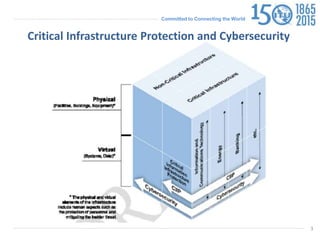
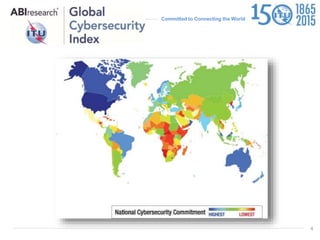
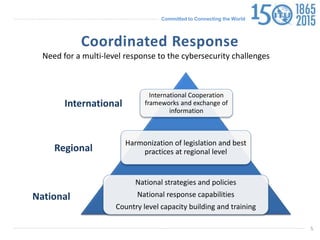
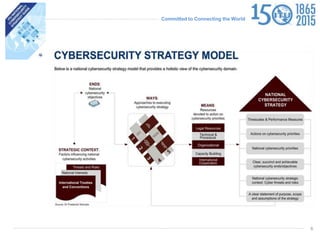
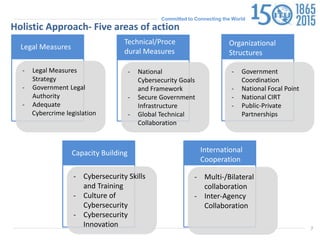
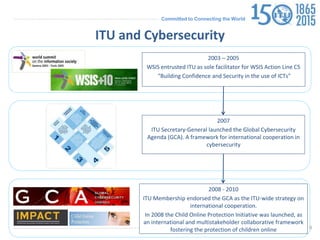
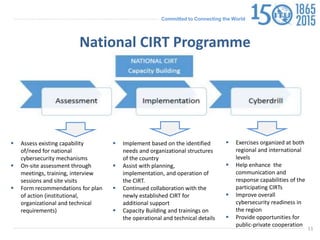
The document discusses protecting critical infrastructure through a multi-layered cybersecurity approach. It notes the increasing dependence on ICTs and rising cyber threats. A coordinated response is needed across international, regional, and national levels. Key aspects include legal measures, technical/procedural measures, organizational structures, capacity building, and international cooperation. The ITU promotes cybersecurity strategies, drives implementation efforts, and fosters a global culture of cybersecurity through activities like its National CIRT Programme and Global Cybersecurity Index.