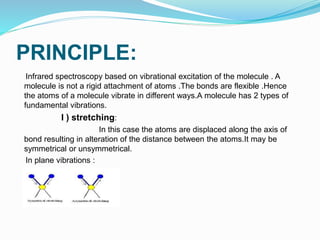
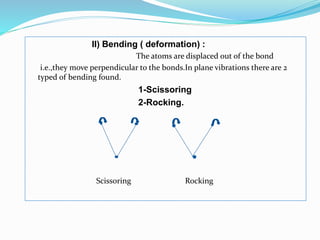
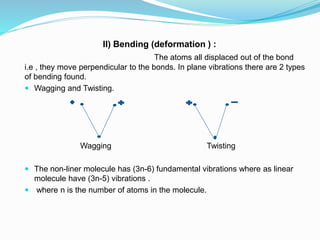
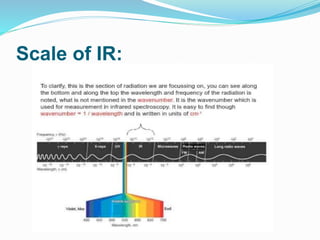
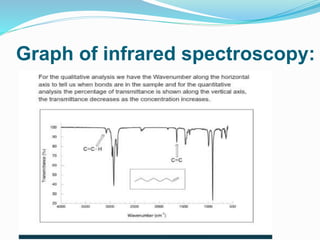
This document is a student paper on infrared spectroscopy for an analytical chemistry course. It introduces infrared spectroscopy as a technique that involves infrared radiation interacting with matter based on molecular vibrations. The document discusses the basic principles of infrared spectroscopy, including the different types of molecular vibrations that can be observed. It provides diagrams of infrared spectrometer instrumentation and describes the basic working of passing infrared radiation through a sample and reference cell to detect the frequencies absorbed by the sample's molecules. The remainder of the document appears to be an outline for the rest of the paper, discussing topics like the scale of infrared measurements, sample graphs, energy of radiation, applications and advantages/disadvantages of infrared spectroscopy.