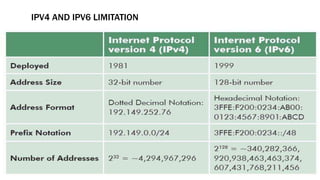
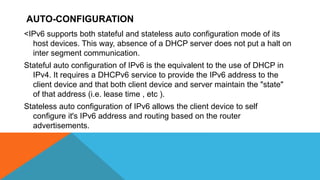
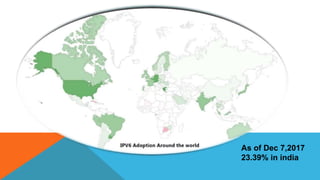
IPv6 was developed as a replacement for IPv4 to address limitations in IPv4 including address depletion. IPv6 uses a 128-bit address space compared to IPv4's 32-bit address space, providing trillions of times more addresses. IPv6 supports features like auto-configuration, end-to-end connectivity without NAT, faster routing, and security through IPsec.