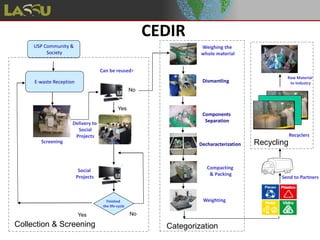
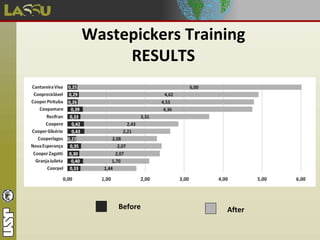
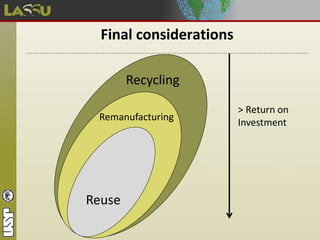
The document discusses e-waste (discarded electronic equipment) which contains toxic substances that are often buried in landfills. It estimates that 1.4 million metric tons of e-waste are discarded annually in Brazil, with 10% from information and communication technology. E-waste is classified into different categories based on the types of electronic products. It poses risks to human health due to hazardous elements like lead, mercury, and others. The CEDIR project at USP works to properly dispose of and recycle e-waste through collection, dismantling, separation, and sending materials to partners for decharacterization and recycling. It also trains wastepickers to increase recycling and their incomes while promoting social inclusion and environmental