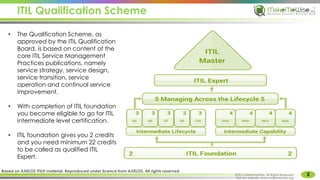
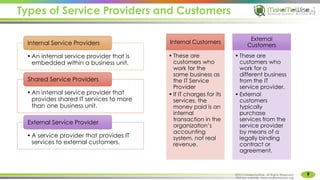
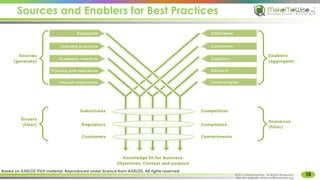
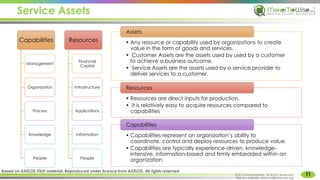
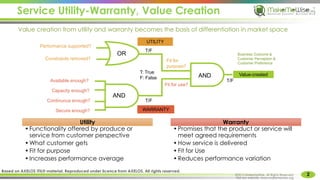
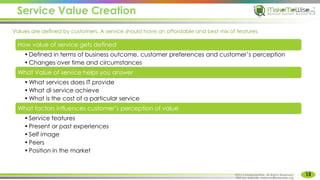
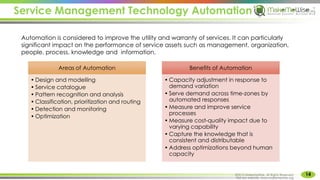
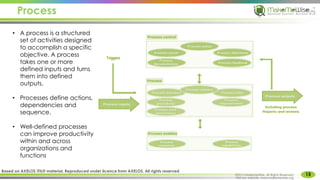
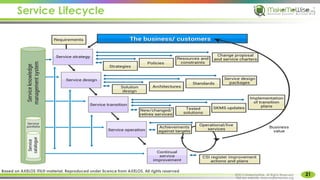
The document provides an introduction to ITIL® 2011 foundation certification, outlining its significance as a globally recognized framework for IT service management (ITSM). It details the qualification scheme, exam structure, and various service management practices, emphasizing the importance of core, enabling, and enhancing services. Additionally, it discusses the roles and responsibilities within service management, alongside the value creation from service utility and warranty.