This document discusses critical information infrastructure protection (CIIP) and the threats and challenges for developing countries. It outlines that CIIs like telecommunications, power, and water systems are essential to modern economies. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of these systems is important. Developing countries face challenges like limited financial resources, technical complexity, and lack of relevant policies and legal frameworks for CIIP. Cooperation and information sharing between stakeholders is key to addressing these challenges and deploying effective CIIP.

![Basic Understanding of CII [1/2] Critical Information Infrastructures (CII) communications and/or information services whose availability, reliability and resilience are essential to the functioning of a modern economy CII also includes: telecommunications, power distribution, water supply, public health services, national defense, law enforcement, government services, and emergency services](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinkoyabe-110610042012-phpapp01/85/CTO-Cybersecurity-2010-Dr-Martin-Koyabe-2-320.jpg)
![Basic Understanding of CII [2/2] Critical Information Infrastructure Protection (CIIP) Focuses on protection of IT systems and assets Telecommunication, computers/software, Internet, Satellite, interconnected computers/networks (Internet) & services they provide Ensures C onfidentiality, I ntegrity and A vailability Required 27/4 (365 days) Part of the daily modern economy and the existence of any country Confidentiality Integrity Availability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinkoyabe-110610042012-phpapp01/85/CTO-Cybersecurity-2010-Dr-Martin-Koyabe-3-320.jpg)


![How about developed economies? Key Cybersecurity threat(s) are diverse, but related “ Established capable states...” Source: UK Cyber Security Strategy [2009] “ The role of nations in exploiting information networks...” Source: US Cyberspace Policy Review [2009] “ The dangers from IT crime, threat to government agencies...” Source: Swedish Emergency Management Agency (SEMA) [2008] “ Financial incentive for online criminal behaviour...” Source: Towards a Belgian strategy on Information Security [2008]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinkoyabe-110610042012-phpapp01/85/CTO-Cybersecurity-2010-Dr-Martin-Koyabe-6-320.jpg)




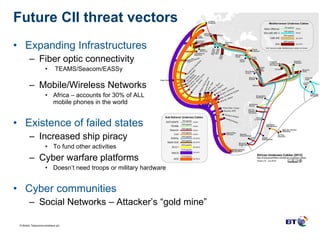

![Q&A Session Thank You [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/martinkoyabe-110610042012-phpapp01/85/CTO-Cybersecurity-2010-Dr-Martin-Koyabe-13-320.jpg)
