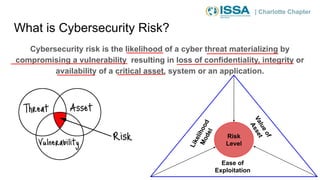
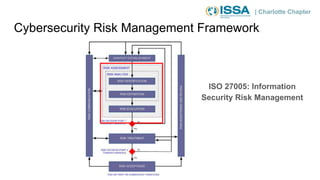
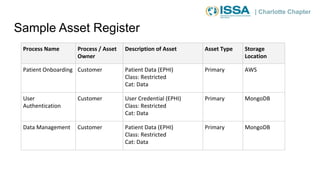
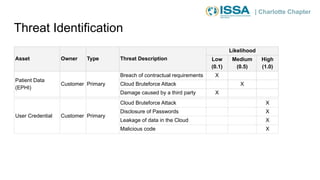
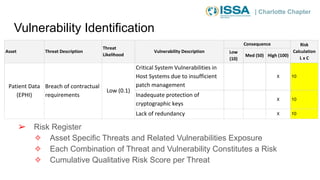
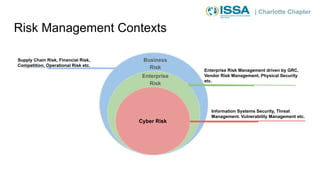
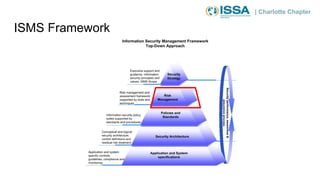
This document summarizes a presentation on cybersecurity risk management. It introduces key concepts such as assets, threats, vulnerabilities, impacts, likelihoods, controls, and risk assessment. It describes the process of identifying assets, threats, vulnerabilities and controls. It also discusses calculating risk scores and evaluating risks. The presentation emphasizes that risk management helps prioritize limited resources and is important for compliance.