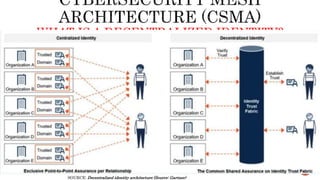
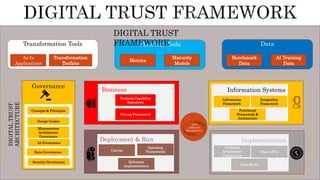
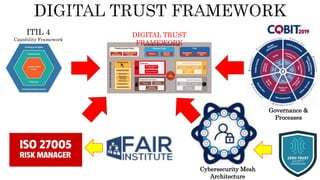
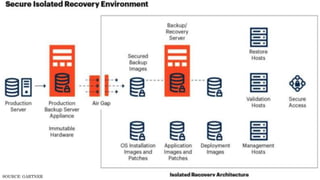
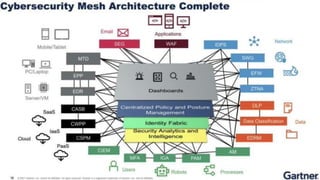
The document discusses the Digital Trust Framework (DTF), which will use the TMForum's Open Digital Architecture (ODA) as a foundation. The DTF is being developed for 4IR environments and will provide a blueprint for modular, cloud-based, open digital platforms that can be orchestrated using AI. It will integrate ODA with other frameworks to ensure an overall digital trust approach for continuously evolving systems.











![STANDARDS ALIGNMENT
1. Threat Detection
STIX /TAXII
SIGMA
2. IAM
SAML
ODIDC
OAUTH
SCIM
XACML
OPA
JWT
3. NETWORK FORMAT
IPFix
4. NASCENT
IDQL
CAEP
4. OTHER
OpenDXL
NIST SCAPv2
5. STANDARD FORMATS
Snort
ZEEK
Yara (Language)
6. FRAMEWORKS
OWASP Top 10
MITRE [ATT&CK, D3FEND]
CVSS
Cyber Kill Chain
CVE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dtf-cybersecuritymesh-211215214934/85/CYBERSECURITY-MESH-DIGITAL-TRUST-FRAMEWORK-17-320.jpg)