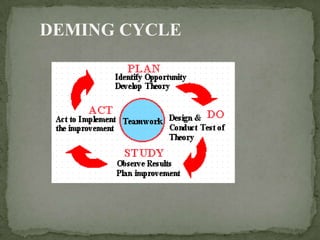
The document discusses W. Edwards Deming's philosophy and the Deming cycle. Deming believed in continually improving products/services and processes. His 14-point management philosophy included putting quality first, building quality into products/processes, and constantly improving. The Deming cycle involves planning improvements, doing by implementing plans, studying results, and acting to standardize successful changes or repeat the cycle. Following this cycle of continual improvement leads to better outcomes.