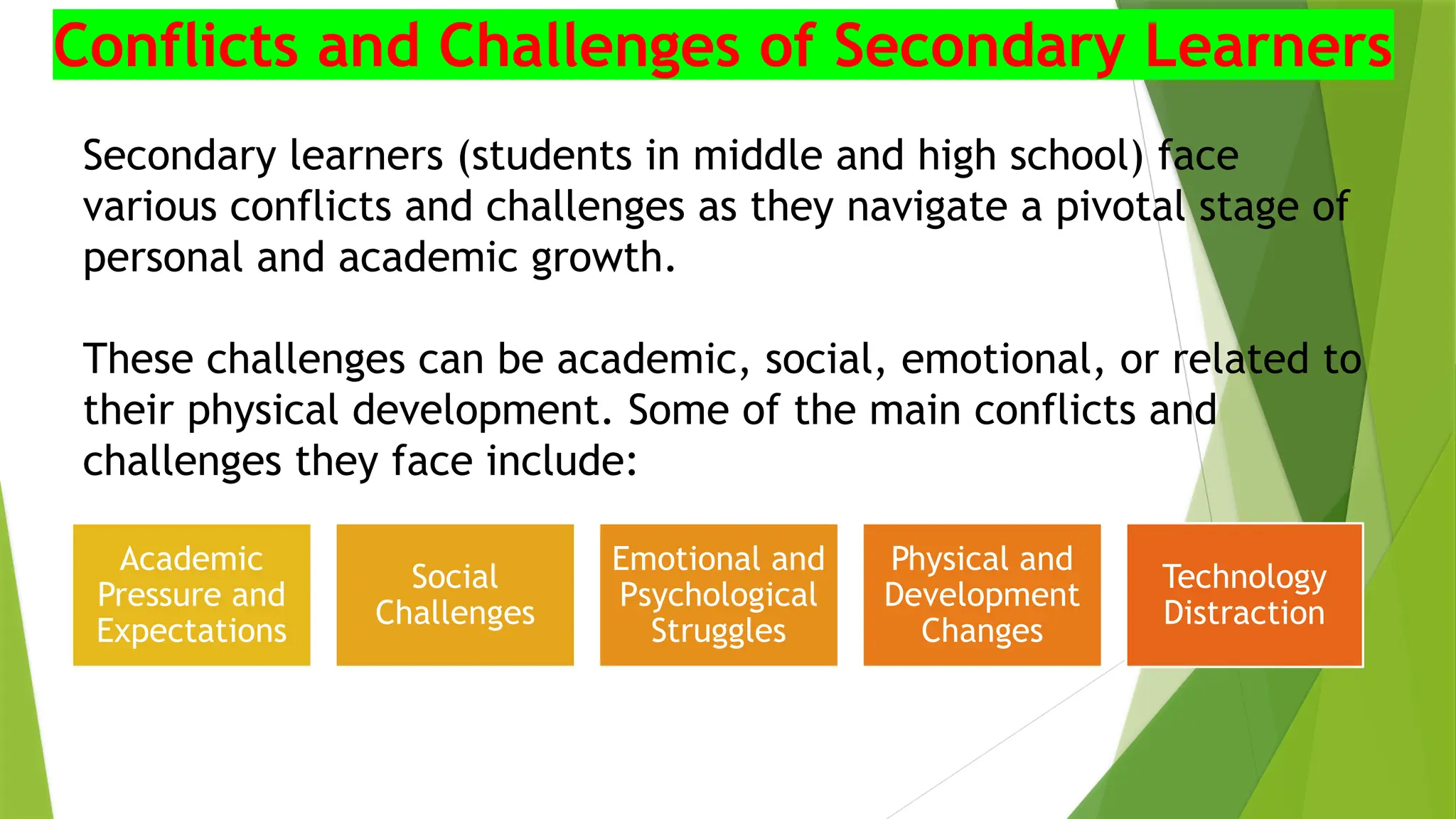
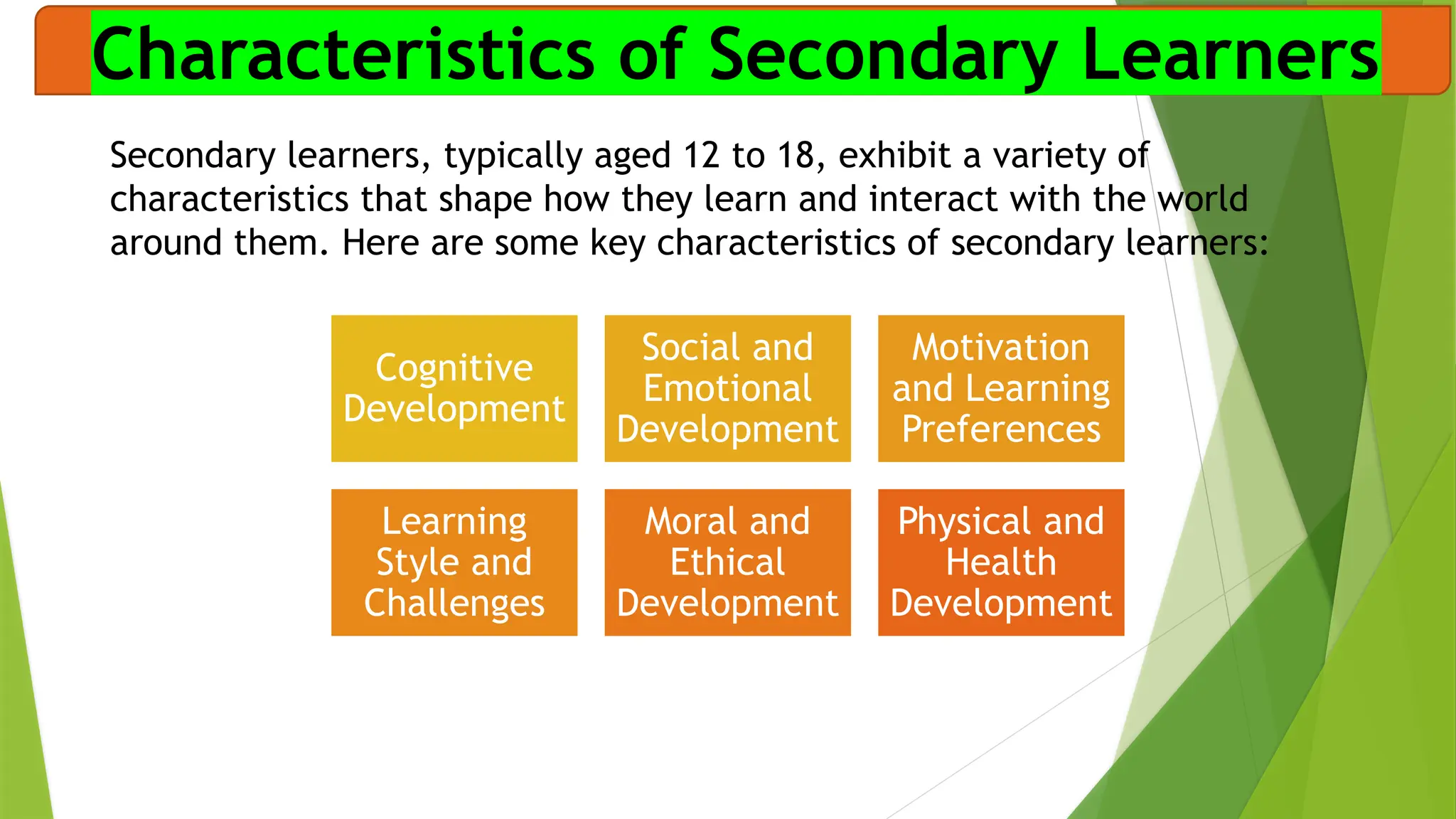
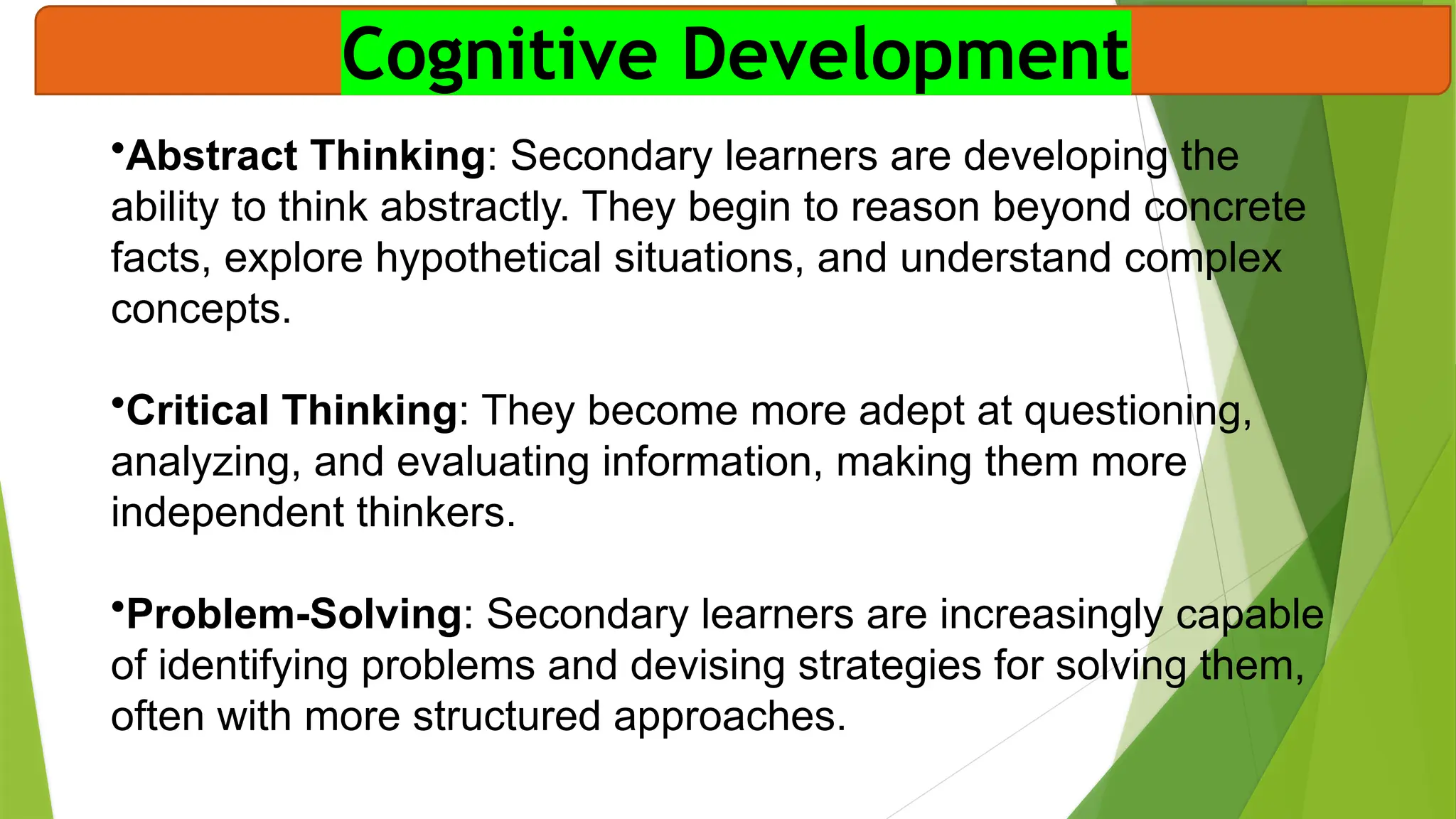
The document discusses the conflicts and challenges faced by secondary learners (ages 12-18) as they navigate personal and academic growth, including academic pressure, social dynamics, emotional struggles, and technological distractions. It outlines key characteristics of these learners, such as cognitive development, social influence, motivation, and moral reasoning, which further impact their learning experiences. Overall, understanding these challenges and characteristics is essential for effective pedagogy at the secondary stage.