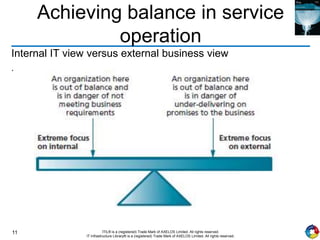
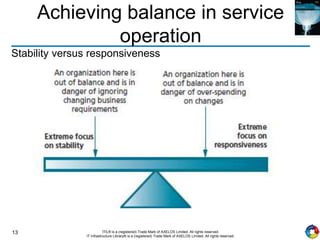
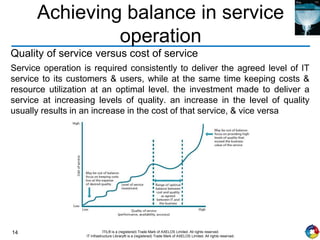
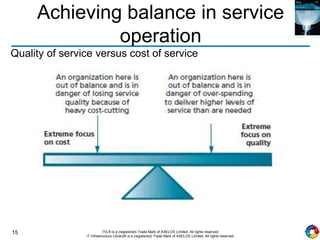
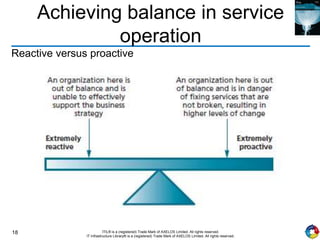
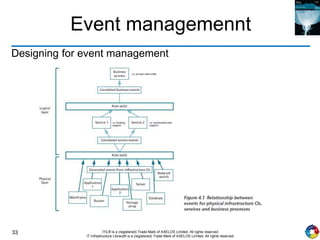
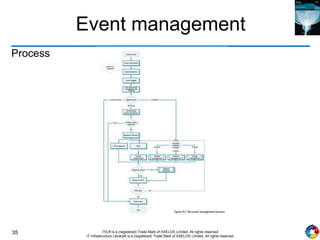
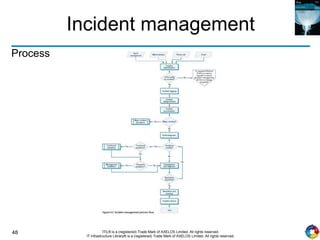
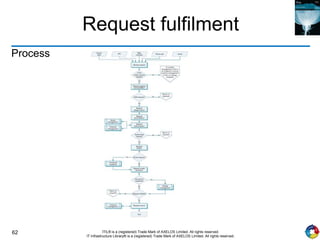
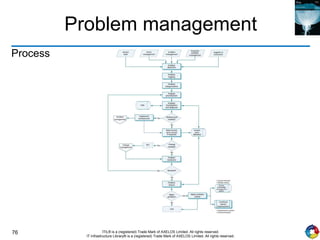
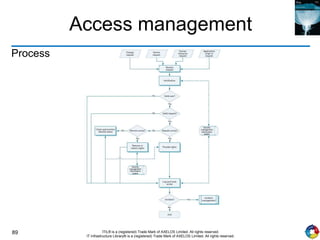
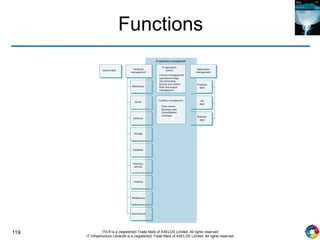
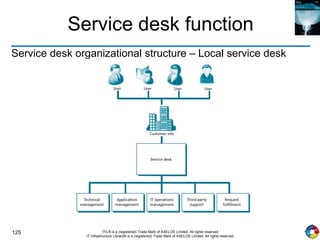
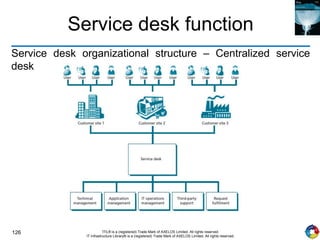
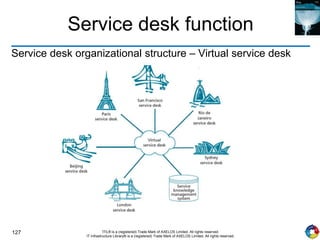
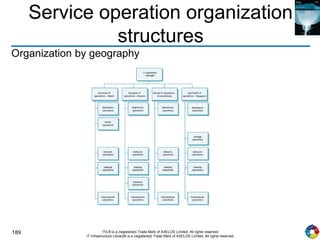
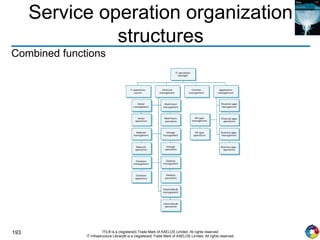
The document outlines the principles and processes of IT service operation as part of the IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL), focusing on delivering efficient services that meet business objectives while ensuring user satisfaction. It emphasizes the importance of balancing various aspects such as internal IT views versus external business views, stability versus responsiveness, and proactive versus reactive approaches. Key processes like event management, incident management, and access management are discussed, along with the significance of effective communication and collaboration across IT teams.