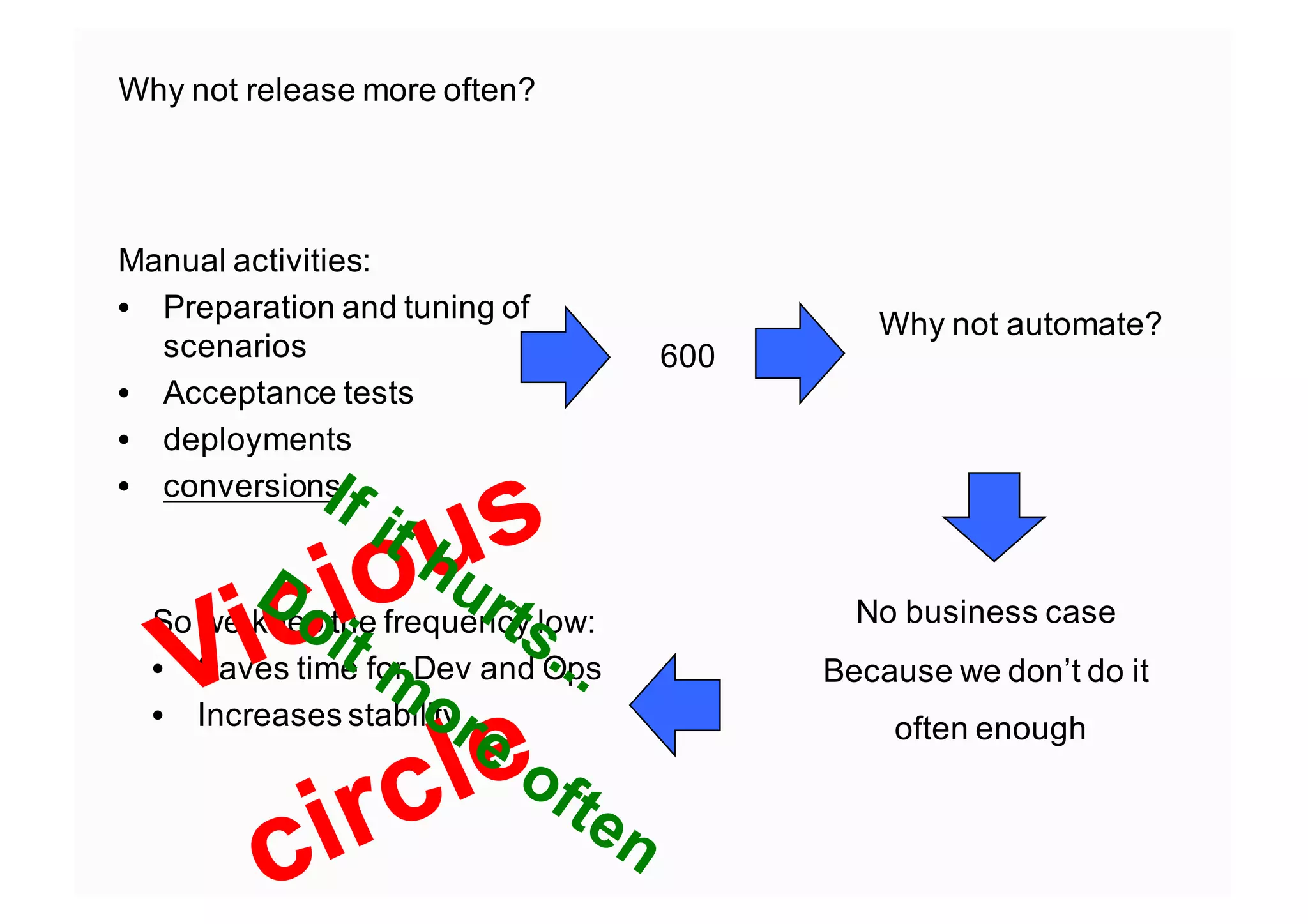
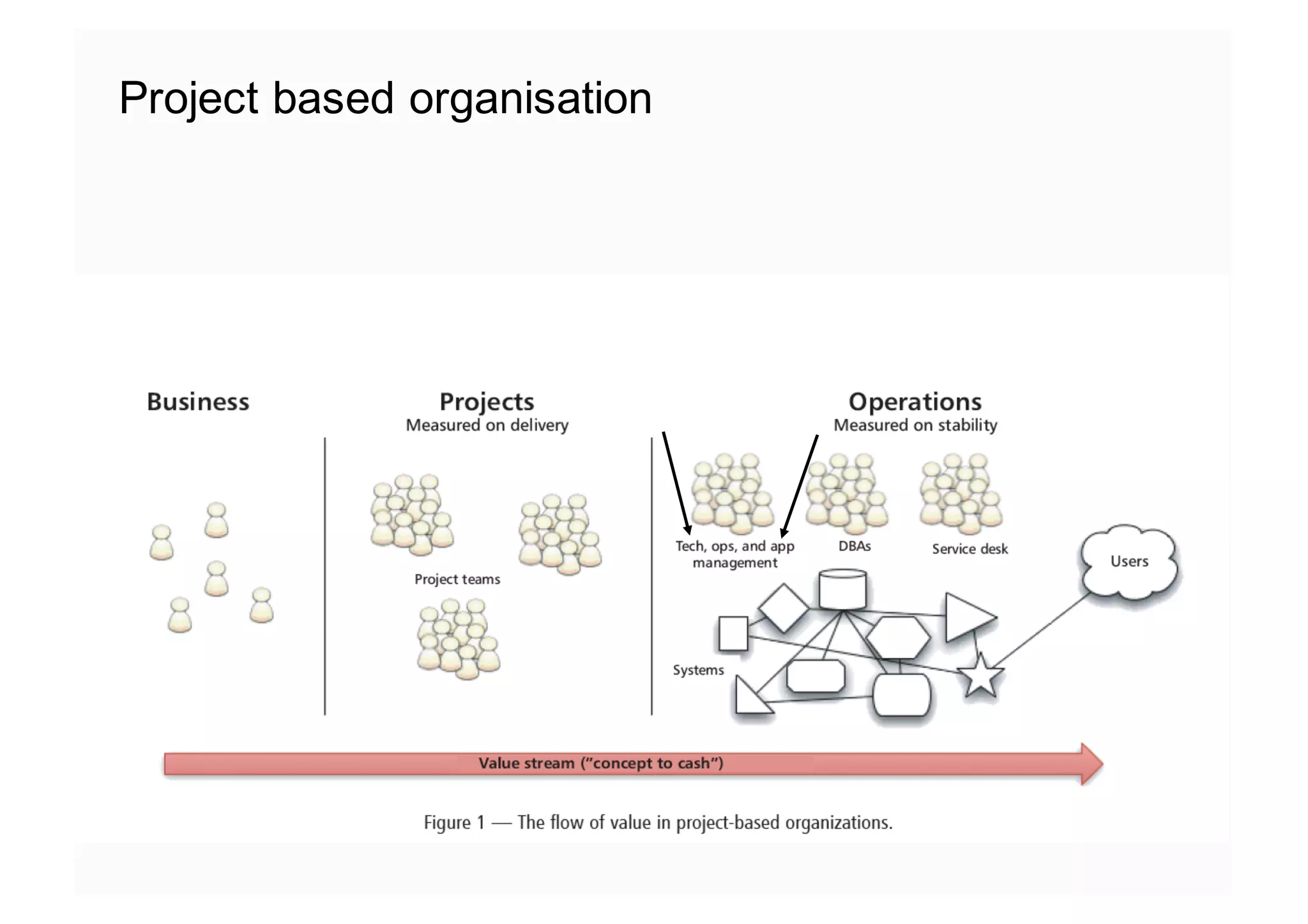
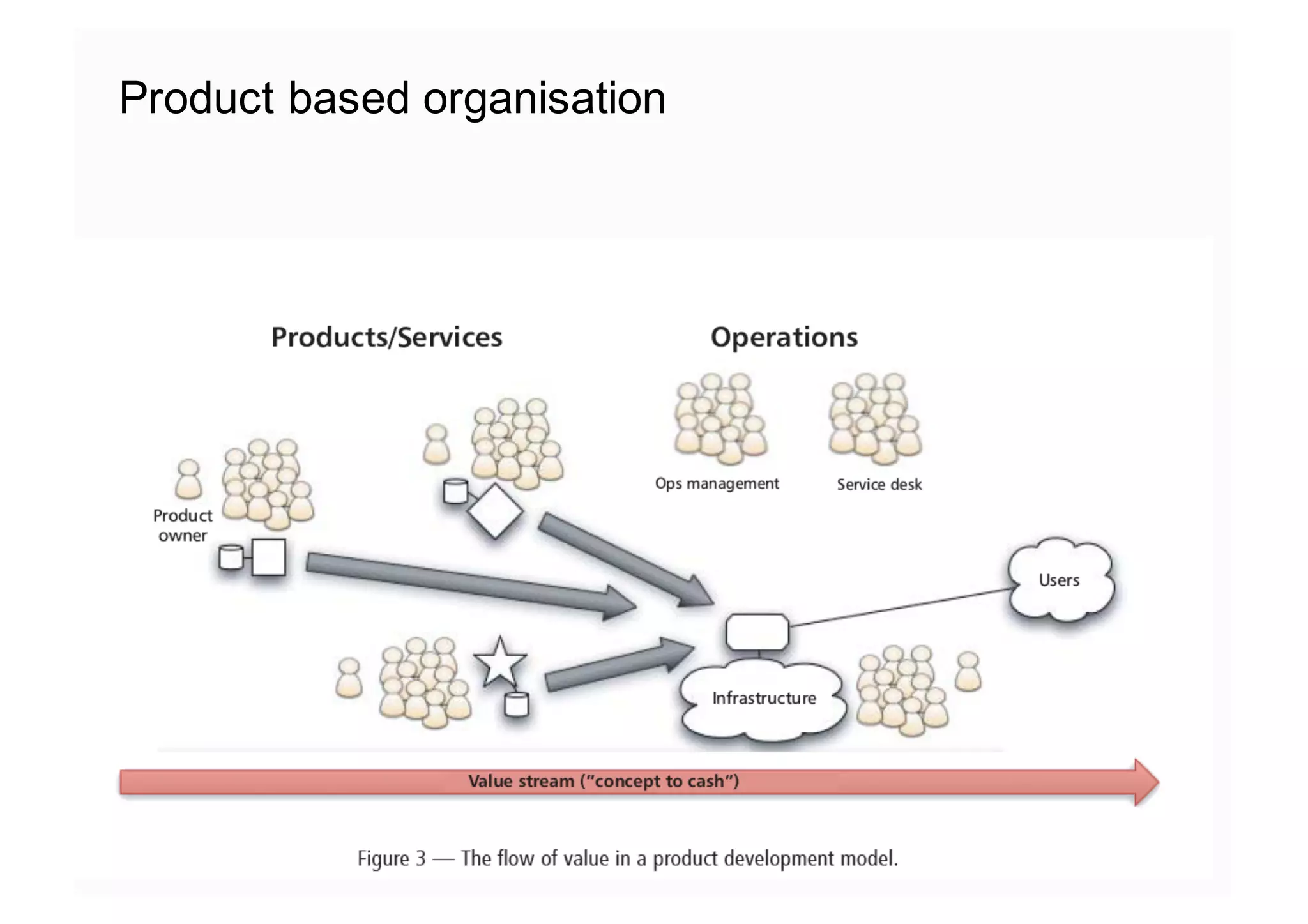
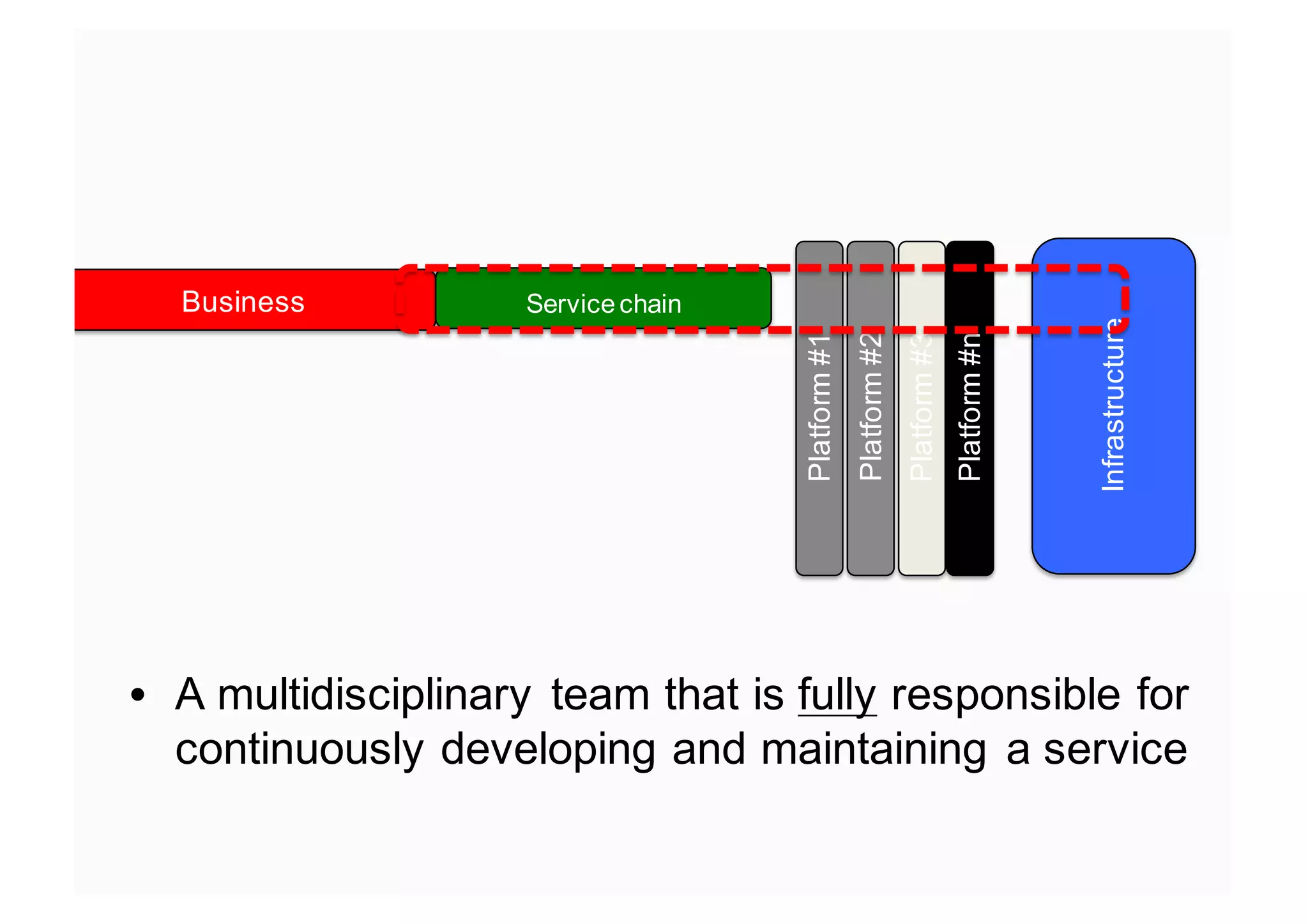
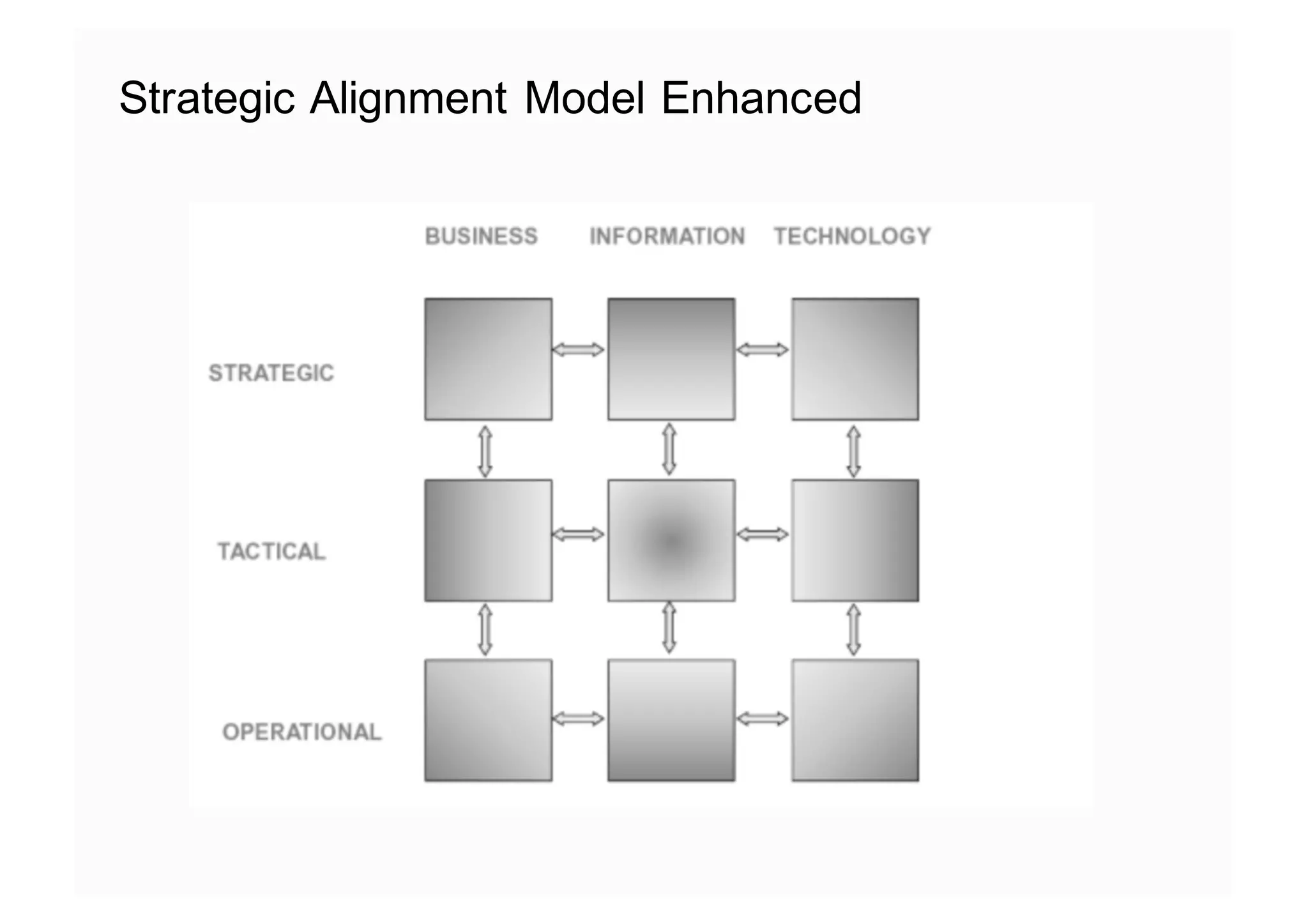
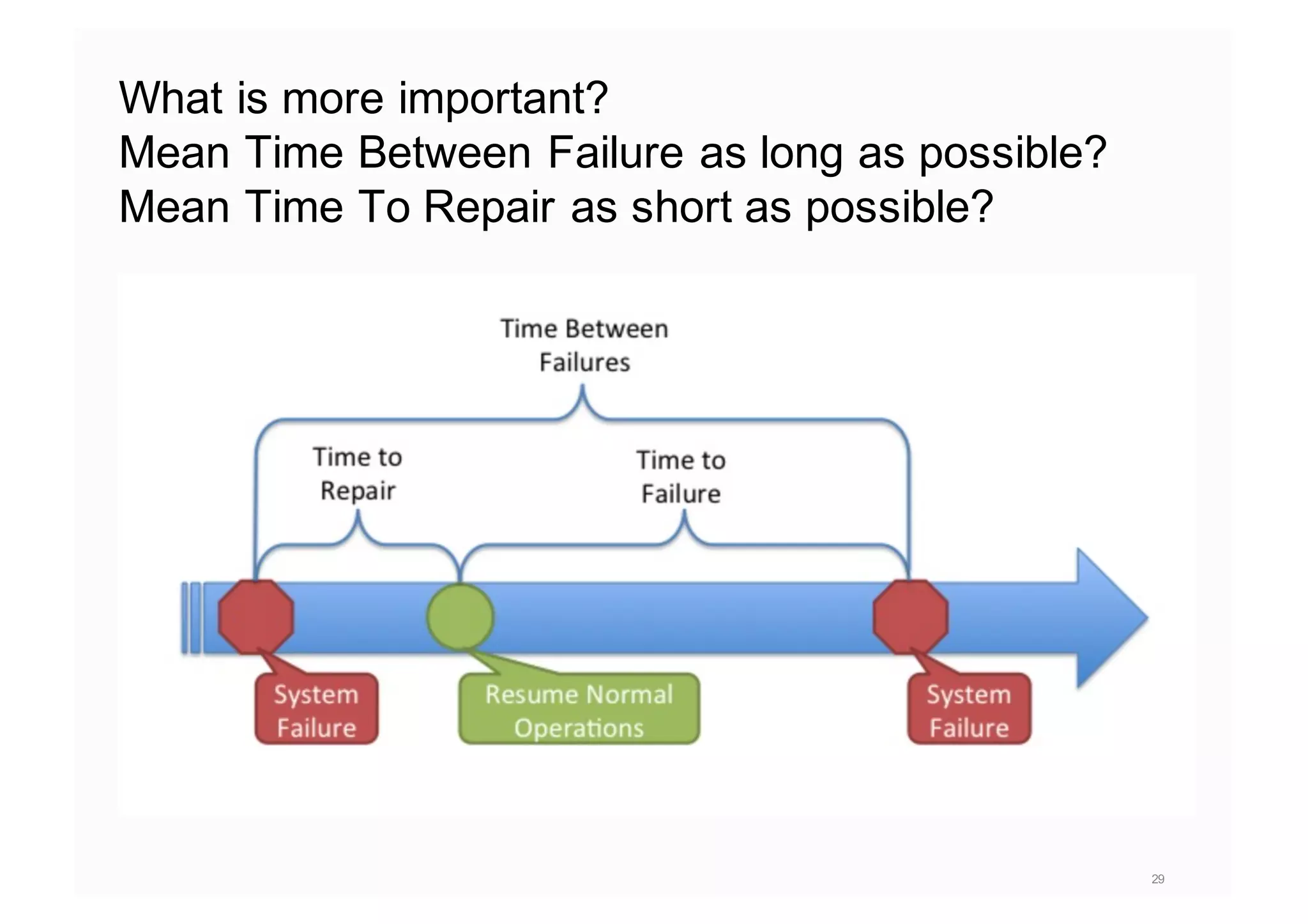
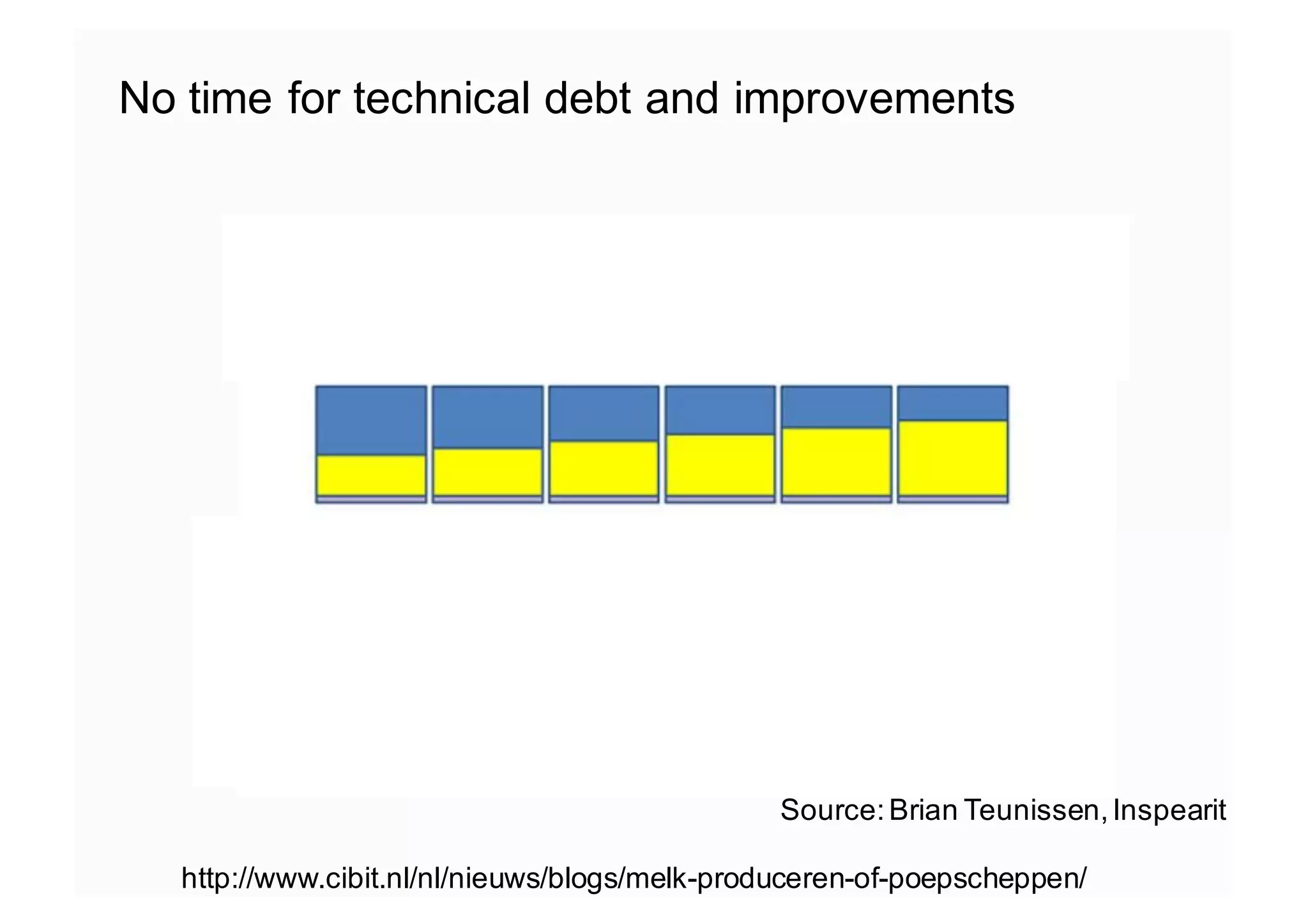
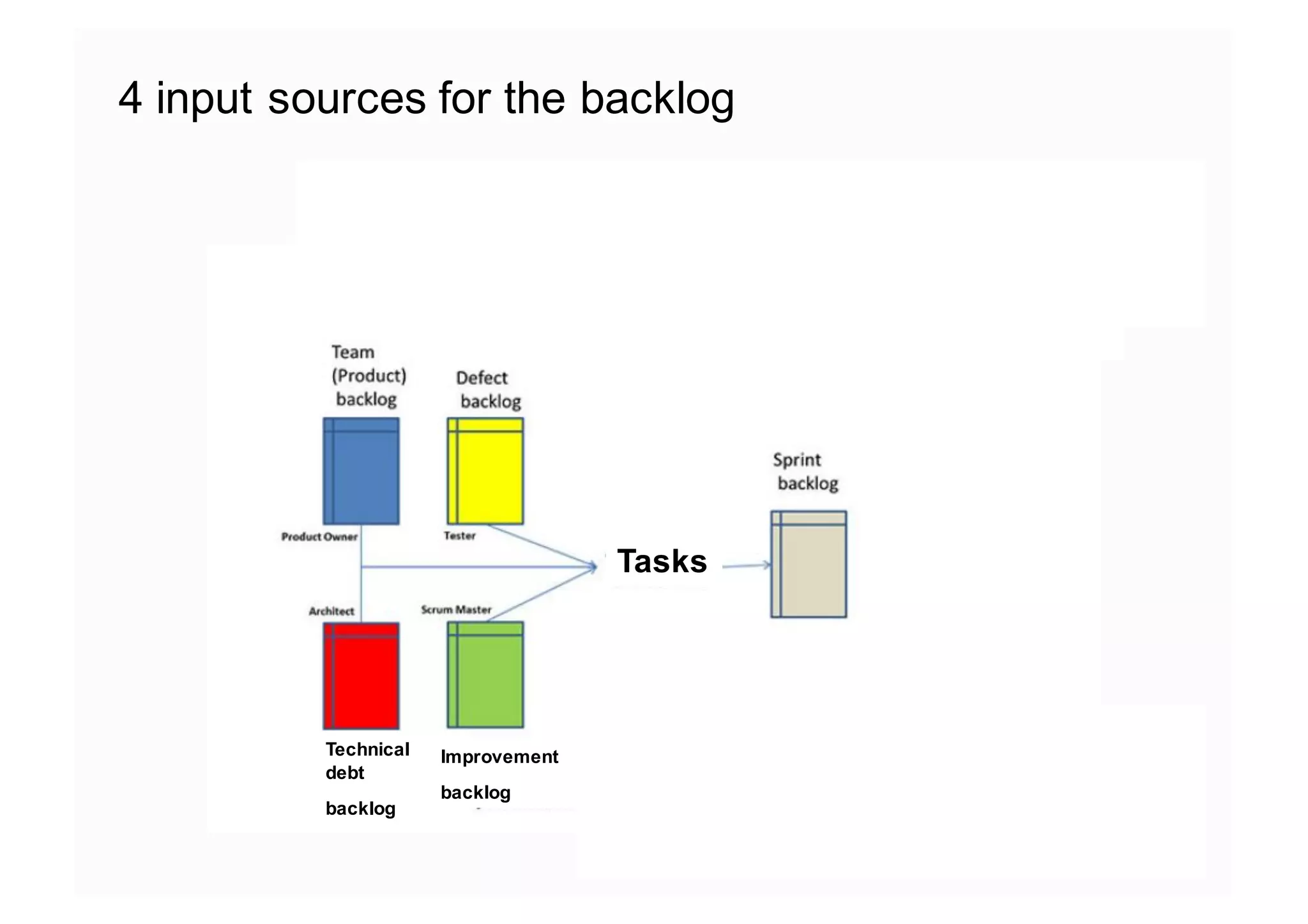
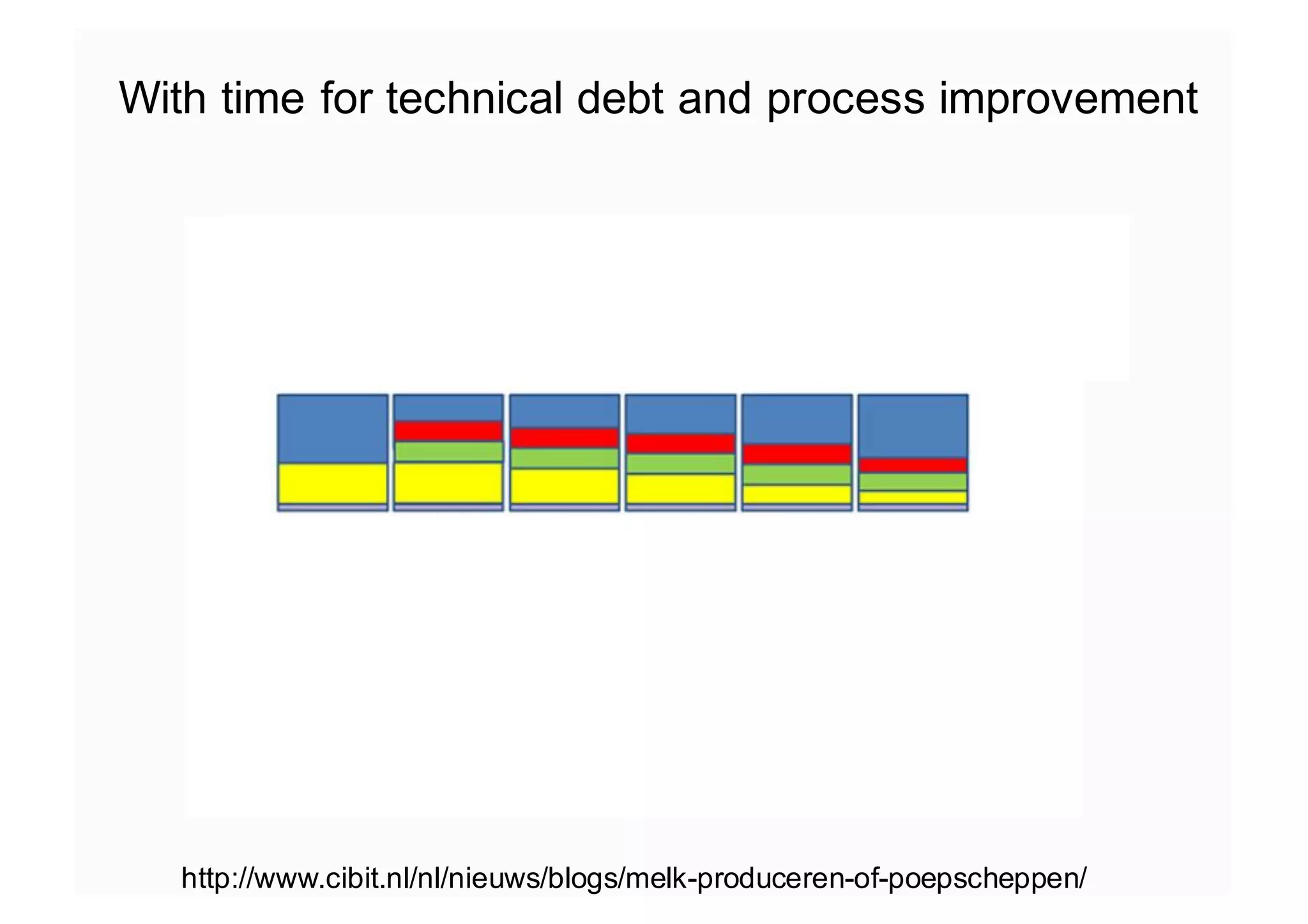
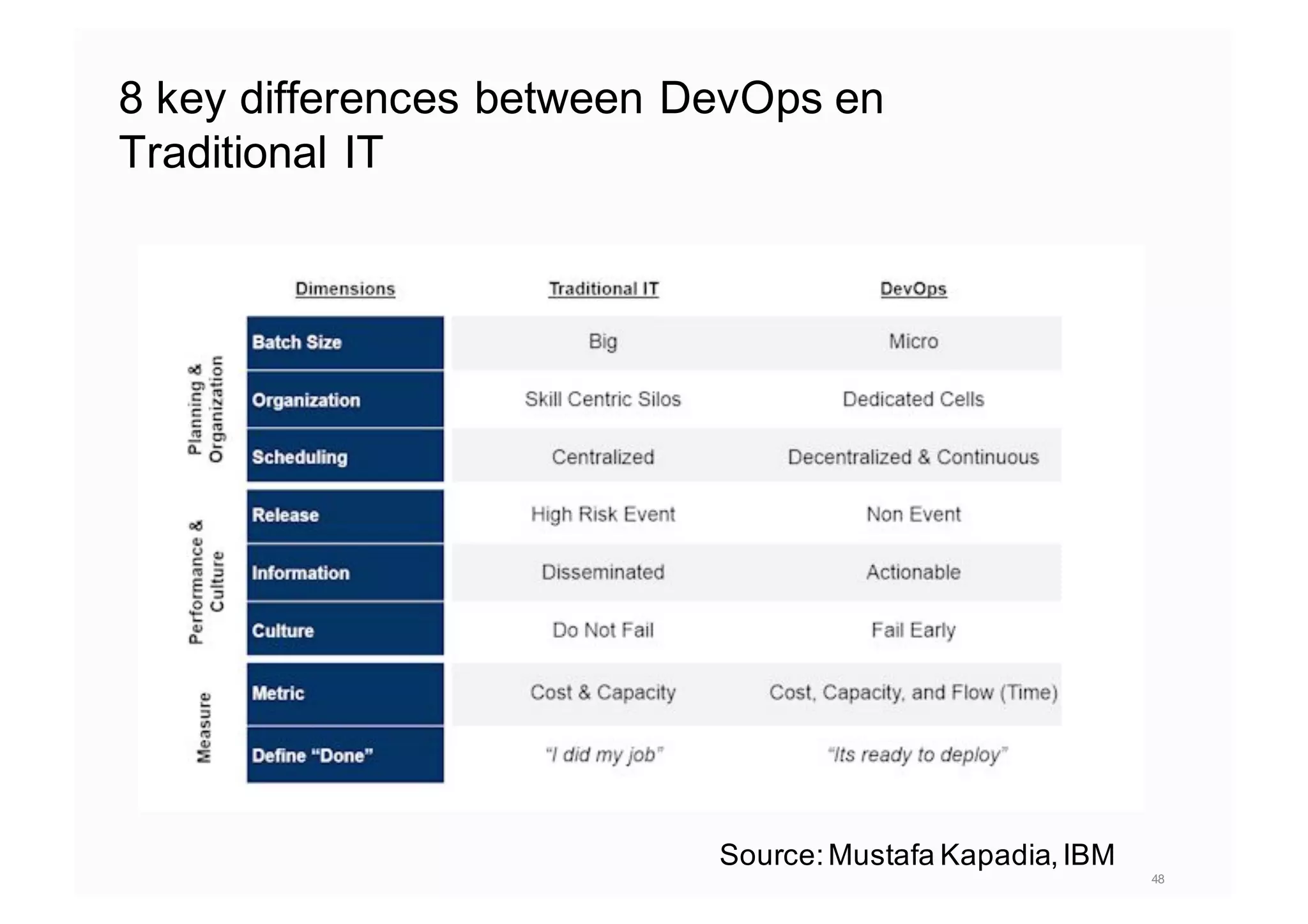
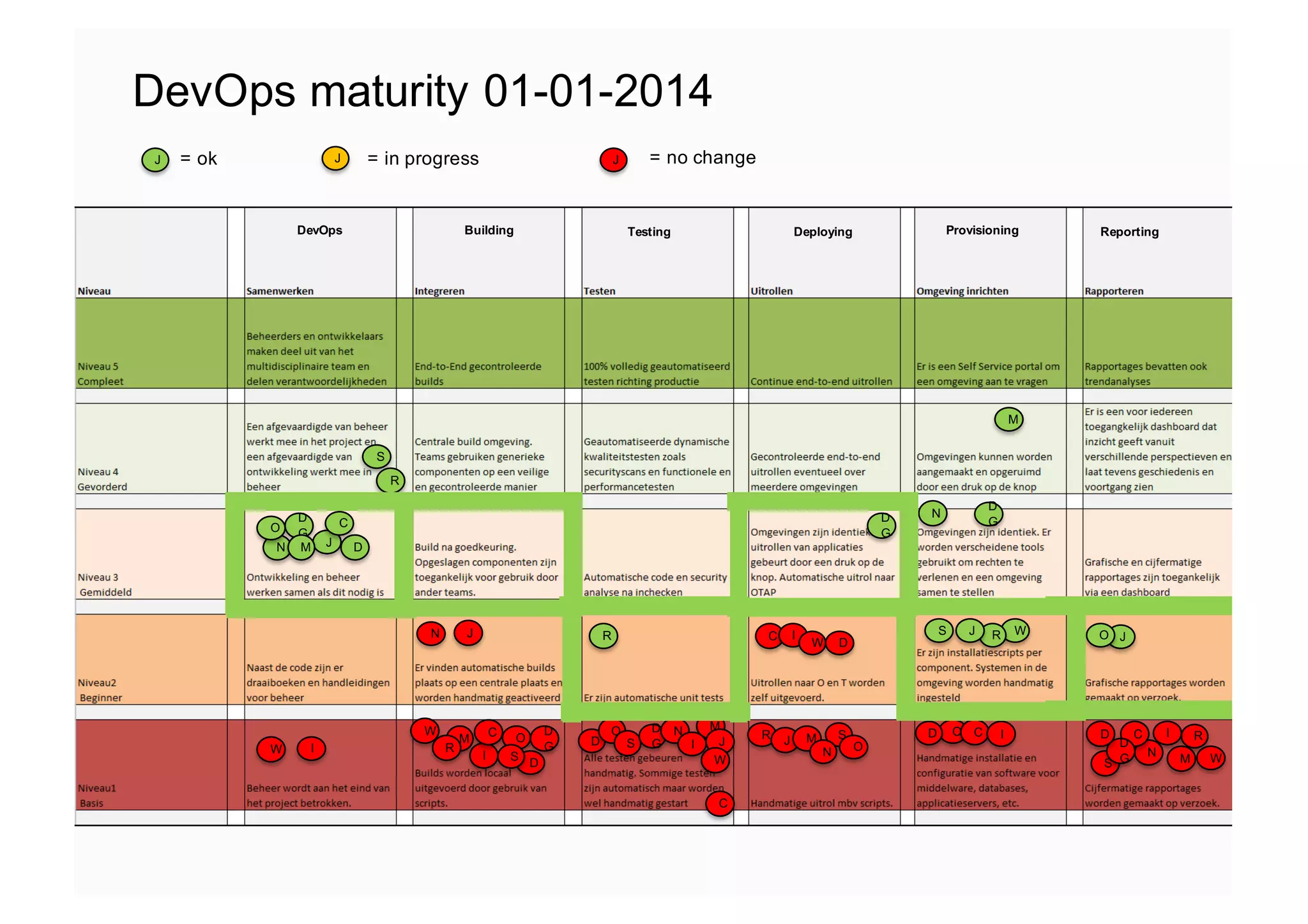
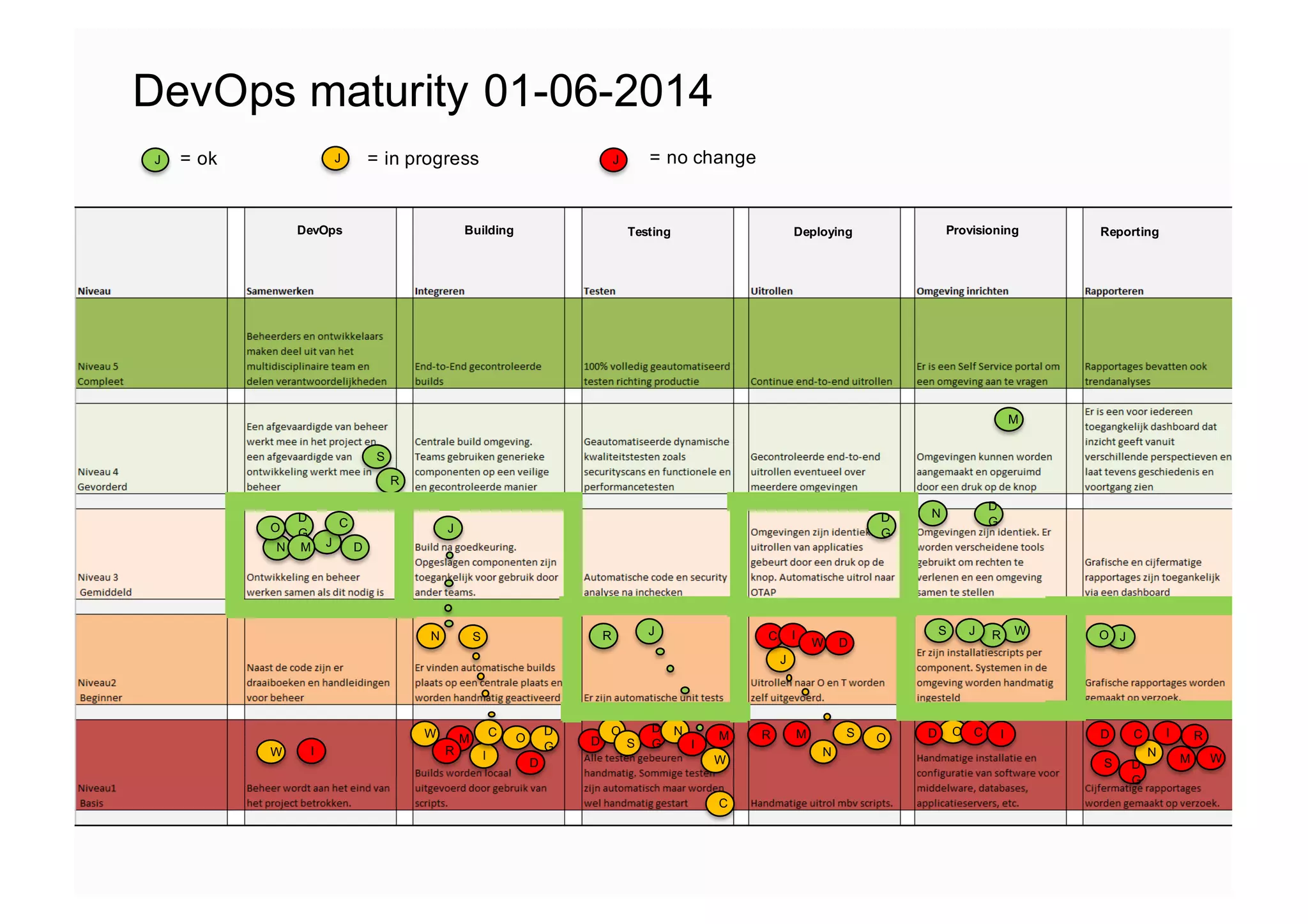
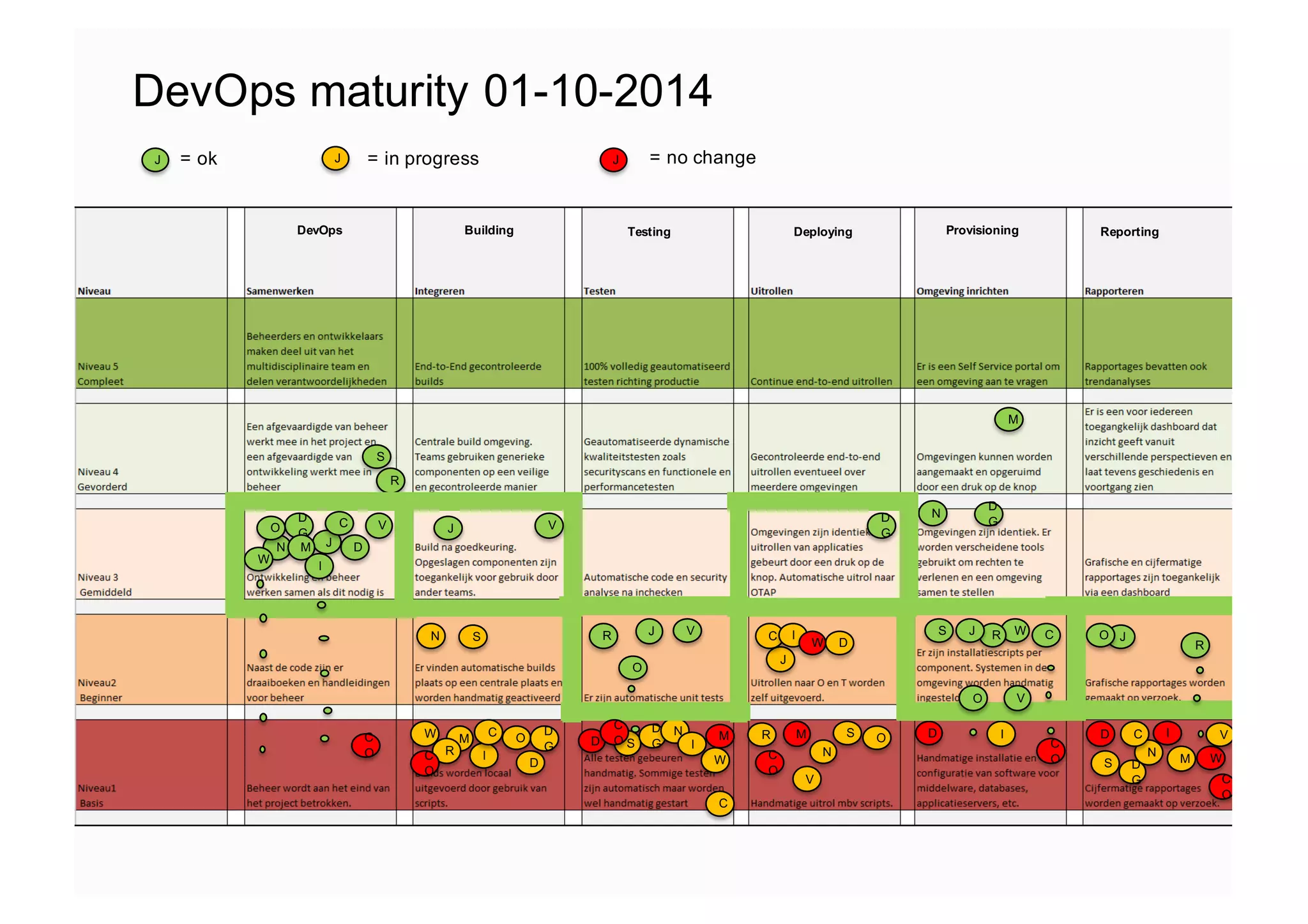
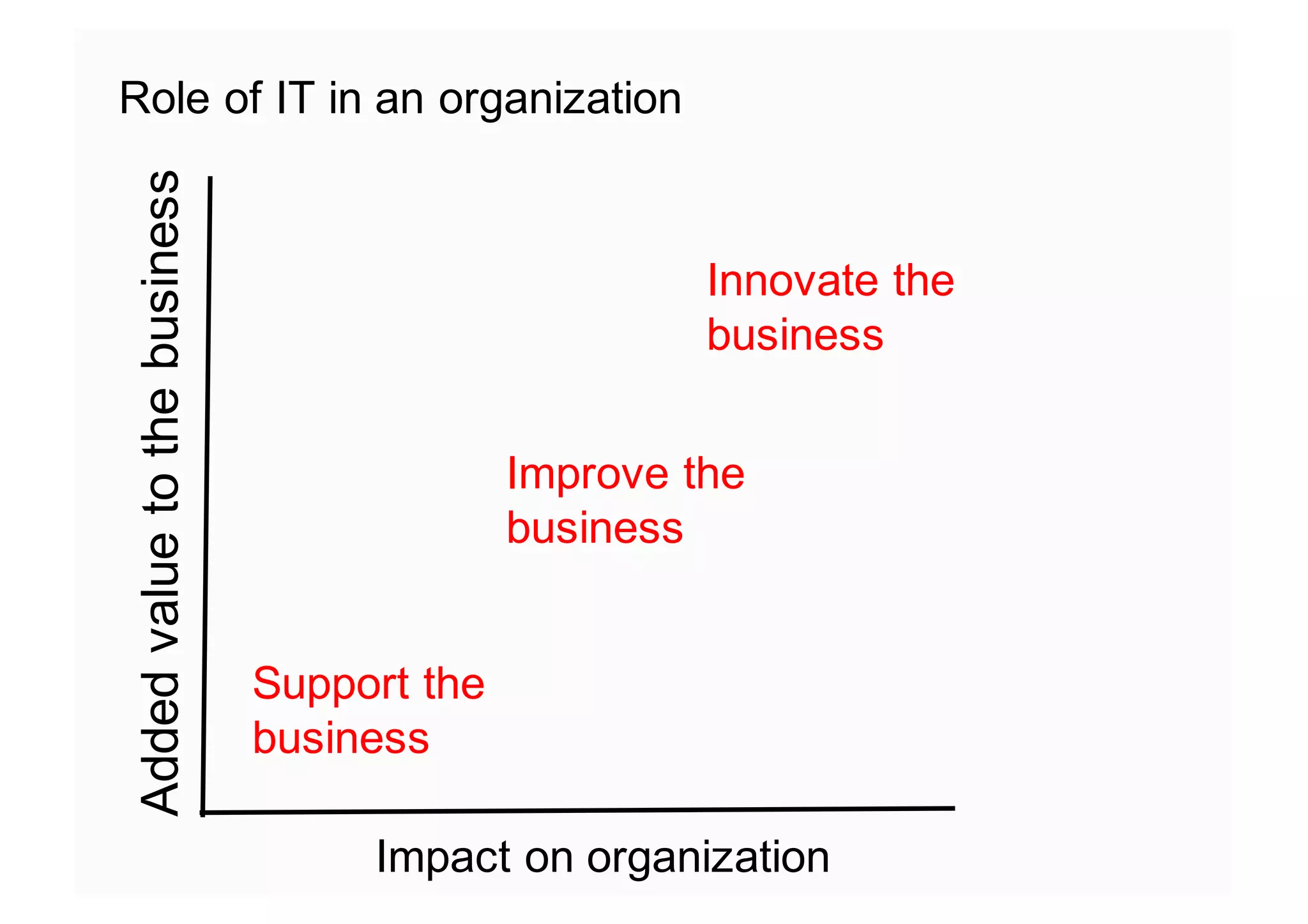
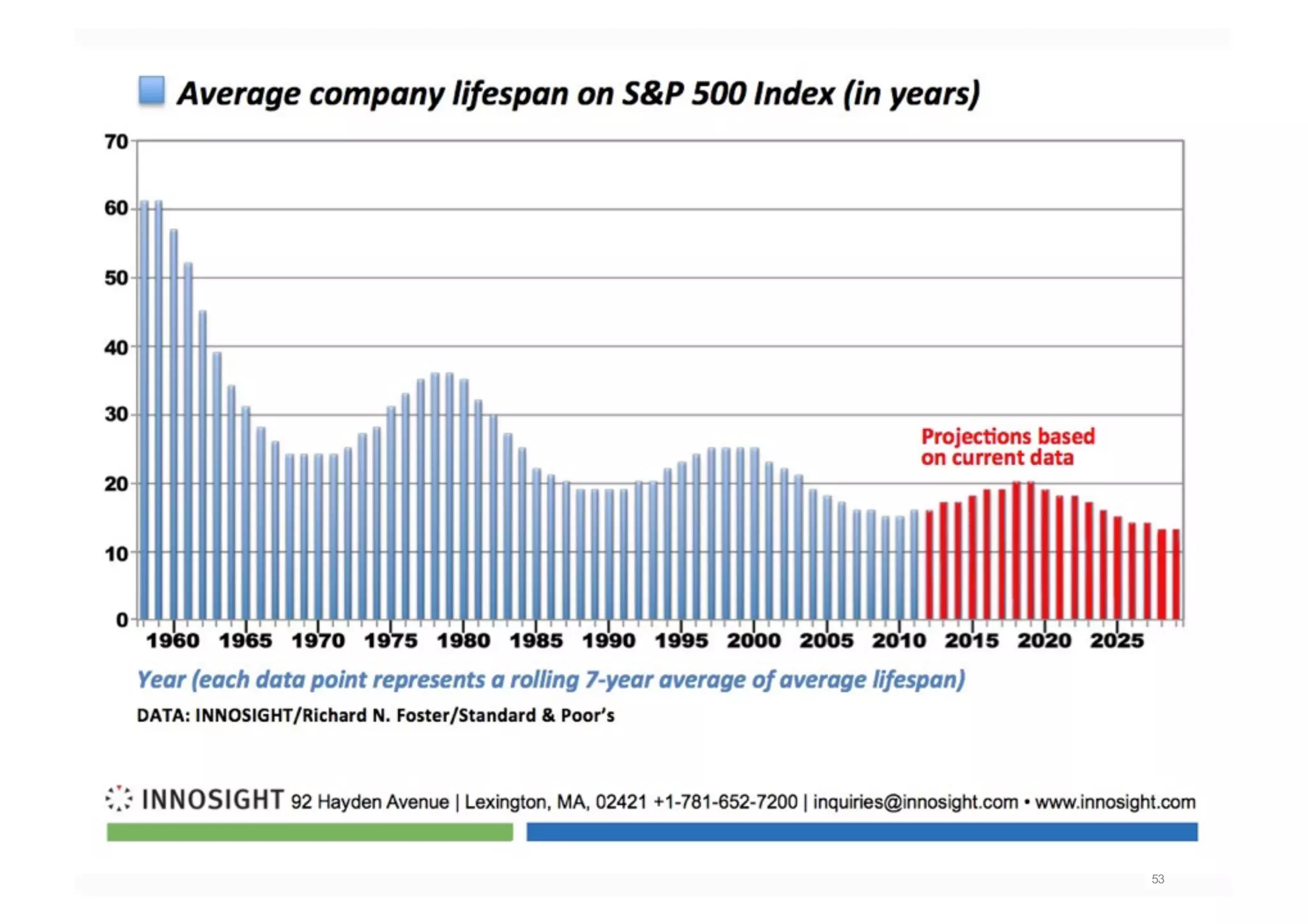
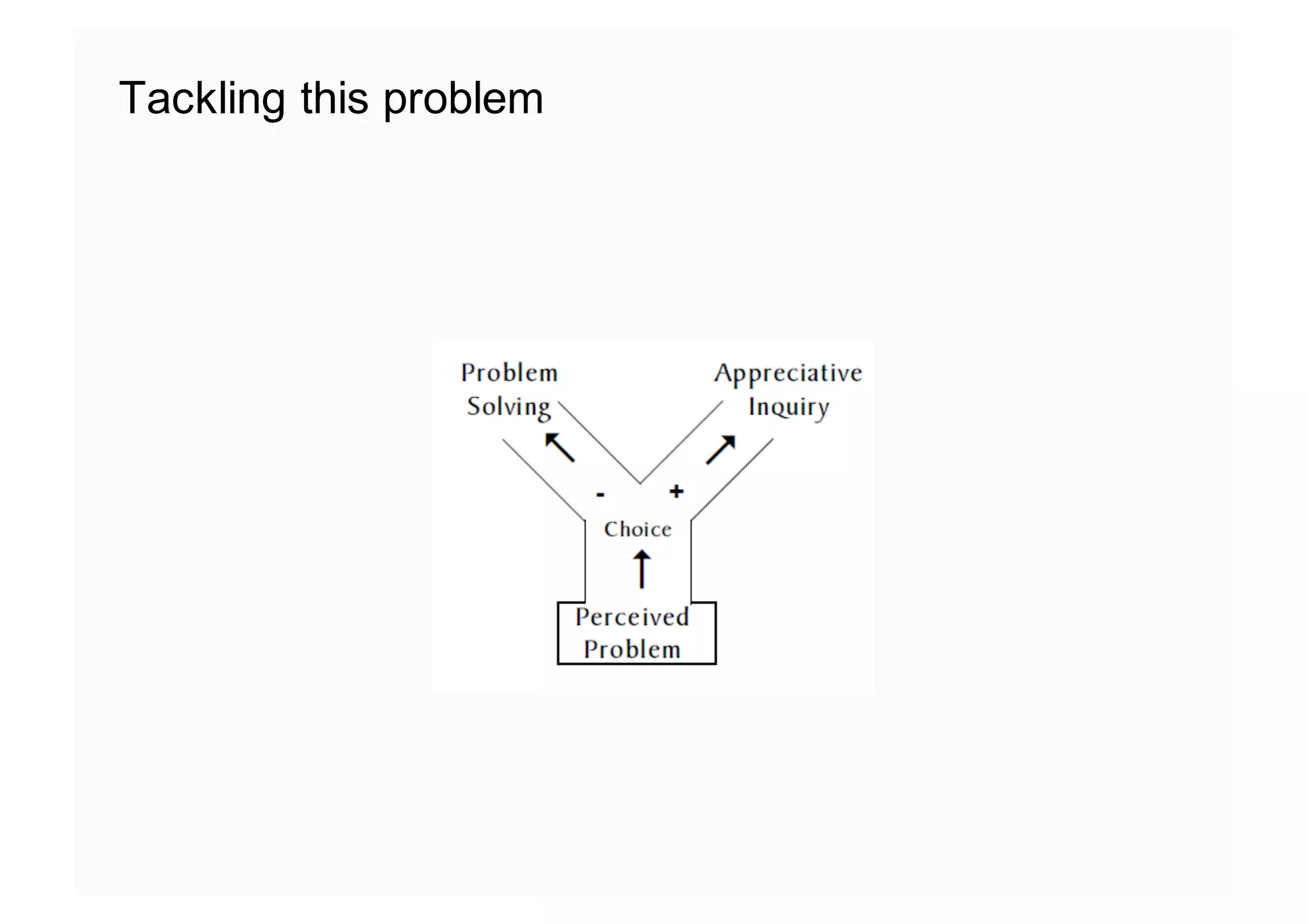
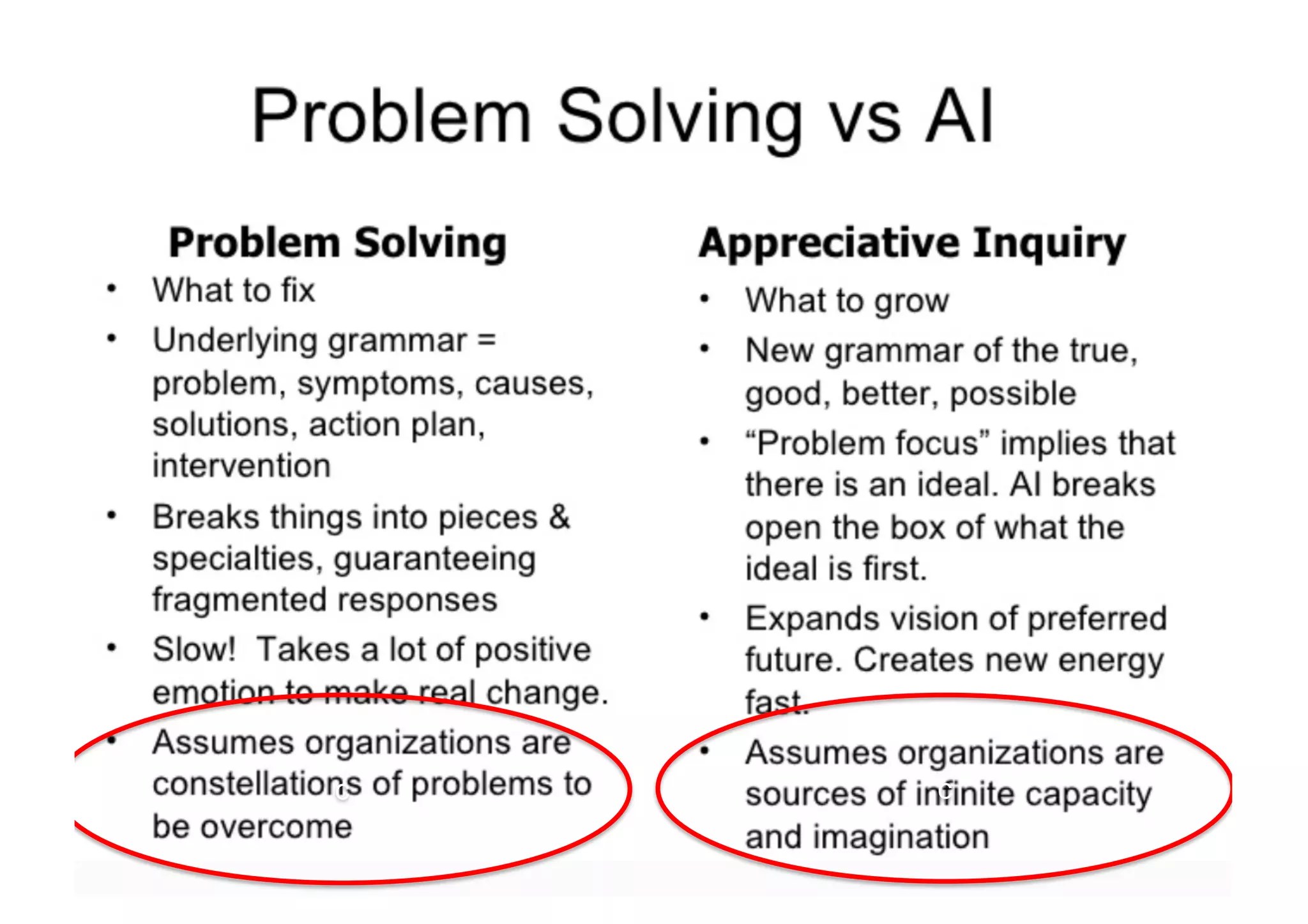
The document elaborates on the implementation of DevOps, emphasizing its role in enhancing organizational efficiency and responsiveness. It discusses strategies for convincing management on the benefits of DevOps, detailing the Appreciative Inquiry method as a means to identify and build on effective practices. The text also touches on various aspects of DevOps maturity, team structure, and the integration of development and operations for improved service delivery.