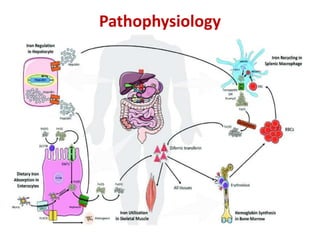
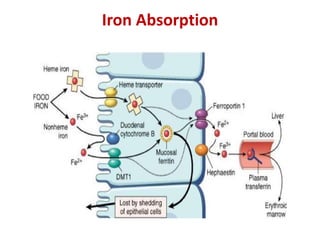
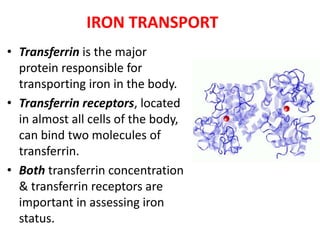
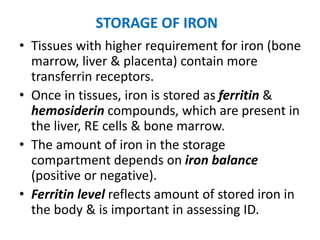
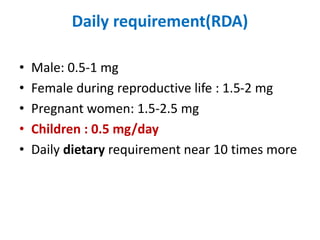
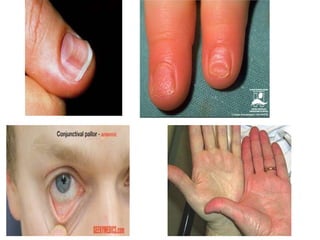
Iron-deficiency anemia is a common nutritional deficiency that affects approximately 25% of the world's population. It occurs when the body does not have enough iron to produce healthy red blood cells. Key points:
- Iron-deficiency anemia is most prevalent in infants, children under 5, pregnant women, and women of childbearing age. It can cause fatigue, weakness, and developmental delays in children.
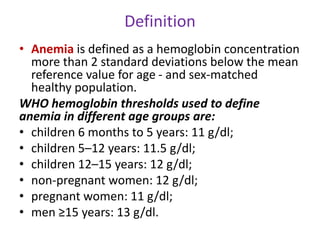
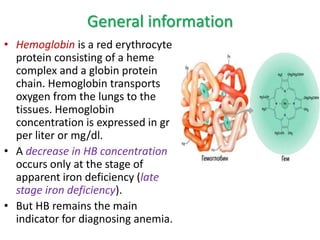
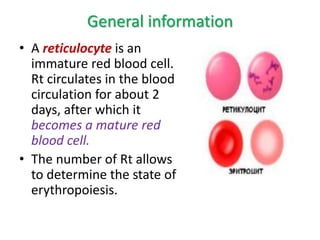
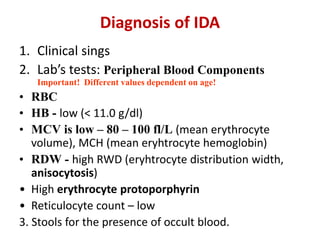
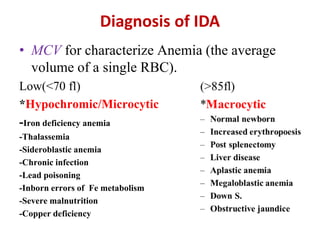
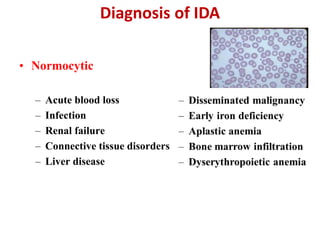
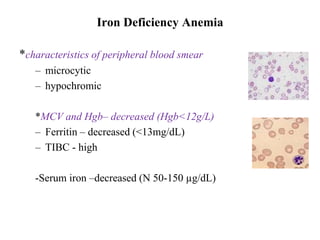
- It is diagnosed based on low hemoglobin and iron levels as well as microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells. Treatment involves oral iron supplements to replenish iron stores.
- Risk factors include low iron intake, poor absorption, blood loss, and certain medical conditions. Prevention