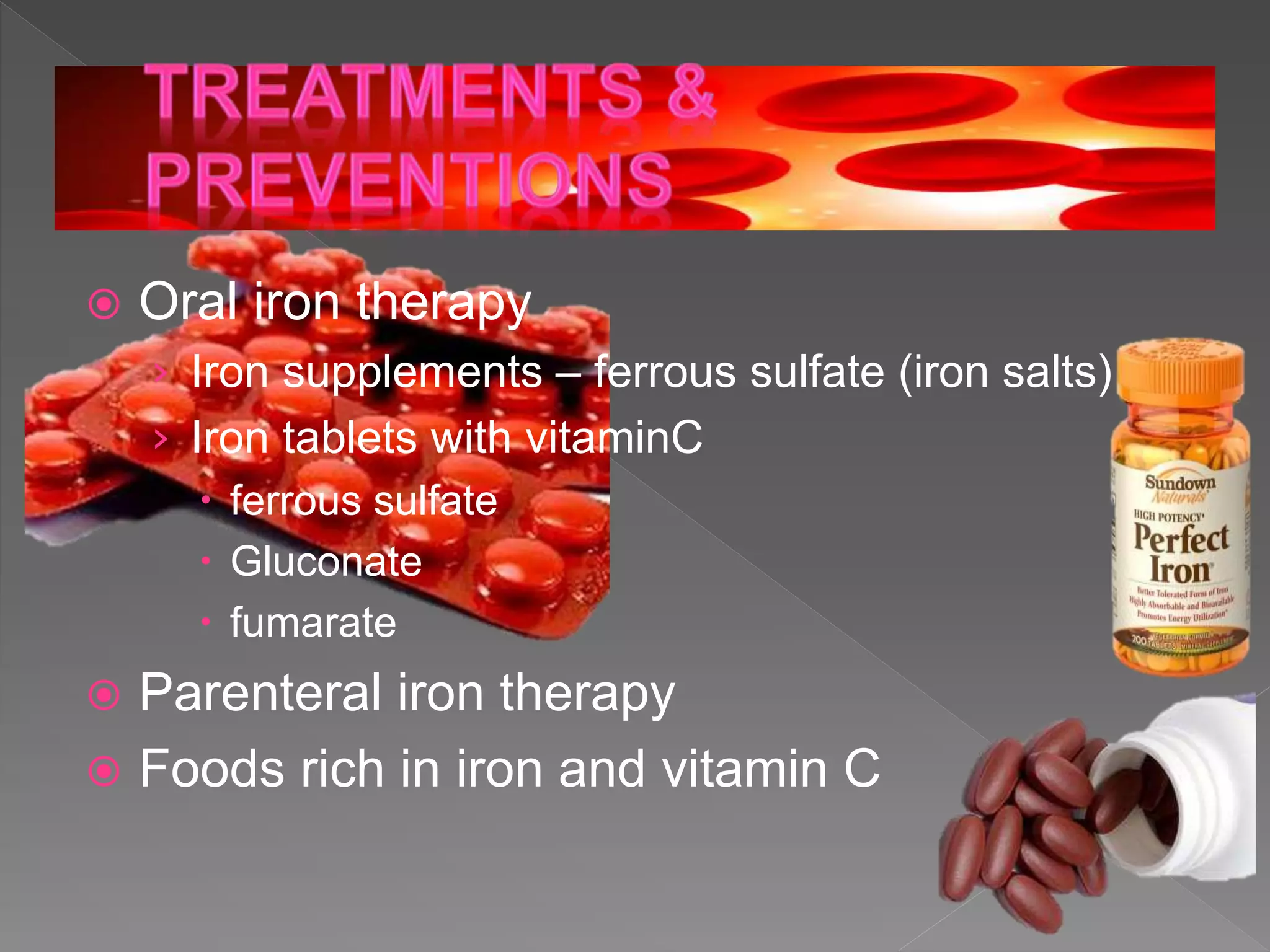
Iron is a mineral that is essential for the formation of hemoglobin in red blood cells. It serves several vital functions in the body including carrying oxygen from the lungs to tissues. Iron deficiency anemia is a condition where the body lacks sufficient red blood cells due to low iron levels, preventing adequate oxygen transport. It is one of the most common nutritional deficiencies worldwide, affecting groups like infants, children, pregnant women, and menstruating women the most. Symptoms include fatigue, pale skin, and shortness of breath.